In the world of precision engineering, where smoothness, stability, and accuracy are essential, the ball bearing rail stands as one of the most vital components. From CNC machines to robotic arms and 3D printers, ball bearing rails ensure effortless linear movement with minimal friction and maximum precision. Without them, modern automation and high-performance machinery would struggle to deliver the accuracy industries demand today.
This comprehensive guide will explore everything about ball bearing rails—their structure, working principle, types, advantages, selection criteria, and the role they play in mechanical motion systems.
Understanding Ball Bearing Rail
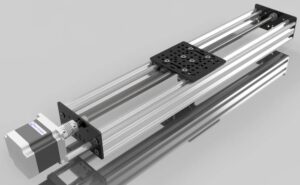
A ball bearing rail—also known as a linear ball bearing rail or ball-type linear guide—is a motion system designed to allow smooth, accurate, and repeatable linear movement of machine components. It comprises a hardened steel rail and a carriage (or block) that travels along it using rolling elements (steel balls) to minimize friction.
These rails provide the precision, stiffness, and load-carrying capacity necessary for applications requiring consistent linear positioning. The key advantage of ball bearing rails is their ability to maintain high accuracy and rigidity even under heavy loads and continuous operation.
Core Components of a Ball Bearing Rail
Each ball bearing rail assembly is engineered with tight tolerances and precision-ground surfaces to ensure smooth, consistent motion. The key components include:
Rail: A hardened, straight steel or stainless steel track that defines the motion path.
Carriage (or Slider): The moving part that houses the rolling elements and supports the load.
Ball Bearings: Precision steel balls that roll between the rail and carriage, reducing friction and enabling smooth movement.
End Caps: Keep the ball bearings inside the circuit and allow continuous recirculation.
Seals: Prevent contamination from dust, dirt, or moisture.
Retainer (Cage): Holds and guides the ball bearings evenly spaced along the raceway.
Lubrication Ports: Enable easy application of lubricants for long-term operation.
Every component works in harmony to ensure reliability, accuracy, and efficiency during linear motion.
Working Principle of a Ball Bearing Rail
The ball bearing rail operates on the principle of rolling motion instead of sliding contact. Inside the carriage, a series of steel balls circulate along a raceway track as the carriage moves along the rail. These balls roll smoothly, carrying the load while reducing friction dramatically compared to traditional sliding mechanisms.
As the carriage travels, the balls recirculate back into their original position via end caps, ensuring continuous motion. This cycle allows for:
Smooth, friction-free linear travel
High precision and repeatability
Reduced wear and energy loss
Longer service life
This efficient motion mechanism is the reason why ball bearing rails are indispensable in high-precision machinery and automation systems.
Types of Ball Bearing Rails
Depending on the design and application, ball bearing rails can be classified into several types:
Standard Linear Ball Bearing Rails
These consist of a single or dual rail and a ball-filled carriage that ensures precise and smooth movement. Commonly used in CNC machines and 3D printers.
Compact Ball Bearing Rails
Designed for tight spaces, they provide the same high precision but with a lower profile, ideal for electronics and medical devices.
Double-Row Ball Bearing Rails
Feature two parallel rows of ball bearings for increased load capacity and rigidity. Perfect for heavy-duty machinery.
Miniature Ball Bearing Rails
Used in lightweight or delicate systems such as laboratory equipment and optical instruments where space and precision are critical.
Self-Lubricating Ball Bearing Rails
Equipped with internal lubrication systems that distribute grease or oil automatically, reducing maintenance.
Advantages of Ball Bearing Rails
High Precision
Ball bearing rails are engineered for exact positioning, maintaining tight tolerances in linear motion applications.
Low Friction
The rolling ball mechanism drastically lowers resistance, leading to smooth motion with minimal energy loss.
Superior Load Capacity
Multiple contact points distribute loads evenly, allowing ball bearing rails to handle both vertical and horizontal forces effectively.
Long Lifespan
With proper lubrication and maintenance, ball bearing rails offer extended operational life and minimal wear.
Compact and Rigid Design
Their compact structure allows for efficient integration into machines while maintaining rigidity and accuracy.
Reduced Noise and Vibration
Thanks to the rolling motion, ball bearing rails operate quietly and dampen vibration during high-speed movement.
Applications of Ball Bearing Rails
Ball bearing rails are widely used across industries requiring reliable and precise linear motion. Some common applications include:
CNC Machines: For accurate cutting, drilling, and shaping processes.
3D Printers: Ensuring precise movement of the print head and bed.
Robotics: Providing controlled linear motion for robotic joints and arms.
Medical Equipment: Used in imaging systems, surgical robots, and automated laboratory devices.
Semiconductor Manufacturing: For clean, accurate movement in sensitive environments.
Automation and Packaging Equipment: Enabling smooth motion in conveyors, pick-and-place systems, and assembly lines.
Optical and Measuring Instruments: Ensuring precise alignment and repeatability.
Ball Bearing Rail vs. Linear Bearing: Key Differences
| Feature | Ball Bearing Rail | Linear Bearing |
|---|---|---|
| Motion Type | Rolling on a fixed rail | Sliding or rolling on a cylindrical shaft |
| Precision | Extremely High | Moderate |
| Load Capacity | High | Medium |
| Friction | Very Low | Moderate |
| Rigidity | Excellent | Average |
| Applications | CNC, robotics, automation | Light-duty systems, DIY projects |
The ball bearing rail provides higher precision and durability, making it the superior choice for industrial-grade equipment.
Design Considerations When Choosing a Ball Bearing Rail
When selecting a ball bearing rail, several design and operational factors must be evaluated:
Load and Force Requirements
Determine both static and dynamic loads. For heavier applications, select double-row or wide-profile rails.
Accuracy and Tolerance
High-end machining or optical applications require rails with fine-tuned tolerances and minimal play.
Speed and Acceleration
For fast-moving systems, choose rails with optimized ball circulation paths to reduce friction and vibration.
Environment
Use stainless steel rails or protective coatings for environments exposed to moisture, chemicals, or dust.
Maintenance
Opt for self-lubricating models or accessible lubrication ports for long-term reliability.
Installation Surface
Ensure the mounting base is perfectly flat and rigid, as even slight misalignments can reduce accuracy and cause uneven wear.
Installation Tips for Ball Bearing Rails
Proper installation ensures longevity, accuracy, and optimal performance. Follow these steps:
Clean and Level the Mounting Surface: Remove debris and ensure a perfectly flat foundation.
Align Rails Precisely: Misalignment can cause binding and premature wear.
Tighten Fasteners Evenly: Apply torque gradually and uniformly to avoid distortion.
Lubricate Before Operation: Use manufacturer-recommended lubricants.
Test for Smoothness: Move the carriage manually to check for any irregular resistance or sticking points.
Maintenance and Care for Ball Bearing Rails
Consistent maintenance ensures reliable operation and prevents premature failure.
Lubricate Regularly: Grease or oil should be replenished based on usage frequency and environment.
Inspect Periodically: Look for signs of wear, pitting, or corrosion.
Clean Thoroughly: Remove contaminants that can damage raceways or bearings.
Check Alignment: Regularly verify parallelism and rail flatness.
Replace Seals if Needed: Worn seals can let in dirt, reducing system life.
Common Issues and Troubleshooting
| Issue | Likely Cause | Recommended Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Rough Movement | Contamination or misalignment | Clean and realign rails |
| Excessive Noise | Insufficient lubrication | Apply proper lubricant |
| Vibration | Uneven mounting or loose fasteners | Re-torque and align |
| Premature Wear | Overloading or improper installation | Reduce load and inspect alignment |
| Corrosion | Exposure to moisture | Use stainless steel rails or protective coating |
Innovations in Ball Bearing Rail Technology
The continuous evolution of motion systems has led to new innovations in ball bearing rail design:
Smart Bearing Systems: Incorporate sensors to monitor load, temperature, and lubrication in real time.
Nano-Coated Surfaces: Provide enhanced corrosion resistance and smoother rolling.
Self-Lubricating Designs: Automatically distribute lubrication, reducing maintenance.
Compact Miniature Rails: Developed for micro-precision equipment and robotics.
Hybrid Ceramic Bearings: Use ceramic balls to reduce friction, weight, and magnetic interference.
These innovations are revolutionizing how industries approach precision linear motion.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Modern ball bearing rails are designed with sustainability in mind. Stainless steel and recyclable materials minimize environmental footprint. Additionally, self-lubricating systems reduce oil waste, and long service lives cut down on equipment replacement rates—supporting sustainable manufacturing practices.
Future Trends in Ball Bearing Rails
As automation, robotics, and AI continue to evolve, ball bearing rails are expected to integrate with smart predictive maintenance systems. These will allow for real-time performance tracking and early detection of wear or alignment issues. The future also points toward lightweight composite materials and magnetic levitation systems for near-frictionless motion.

Frequently Asked Questions
What is a ball bearing rail used for?
It provides smooth, precise linear motion in machinery such as CNC machines, automation systems, and robotics.
How does a ball bearing rail work?
It uses recirculating steel balls that roll between a rail and carriage, reducing friction and ensuring stable linear movement.
Do ball bearing rails need lubrication?
Yes. Lubrication is essential to minimize friction, prevent wear, and extend service life.
Can ball bearing rails handle heavy loads?
Absolutely. Double-row or wide-profile ball bearing rails are designed for high load capacities and rigidity.
What materials are used for ball bearing rails?
Typically made from hardened carbon steel or stainless steel for corrosion resistance and strength.
Are ball bearing rails suitable for clean rooms?
Yes, especially stainless steel or sealed types that prevent contamination and require minimal maintenance.
Conclusion
A ball bearing rail is far more than just a mechanical part—it’s the foundation of precision motion in modern machinery. Its ability to deliver stable, accurate, and friction-free linear movement makes it indispensable in countless industries. Whether in robotics, manufacturing, or medical technology, the ball bearing rail ensures smooth operation, minimal energy loss, and long-lasting reliability.
By understanding its structure, benefits, and proper maintenance, engineers can optimize system performance and ensure the longevity of their machinery—making the ball bearing rail a true cornerstone of precision motion engineering.
Suggested Internal Links
Linear Guide Bearing: Design and Benefits
Precision Motion Control Systems Explained
Maintenance Guide for CNC Machinery
Suggested External Links
ISO Standards for Linear Motion Components
Advances in Smart Manufacturing Technology
Materials and Coatings for Ball Bearing Rails