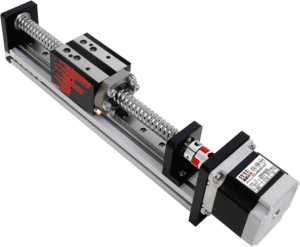
Introduction
In CNC machining, precision and repeatability are non-negotiable. Whether it is milling, turning, drilling, or engraving, every movement must follow a controlled and accurate path. This is where the CNC linear guide plays a critical role.
A CNC linear guide provides smooth, precise, and stable linear motion for machine axes, ensuring high positioning accuracy, minimal friction, and long-term reliability. These guides are fundamental components in CNC machining centers, lathes, routers, and automation equipment, enabling consistent performance even under heavy loads and high-speed operation.
This article offers a comprehensive overview of CNC linear guides, including their structure, working principles, types, advantages, applications, selection criteria, and maintenance considerations.
What Is a CNC Linear Guide?
A CNC linear guide is a precision-engineered linear motion component designed to guide machine parts along a straight path with minimal resistance. It typically consists of a hardened guide rail and a bearing carriage containing rolling elements such as balls or rollers.
In CNC machines, linear guides are installed on machine axes (X, Y, and Z) to support moving components like the table, spindle head, or gantry. Their purpose is to maintain high accuracy, rigidity, and smooth motion under varying loads and speeds.
Main Components of a CNC Linear Guide System
1. Guide Rail
Precision-ground and hardened steel rail
Provides a straight, rigid reference for motion
Mounted to the machine base or frame
2. Bearing Carriage (Slider)
Moves along the rail while carrying the load
Houses rolling elements for low-friction motion
3. Rolling Elements
Recirculating steel balls or cylindrical rollers
Distribute loads evenly and reduce friction
4. End Caps, Seals, and Wipers
Prevent dust, chips, coolant, and debris from entering the guide
Extend service life and maintain accuracy
5. Lubrication System
Grease or oil ports ensure smooth and consistent operation
Critical for long-term performance in CNC environments
How CNC Linear Guides Work
CNC linear guides operate based on rolling contact motion:
The guide rail is fixed to a precisely machined mounting surface.
The bearing carriage moves along the rail.
Rolling elements circulate inside the carriage, rolling between the rail and carriage raceways.
Friction is minimized, enabling smooth and precise movement.
Loads are supported in multiple directions, including radial, axial, and moment loads.
This design allows CNC linear guides to maintain high accuracy, rigidity, and stability, even during rapid acceleration and deceleration.
Types of CNC Linear Guides
1. Ball-Type CNC Linear Guides
Use recirculating steel balls
Provide smooth motion and high precision
Suitable for most CNC machines and light-to-medium loads
2. Roller-Type CNC Linear Guides
Use cylindrical rollers instead of balls
Higher load capacity and rigidity
Ideal for heavy-duty CNC machining centers
3. Profile Rail CNC Linear Guides
Rectangular rail profile with integrated raceways
Excellent stiffness and multi-directional load support
Widely used in modern CNC equipment
4. Miniature CNC Linear Guides
Compact design for limited space
Used in desktop CNC machines, engraving machines, and small automation systems
Materials Used in CNC Linear Guides
Hardened Carbon Steel – High strength and wear resistance
Stainless Steel – Corrosion resistance for coolant-heavy or humid environments
Surface-Treated Rails – Black oxide, chrome plating, or anti-corrosion coatings
Material selection depends on cutting forces, operating environment, and machine design.
Advantages of CNC Linear Guides
High Positioning Accuracy
Low Friction and Smooth Motion
Excellent Load Capacity
High Rigidity and Stability
Reduced Wear and Longer Service Life
Improved Machining Surface Quality
Consistent Performance at High Speeds
These advantages directly impact machining accuracy, productivity, and machine reliability.
Applications of CNC Linear Guides
CNC linear guides are used in a wide range of machining and automation equipment:
CNC Milling Machines
CNC Lathes
CNC Routers and Engraving Machines
Vertical and Horizontal Machining Centers
Gantry CNC Systems
Automated Tool Changers
Robotic CNC Loading Systems
How to Select the Right CNC Linear Guide
When choosing a CNC linear guide, consider:
Load Requirements – Cutting forces and machine weight
Accuracy Class – Standard, high-precision, or ultra-precision
Travel Length – Total axis stroke
Speed and Acceleration – Rapid traverse and feed rates
Operating Environment – Chips, coolant, dust, temperature
Mounting Conditions – Flatness and rigidity of mounting surfaces
Maintenance Needs – Lubrication intervals and accessibility
Correct selection ensures stable machining accuracy and long-term performance.
Installation Best Practices
Machine mounting surfaces to required flatness and parallelism
Align rails carefully to avoid binding or uneven wear
Use specified tightening torque for rail bolts
Apply recommended lubrication before initial operation
Perform run-in procedures after installation
Proper installation is essential for achieving maximum precision and service life.
Maintenance of CNC Linear Guides
Clean rails regularly to remove chips and coolant residue
Re-lubricate according to operating conditions
Inspect seals and wipers for damage
Check for abnormal noise, vibration, or increased resistance
Regular maintenance minimizes downtime and protects machining accuracy.
Future Trends in CNC Linear Guide Technology
Higher Load and Rigidity Designs for heavy cutting applications
Integrated Condition Monitoring Sensors
Maintenance-Free or Long-Life Lubrication Systems
Advanced Coatings for Wear and Corrosion Resistance
Energy-Efficient Low-Friction Designs
These advancements support the demand for high-speed, high-precision CNC machining.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. Why are linear guides important in CNC machines?
They ensure accurate, stable, and smooth movement of machine axes, directly affecting machining precision.
2. What is the difference between ball and roller CNC linear guides?
Ball guides offer smooth motion and versatility, while roller guides provide higher load capacity and rigidity.
3. How long do CNC linear guides last?
With proper installation and maintenance, they can operate reliably for many years.
4. Do CNC linear guides require lubrication?
Yes, lubrication is essential to reduce wear and maintain precision.
5. Can CNC linear guides handle high-speed motion?
Yes, they are designed to perform accurately under high speed and acceleration.
Conclusion
A CNC linear guide is a cornerstone component in modern CNC machines, enabling high precision, rigidity, and smooth motion. Its performance directly affects machining accuracy, surface quality, and machine reliability.
By selecting the appropriate guide type, installing it correctly, and maintaining it properly, manufacturers can achieve consistent, high-quality CNC machining results. As CNC technology continues to evolve, linear guide systems will remain central to advancements in speed, accuracy, and automation.