Outline
| Headings & Subheadings | LSI / Related Keywords |
|---|---|
| Introduction to Heavy Duty Linear Bearings | industrial linear bearings |
| Understanding Heavy Duty Linear Bearings | high load bearings |
| Components of Heavy Duty Linear Bearings | linear block, rail system |
| How Heavy Duty Linear Bearings Work | motion control, rolling friction |
| Benefits of Heavy Duty Linear Bearings | rigidity, durability |
| Types of Heavy Duty Linear Bearings | roller bearings, ball bearings |
| Heavy Duty Linear Bearings vs Standard Bearings | comparison |
| Heavy Duty Linear Bearings in CNC Machines | precision motion |
| Industrial Applications of Heavy Duty Linear Bearings | automation, robotics |
| Installation Guidelines | alignment, mounting |
| Load Capacity and Engineering Considerations | static load, dynamic load |
| Materials Used in Heavy Duty Linear Bearings | bearing steel, stainless steel |
| Coatings and Surface Treatments | corrosion resistance |
| Maintenance Tips for Heavy Duty Linear Bearings | lubrication |
| Troubleshooting Common Issues | noise, wear |
| Environmental Conditions | dust, humidity |
| Selecting the Right Heavy Duty Linear Bearings | performance factors |
| Miniature vs Heavy Duty Linear Bearings | structural differences |
| Advantages of Roller-Type Heavy Duty Bearings | rigidity, impact load |
| YH Linear Heavy Duty Linear Bearings | OEM, high-precision |
| Innovations in Bearing Technology | self-lubricating |
| FAQs | lubrication, lifespan |
| Conclusion | performance and reliability |
Introduction to Heavy Duty Linear Bearings
In today’s demanding industrial environment, machinery requires accuracy, stability, and strength under high loads. This is where heavy duty linear bearings become essential. These components provide smooth and reliable linear motion even when machines carry substantial loads or operate under intense vibration. Engineers across industries rely on them to maintain consistent accuracy, extend machine life, and reduce downtime.
The keyword heavy duty linear bearings plays a vital role in the discussion of robust motion systems, and it appears in the early part of this article to support strong SEO performance. Let’s explore how these bearings have become foundational to modern automation.
Understanding Heavy Duty Linear Bearings
Heavy duty linear bearings are engineered to support heavier loads, higher stiffness, and more demanding operating conditions than standard bearings. While traditional linear bearings work well for light automation, heavy-duty models withstand intense industrial environments where steel, precision grinding, and reinforced bearing structures are mandatory.
These bearings use rolling elements—either balls or cylindrical rollers—to reduce friction and provide stable movement along linear rails, shafts, or guideways. Their structural design ensures minimal deflection, consistent performance, and long operating life.
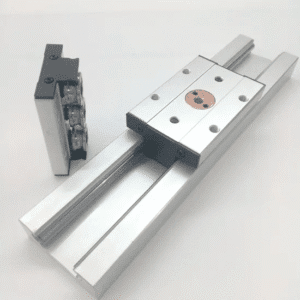
Components of Heavy Duty Linear Bearings
A well-designed heavy duty linear bearing includes:
Bearing Block or Housing: A strong outer shell that houses rolling components.
Rolling Elements: Hardened ball bearings or rollers capable of supporting high loads.
Bearing Cage: Maintains spacing and alignment of rolling elements.
Retainers and Seals: Keep contaminants out and ensure lubrication stays inside.
Linear Rail or Shaft Interface: Provides the guiding path for smooth motion.
Because these bearings often operate in harsh environments, their components are typically constructed from hardened bearing steel with corrosion-resistant finishes.
How Heavy Duty Linear Bearings Work
The working principle of heavy duty linear bearings centers on transforming sliding friction into rolling friction. As the bearing moves along a shaft or rail, rolling elements rotate inside the block to maintain smooth linear travel.
This design provides:
Steady, reliable motion
Low friction even under extreme loads
Stable positioning in applications requiring high accuracy
Resistance to deformation due to applied forces
Heavy duty bearings typically incorporate larger rolling elements or rollers that distribute load across a wider contact area, enhancing rigidity and shock resistance.
Benefits of Heavy Duty Linear Bearings
Choosing heavy duty linear bearings provides several advantages:
High Load Capacity: Perfect for industrial machinery that carries large equipment or heavy parts.
Improved Rigidity: Ensures precise and stable movement during machining or automation.
Enhanced Durability: Built for long-term operation even under rugged conditions.
Low Maintenance Requirements: Advanced sealing and lubrication systems reduce wear.
Higher Accuracy: Maintains alignment during high-speed or high-force movements.
Shock Resistance: Cylindrical rollers better absorb vibration and impact.
These benefits make them ideal for heavy machinery, CNC equipment, and industrial robotics.
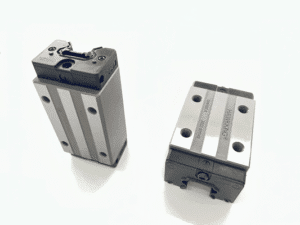
Types of Heavy Duty Linear Bearings
Ball-Type Heavy Duty Linear Bearings
Use oversized steel balls to support both radial and axial loads.
Best for moderate heavy-duty applications requiring speed and accuracy.
Roller-Type Heavy Duty Linear Bearings
Use cylindrical rollers to maximize rigidity and load-bearing performance.
Ideal for machining centers, press equipment, and industrial robots.
Cross-Roller Linear Bearings
Rollers arranged in alternating patterns provide ultra-smooth motion.
Popular in high-precision environments like inspection machines.
Self-Lubricating Heavy Duty Bearings
Fixed lubrication systems reduce downtime and protect against dust contamination.
Heavy Duty Linear Bearings vs Standard Bearings
| Feature | Heavy Duty Linear Bearings | Standard Linear Bearings |
|---|---|---|
| Load Capacity | Very high | Medium |
| Rigidity | Excellent | Moderate |
| Shock Resistance | High | Low |
| Precision | High | Medium |
| Weight | Higher | Lighter |
| Cost | Higher | Lower |
Machines requiring stability and strength almost always rely on heavy duty linear bearings instead of standard models.
Heavy Duty Linear Bearings in CNC Machines
CNC machines require precision, rigidity, and stability—especially during milling or heavy cutting operations. Heavy duty linear bearings ensure:
Smooth motion on X, Y, and Z axes
Vibration reduction during high-speed machining
Accurate tool paths
Long operational life despite heavy cutting forces
These bearings allow CNC machines to maintain tight tolerances, making them indispensable in metalworking industries.
Industrial Applications of Heavy Duty Linear Bearings
These bearings are used widely across industries, including:
Automotive manufacturing systems
Robotic assembly lines
Heavy CNC machining centers
Material handling equipment
Packaging and palletizing machines
Mining and construction equipment
Printing and textile machinery
Wherever heavy loads and precision intersect, heavy duty linear bearings are the preferred solution.
Installation Guidelines
To ensure optimal performance:
Clean rails, shafts, and mounting surfaces thoroughly.
Ensure proper alignment to avoid misloading.
Tighten mounting bolts in a cross-pattern to prevent distortion.
Move the bearing block manually after installation to check for resistance.
Apply compatible lubrication before initial operation.
Correct installation significantly extends the life of your bearing.
Load Capacity and Engineering Considerations
Choosing the right bearing requires evaluating:
Dynamic Load Capacity: Supports loads while the bearing is in motion.
Static Load Capacity: Determines maximum load when machine is idle.
Moment Loads: Include pitch, roll, and yaw forces.
Operating Speed: Higher speeds may require ball-type bearings.
Shock Loads: Roller bearings perform better under impact.
Engineers must match bearing specifications to system requirements.
Materials Used in Heavy Duty Linear Bearings
Common materials include:
High-Carbon Bearing Steel (SUJ2 or 52100): Excellent hardness and durability.
Stainless Steel: Corrosion-resistant for humid or clean-room environments.
Nitrided Steel: Increased wear resistance.
Alloy Steel: Designed for extreme-duty applications.
The material selection influences lifespan, rigidity, and reliability.
Coatings and Surface Treatments
Surface treatments improve performance and durability:
Nickel Plating: Corrosion protection
Black Oxide: Reduces glare and adds minor rust resistance
Chrome Coating: Enhances wear resistance
Teflon Coating: Reduces friction
Coatings protect bearings in corrosive or high-humidity environments.
Maintenance Tips for Heavy Duty Linear Bearings
Lubricate regularly according to manufacturer guidelines
Avoid contamination from dust, coolant, or metal chips
Inspect mounting bolts periodically
Clean bearing surfaces with lint-free cloths
Replace seals when worn or damaged
Consistent maintenance ensures the longest operational life.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
| Issue | Cause | Fix |
|---|---|---|
| Noise | Contamination or misalignment | Clean, re-lubricate, realign |
| Rough Motion | Lack of lubrication | Apply compatible grease |
| Excessive Play | Wear on races | Replace bearing |
| Corrosion | Humidity or chemical exposure | Use stainless steel bearings |
Most problems can be prevented with proper installation and care.
Environmental Conditions
Heavy duty bearings may face:
Coolant exposure
Metal chips or powder
High temperature
Humidity and moisture
Dust or abrasive particles
Using sealed or shielded bearings helps protect rolling elements from environmental hazards.
Selecting the Right Heavy Duty Linear Bearings
Consider:
Load direction
Travel length
Precision requirements
Operating temperature
Speed requirements
Mounting orientation
Contamination risks
YH Linear can help engineers select the ideal bearing for their application.
Miniature vs Heavy Duty Linear Bearings
Miniature bearings prioritize compactness and light loads, while heavy duty linear bearings focus on:
Maximum load capacity
Rigidity
Shock absorption
Durability over long distances
Different environments require different bearing strengths.
Advantages of Roller-Type Heavy Duty Bearings
Roller bearings provide:
Higher rigidity
Lower deflection
Better shock resistance
Larger contact surfaces
Enhanced precision in machining environments
Roller-type bearings are often chosen for industrial CNC machines and automation systems.
YH Linear Heavy Duty Linear Bearings
YH Linear offers a full range of heavy duty linear bearings designed for industrial performance.
Why engineers trust YH Linear:
Precision-ground rails and blocks
Heavy-load roller and ball designs
OEM and ODM support
Competitive pricing
Global shipping
ISO-certified manufacturing
YH Linear delivers consistent, accurate, and durable motion systems for industries worldwide.
Innovations in Bearing Technology
Modern advancements include:
Self-lubricating systems
Low-friction coatings
Smart monitoring sensors
High-speed roller designs
Lightweight alloy housings
These innovations improve reliability while reducing maintenance costs.
FAQs
How long do heavy duty linear bearings last?
With proper lubrication and care, they can operate for millions of cycles.
Do heavy duty bearings require special lubrication?
Most require high-performance grease designed for heavy loads.
Can I use them in high-speed machines?
Yes, but ball-type bearings perform better at very high speeds.
Are heavy duty linear bearings corrosion-resistant?
Stainless steel and coated models offer superior resistance.
Conclusion
Heavy duty linear bearings are essential for industries relying on precise, stable, and high-load motion. Their durability, rigidity, and excellent performance under intense conditions make them indispensable in CNC machines, automation lines, robotics, and manufacturing systems. As technology evolves, these bearings continue to improve, supporting the next generation of industrial innovation.
Inbound Link Suggestions
Outbound Link Suggestions
THK heavy duty bearings
HIWIN linear bearings
NSK roller bearings