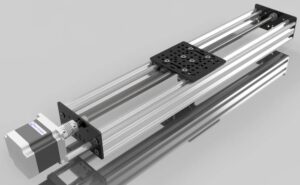
The round linear rail is one of the unsung heroes of modern mechanical design. It plays a vital role in countless automation systems, CNC machines, and industrial tools. Known for its simplicity, adaptability, and cost-effectiveness, this rail type delivers reliable linear motion in both light and heavy-duty applications. In this detailed guide, we’ll explore everything there is to know about the round linear rail — its structure, types, working mechanism, benefits, and maintenance tips. Whether you’re an engineer, machinist, or DIY builder, this comprehensive article will give you all the insights you need to select and use round linear rails effectively.
Outline
| Headings and Subheadings | Description |
|---|---|
| Introduction to Round Linear Rail | Overview and purpose of the rail |
| What Is a Round Linear Rail? | Basic definition and construction |
| History of Linear Rail Systems | Evolution from sliding to rolling systems |
| Structural Design of Round Linear Rail | Key components and their functions |
| Materials Used in Round Linear Rails | Common metals and coatings |
| Working Principle of Round Linear Rail | How it facilitates linear motion |
| Types of Round Linear Rails | Fixed, supported, and floating variants |
| Advantages of Using Round Linear Rail | Major benefits and performance aspects |
| Comparison: Round vs Square Linear Rail | Structural and performance differences |
| Load Capacity and Performance | Factors affecting load and speed |
| Installation Guide for Round Linear Rails | Step-by-step mounting process |
| Common Mounting Mistakes to Avoid | Tips for proper setup |
| Lubrication and Maintenance | How to ensure smooth operation |
| Applications in CNC Machines | Role in industrial precision machinery |
| Use in Automation and Robotics | Integration in robotics and conveyors |
| Round Linear Rails in 3D Printing | Importance for precision layer alignment |
| Durability and Environmental Resistance | Factors influencing longevity |
| Selecting the Right Round Linear Rail | Buying guide for professionals |
| Cost and Value Considerations | Price analysis and ROI |
| Top Manufacturers and Brands | Reliable global brands |
| Troubleshooting Common Problems | How to fix motion and alignment issues |
| Safety Precautions During Use | Handling and installation safety |
| Emerging Innovations in Linear Rail Technology | Smart sensors and new materials |
| Future of Round Linear Rail Systems | Trends in automation and precision tech |
| FAQs About Round Linear Rail | Commonly asked questions |
| Final Thoughts on Round Linear Rail | Closing insights |

Introduction to Round Linear Rail
The round linear rail has carved out a niche as one of the most versatile components in modern motion systems. Its cylindrical design allows for smooth and precise linear movement, making it a mainstay in both industrial and consumer-grade machines. Whether used in 3D printers, CNC routers, or automation lines, the round linear rail ensures accuracy, stability, and efficiency.
Its cost-effectiveness and ease of installation make it a top choice for engineers and designers seeking high performance without complex setup requirements.
What Is a Round Linear Rail?
A round linear rail is a precision-engineered cylindrical shaft that guides a linear bearing or carriage in a straight line. Typically, it is hardened and polished to reduce friction and wear. The rail, combined with bushings or linear ball bearings, supports and guides motion smoothly under varying loads.
Its fundamental role is to ensure a straight, precise movement while minimizing energy loss and mechanical resistance.
History of Linear Rail Systems
Linear motion systems have evolved significantly. Early machines relied on plain sliding mechanisms, which wore out quickly and required frequent lubrication. The introduction of ball bearing guides in the 20th century marked a revolution — drastically reducing friction and improving accuracy. The round linear rail was one of the first commercially successful designs, offering a perfect blend of simplicity and performance.
Structural Design of Round Linear Rail
A typical round linear rail includes:
Hardened steel shaft: Acts as the guide for the bearing movement.
Linear bearing block: Houses rolling elements for smooth motion.
End supports (optional): Used to fix and stabilize the rail.
Retaining rings or caps: Hold the bearing in place during operation.
Its smooth cylindrical geometry ensures low friction, making it ideal for applications where vibration control and precision are key.
Materials Used in Round Linear Rails
Round rails are usually made from hardened carbon steel, stainless steel, or chrome-plated steel. For corrosive environments, stainless steel variants are preferred. In lightweight applications, aluminum or composite shafts may also be used.
Protective coatings such as nickel plating or black oxide improve corrosion resistance and surface hardness, extending the rail’s life.
Working Principle of Round Linear Rail
The round linear rail works on the rolling motion principle. As the carriage or bearing moves along the rail, a set of steel balls rolls between the rail and bearing housing, minimizing friction. This mechanism enables effortless, precise motion, even at high speeds or under variable loads.
Types of Round Linear Rails
There are three main types:
Unsupported round rails: Simple shafts fixed only at the ends — suitable for light loads.
Fully supported rails: Mounted along their entire length, increasing rigidity.
Floating or self-aligning rails: Allow compensation for misalignment, useful in multi-axis setups.
Each type caters to different load conditions and accuracy requirements.
Advantages of Using Round Linear Rail
The round linear rail offers several unique benefits:
Simple alignment and installation
Reduced maintenance due to self-lubricating bearings
High-speed capability
Cost-effective compared to profiled rails
Tolerant to minor mounting inaccuracies
Its flexibility makes it an excellent choice for both small-scale automation and large industrial setups.
Comparison: Round vs Square Linear Rail
| Feature | Round Linear Rail | Square Linear Rail |
|---|---|---|
| Rigidity | Moderate | High |
| Ease of Installation | Easy | Requires precision |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
| Load Handling | Moderate | High |
| Self-Alignment | Yes | No |
| Best Use | Light to medium loads | Heavy industrial use |
This comparison shows that round linear rails are ideal for systems prioritizing affordability, flexibility, and simplicity over extreme rigidity.
Load Capacity and Performance
The load capacity of a round linear rail depends on its diameter, bearing type, and support configuration. Common diameters range from 8mm to 30mm, handling loads from a few kilograms to several hundred. Supported rails can handle heavier loads without bending or deflection.
Performance metrics include speed, accuracy, and repeatability — all influenced by the rail’s material, bearing design, and lubrication.
Installation Guide for Round Linear Rails
Installing a round linear rail involves these key steps:
Prepare the surface: Ensure it’s flat and debris-free.
Mount end supports: Align them precisely.
Insert the rail: Fix securely using clamps or bolts.
Install bearings or carriage: Slide them gently onto the rail.
Test motion: Move the carriage manually to check smoothness.
Accuracy during installation directly affects system performance.
Common Mounting Mistakes to Avoid
Mounting on uneven surfaces.
Over-tightening bolts, which causes deformation.
Forgetting to lubricate bearings.
Misalignment between parallel rails.
Even minor installation errors can lead to vibration, wear, or premature failure.
Lubrication and Maintenance
Lubrication reduces friction and extends bearing life. For most round linear rails, use lithium-based grease or light machine oil. Clean the rail regularly with a lint-free cloth to remove dust or chips.
Supported rails often have lubrication ports, allowing easy re-greasing without disassembly.
Applications in CNC Machines
Round linear rails are widely used in CNC routers, laser cutters, and engraving machines. Their smooth, low-friction motion ensures precision, while their cost-effectiveness makes them ideal for mid-range CNC equipment.
Use in Automation and Robotics
In robotics, these rails provide linear guidance for actuators and pick-and-place arms. Their self-aligning feature simplifies multi-axis motion and allows smooth travel even when surfaces aren’t perfectly aligned.
Round Linear Rails in 3D Printing
3D printers rely on round linear rails for precise nozzle and bed movement. Their low noise and smooth sliding action improve print quality and reduce vibration — essential for high-resolution printing.
Durability and Environmental Resistance
Round rails are robust but can corrode if exposed to moisture or chemicals. Choosing stainless steel variants or applying protective coatings can significantly improve durability in harsh environments.
Selecting the Right Round Linear Rail
When selecting a rail, consider:
Load and speed requirements
Operating environment
Rail length and diameter
Bearing type (ball vs bushing)
Budget constraints
Matching these factors ensures optimal system performance and longevity.
Cost and Value Considerations
A round linear rail system is often 20–30% cheaper than square rails. For small automation projects or prototyping, it delivers an excellent return on investment. Supported rails cost more but provide higher load capacity and stability.
Top Manufacturers and Brands
Some top-rated brands include:
Hiwin
THK
Misumi
NSK
Igus (drylin series)
Each brand offers specialized round rail solutions for different performance and budget levels.
Troubleshooting Common Problems
| Problem | Possible Cause | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Uneven movement | Misalignment or dirt | Clean and realign |
| Noise during travel | Dry bearings | Lubricate properly |
| Vibration | Loose mounting | Tighten and inspect |
| Rust spots | Poor environment protection | Use stainless or coated rails |
Routine inspection can prevent most performance issues before they escalate.
Safety Precautions During Use
Always wear gloves when handling round linear rails, as edges can be sharp. Avoid bending the rail during installation. When using power tools nearby, cover rails to prevent chip contamination.
Emerging Innovations in Linear Rail Technology
New developments include self-lubricating polymer bearings, composite shafts, and IoT-enabled monitoring systems. These innovations help predict wear, reduce maintenance, and improve efficiency — paving the way for smarter motion systems.
Future of Round Linear Rail Systems
The future of round linear rails lies in integration with smart automation and AI-driven manufacturing. As machines become more precise and interconnected, these rails will continue evolving to meet higher performance demands with minimal human intervention.
Final Thoughts on Round Linear Rail
The round linear rail remains a timeless, reliable, and cost-effective component in motion control systems. Its adaptability and simplicity make it indispensable for countless industries — from CNC machining to advanced robotics. With proper care, a quality round rail can offer decades of smooth, silent, and precise performance.
FAQs About Round Linear Rail
What is the main difference between round and square linear rails?
Round rails are more flexible and easier to install, while square rails offer greater rigidity.
Can I cut round linear rails to size?
Yes, but use precision cutting tools and deburr the ends before installing bearings.
Do round linear rails need lubrication?
Yes. Regular lubrication is essential for long-lasting smooth operation.
Are round linear rails suitable for heavy loads?
Supported round rails can handle moderate to heavy loads effectively.
Can I use round linear rails in outdoor environments?
Yes, but choose stainless steel variants or apply protective coatings.
What is the typical lifespan of a round linear rail?
With proper care and lubrication, it can last over 10 years in continuous use.