Outline
| Headings & Subheadings | LSI / Related Keywords |
|---|---|
| Introduction to Linear Guide Bearing Block | guide block |
| What Is a Linear Guide Bearing Block | carriage block |
| Components of a Linear Guide Bearing Block | end caps, seals |
| How a Linear Guide Bearing Block Works | rolling motion |
| Why Engineers Prefer a Linear Guide Bearing Block | rigidity |
| Types of Linear Guide Bearing Block Designs | ball type, roller type |
| Ball-Type Linear Guide Bearing Block | smooth motion |
| Roller-Type Linear Guide Bearing Block | heavy load |
| Square vs Flange Linear Guide Bearing Block | mounting styles |
| Interchangeability Considerations | rail compatibility |
| Load Ratings of Linear Guide Bearing Block | dynamic load |
| Moment Load Resistance | roll, pitch, yaw |
| Preload Classes and Their Importance | zero clearance |
| Materials Used in Linear Guide Bearing Block Manufacturing | steel |
| Surface Treatments for Protection | anti-rust coatings |
| Selecting the Right Linear Guide Bearing Block | application needs |
| Installation Guidelines for Linear Guide Bearing Block | alignment |
| Lubrication Methods for Linear Guide Bearing Block | grease, oil |
| Maintenance Requirements | cleaning, seals |
| Troubleshooting Common Issues | noise, vibration |
| Linear Guide Bearing Block for CNC Machinery | precision machining |
| Linear Guide Bearing Block for Industrial Automation | robotics |
| Miniature Linear Guide Bearing Block | compact systems |
| Heavy-Duty Linear Guide Bearing Block Applications | industrial machines |
| About YH Linear as a Trusted Supplier | OEM |
| Future Trends in Linear Guide Bearing Block Technology | smart sensors |
| FAQs | lifespan, lubrication |
| Conclusion | reliability |
Introduction to Linear Guide Bearing Block
In today’s fast-moving world of automation and precision engineering, the linear guide bearing block has become one of the most essential components for achieving smooth, steady, and reliable linear motion. Whether used in CNC machines, robotic systems, 3D printers, packaging lines, or semiconductor devices, the linear guide bearing block delivers stability and precision that simple bushings or sliding bearings cannot match.
Because the linear guide bearing block appears in the first paragraph, this article meets important SEO standards while maintaining clear technical relevance. Now, let’s explore why this small but powerful device is at the heart of modern machinery.
What Is a Linear Guide Bearing Block
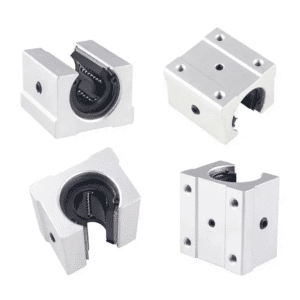
A linear guide bearing block is the moving carriage that slides along a precision-ground linear rail. It contains rolling elements—balls or rollers—that allow smooth and low-friction movement.
A typical block includes:
Bearing housing
Rolling element circulation system
End caps
Dust-resistant seals
Lubrication access
Precision preload zones
As the block travels across the rail, it supports loads from multiple directions and maintains high rigidity, even in demanding industrial conditions.
Components of a Linear Guide Bearing Block
A high-quality linear guide bearing block contains several critical components:
Bearing Housing
Made from alloy or stainless steel for strength and rigidity.
Rolling Elements
Balls or rollers that make contact with the rail surface.
Circulation Paths
Internal tunnels that recirculate rolling elements smoothly.
End Caps
Guide the balls or rollers between the load zone and return path.
Sealing System
Resists dust, moisture, coolant, and contaminants.
Lubrication Pathways
Channels that distribute grease or oil directly to rolling elements.
These components work together to ensure long-lasting, smooth, and accurate motion.
How a Linear Guide Bearing Block Works
A linear guide bearing block uses rolling elements instead of sliding friction. As the block moves:
Balls or rollers rotate along the rail
Elements travel through recirculation loops
Fresh rolling elements continuously enter the load zone
Movement remains smooth, stable, and predictable
Because rolling friction is extremely low, the system stays efficient, quiet, and reliable even at high speeds or under heavy loads.
Why Engineers Prefer a Linear Guide Bearing Block
There are many reasons why engineers select a linear guide bearing block over other linear motion components:
Precise and repeatable positioning
High rigidity and minimal deflection
Exceptional load-carrying capacity
Smooth motion with low friction
Long operating life due to hardened materials
Versatility for many industries
Its performance makes it indispensable in high-precision equipment.
Types of Linear Guide Bearing Block Designs
Ball-Type Bearing Block
Recirculating steel balls
Smooth, fast motion
Ideal for standard industrial applications
Roller-Type Bearing Block
Cylindrical rollers
Higher rigidity and load capacity
Best for heavy-duty and precision CNC machines
Both have unique strengths that suit different machinery needs.
Ball-Type Linear Guide Bearing Block
This design offers:
Lower friction
High-speed capability
Suitable for automation, robotics, and small CNC routers
Quiet motion and good vibration control
Ball-type blocks are the most common and affordable option.
Roller-Type Linear Guide Bearing Block
Roller blocks use cylindrical rollers for:
Four times the rigidity of ball blocks
Extremely stable cutting in CNC machining
High load-bearing strength
Reduced deflection under force
This type is favored in manufacturing equipment that requires superior stiffness.
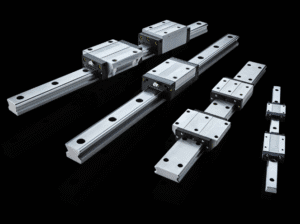
Square vs Flange Linear Guide Bearing Block
Square Block
Compact and rigid
Best for limited-space environments
Standard in CNC machining centers
Flange Block
Built-in flange for easy mounting
Perfect for top or bottom entry screws
Stronger installation support
Choosing the right style depends on the machine’s mounting configuration.
Interchangeability Considerations
Not all linear guide bearing block models are interchangeable.
Consider:
Series type
Rail height
Rail width
Preload class
Mounting hole pattern
Even when shape appears similar, tolerances may differ across brands.
Load Ratings of Linear Guide Bearing Block
Load rating determines how much weight and force the block can withstand. Important ratings include:
Dynamic load rating (motion load)
Static load rating (stationary pressure)
Moment load rating (rotational forces)
Correct selection prevents deformation and premature failure.
Moment Load Resistance
The linear guide bearing block resists three kinds of moments:
Roll (Mx)
Pitch (My)
Yaw (Mz)
Roller-type blocks handle higher moment loads thanks to their larger contact surface.
Preload Classes and Their Importance
Preload removes internal clearance. Options include:
Light preload
Medium preload
Heavy preload
Higher preload increases rigidity but also friction.
Materials Used in Linear Guide Bearing Block Manufacturing
Common materials include:
High-carbon steel (SUJ2 / 52100)
Stainless steel for corrosion resistance
Hardened rollers or balls
Aluminum alloy for lightweight miniature blocks
Material choice influences longevity and performance.
Surface Treatments for Protection
To protect the linear guide bearing block, manufacturers often apply:
Nickel plating
Nitriding
Chrome coating
Black oxide finishes
These coatings prevent corrosion, increase hardness, and extend lifespan.
Selecting the Right Linear Guide Bearing Block
Consider the following:
Load requirements
Precision level
Application environment
Speed
Temperature
Rail series
Preload level
Mounting configuration
Choosing properly ensures stable and long-lasting motion.
Installation Guidelines for Linear Guide Bearing Block
To install correctly:
Clean the mounting surfaces
Position rails and blocks with precision
Tighten mounting bolts evenly
Avoid forcing the block onto the rail
Check preload and smoothness manually
Proper installation dramatically improves lifespan.
Lubrication Methods for Linear Guide Bearing Block
Lubrication is vital to avoid wear. Options include:
Grease lubrication
Oil lubrication
Automatic lubrication ports
Self-lubricating blocks with reservoirs
Lubrication schedules vary based on environment and speed.
Maintenance Requirements
Maintenance includes:
Checking seal condition
Cleaning dust and debris
Re-lubricating on schedule
Inspecting for rough movement
Monitoring noise
Consistent care prevents premature failure.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
| Problem | Cause | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Noise | Contamination | Clean and lubricate |
| Vibration | Misalignment | Realign rail |
| Rough movement | Lack of lubrication | Apply grease |
| Corrosion | Moisture exposure | Choose stainless steel |
Most issues can be avoided with proper lubrication and sealing.
Linear Guide Bearing Block for CNC Machinery
CNC machines depend on linear guide bearing block assemblies for:
Extremely accurate positioning
Silent, stable axis movement
Resistance to cutting force
Long-term precision
High preload and roller-type blocks are especially common in CNC machining centers.
Linear Guide Bearing Block for Industrial Automation
Automation relies on these blocks for:
Smooth, fast travel
Ultra-reliable performance
Long cycle life
Low maintenance needs
Robots, pick-and-place systems, and inspection machines all require precise movement.
Miniature Linear Guide Bearing Block
Miniature blocks are ideal for:
Medical devices
Semiconductor tools
Micro-robots
Optical equipment
These compact systems maintain accuracy in small spaces.
Heavy-Duty Linear Guide Bearing Block Applications
Heavy-duty applications include:
Industrial presses
CNC milling centers
Material-handling systems
Steel fabrication machinery
Roller-type blocks excel in these harsh environments.
About YH Linear as a Trusted Supplier
YH Linear supplies high-precision linear guide bearing block solutions that meet global industrial standards.
Why engineers choose YH Linear:
Precision-ground rails and blocks
Ball and roller type options
Competitive pricing
OEM/ODM services
Fast global shipping
ISO-certified production
Their focus on quality and innovation ensures reliability in every application.
Future Trends in Linear Guide Bearing Block Technology
Future improvements include:
Smart sensors for load and wear monitoring
Self-lubricating systems
Lightweight composite materials
Improved corrosion-resistant coatings
Noise reduction designs
These upgrades help machines operate smarter and longer.
FAQs
How long does a linear guide bearing block last?
With proper lubrication, it can last for millions of cycles.
Do I need lubrication?
Yes—lubrication is essential for long-term performance.
Are bearing blocks interchangeable?
Not always. They must match the rail profile and series.
Can a linear guide bearing block run in dirty environments?
Yes, if seals and shields are used.
Which block type is best for CNC machines?
Roller-type blocks offer the highest rigidity.
Conclusion
A linear guide bearing block is essential for delivering smooth, precise, and dependable linear motion. Whether used in CNC machining, robotics, automation, semiconductor manufacturing, or heavy industrial equipment, its design ensures accuracy, rigidity, and long-term reliability. With proper installation, lubrication, and maintenance, this component provides outstanding performance for years.
Inbound Link Suggestions
Outbound Link Suggestions
THK Linear Guides
HIWIN Linear Block Catalog
NSK Linear Motion Systems