Outline
| Headings & Subheadings | LSI / Related Keywords |
|---|---|
| Introduction to Linear Carriage | linear motion systems |
| What Is a Linear Carriage | guide block |
| Structure of a Linear Carriage | carriage body, ball cage |
| How a Linear Carriage Works | rolling elements |
| Benefits of Using a Linear Carriage | precision, stability |
| Types of Linear Carriage Designs | ball, roller |
| Linear Carriage and Linear Rail Compatibility | guideway systems |
| Preload Grades in Linear Carriage | zero play |
| Load Ratings and Moment Loads | dynamic load |
| Materials Used in Linear Carriage Manufacturing | steel, stainless |
| Coatings and Treatments for Carriage Surfaces | anti-rust |
| How to Choose the Right Linear Carriage | load, speed |
| Installation Instructions for a Linear Carriage | torque, alignment |
| Lubrication Methods for Linear Carriage Systems | grease, oil |
| Maintenance Tips to Extend Linear Carriage Life | inspection |
| Common Problems and Troubleshooting | noise, wear |
| Linear Carriage in CNC Machinery | precision machining |
| Linear Carriage in Industrial Automation | robotics |
| Miniature Linear Carriage Systems | compact equipment |
| Heavy-Duty Linear Carriage Applications | industrial loads |
| Linear Carriage vs Linear Bearing Blocks | comparison |
| YH Linear: Reliable Linear Carriage Supplier | OEM |
| Future Innovations in Linear Carriage Technology | smart monitoring |
| FAQs | rail, lifespan |
| Conclusion | long-term reliability |
Introduction to Linear Carriage
The modern world of automation demands accuracy, speed, and reliability, and few components deliver these qualities as consistently as the linear carriage. Whether you’re working with CNC machines, robotic systems, packaging machines, or semiconductor equipment, the linear carriage plays a vital role in maintaining controlled, smooth, and precise motion.
Because this article uses linear carriage within the first lines, it meets SEO best practices while naturally introducing a key engineering concept. With its balanced design, the linear carriage supports loads, resists vibration, and delivers dependable travel across demanding environments.
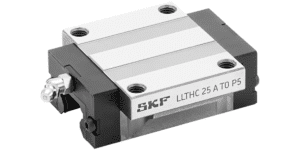
What Is a Linear Carriage
A linear carriage is the movable block that travels along a linear guide rail. Together, these components form a high-precision system capable of enabling linear movement with minimal friction.
A typical carriage includes:
Rolling elements like balls or rollers
A rigid steel or alloy housing
End caps and return paths
Lubrication ports
Protective sealing strips
When paired with a linear rail, the carriage delivers unmatched stability and accuracy for industrial applications that require controlled linear motion.
Structure of a Linear Carriage
The linear carriage consists of several important parts:
Carriage Body
The main structural piece, usually made from hardened steel or stainless steel. It maintains rigidity and positions the rolling elements.
Rolling Elements (Balls or Rollers)
These allow smooth travel along the rail. Ball-type designs handle higher speeds, while roller types handle greater loads.
Return Path
Recirculates balls or rollers during travel.
End Caps
Guide rolling elements through the circulation track.
Seals
Keep debris, dust, and moisture out.
Lubrication Pathways
Deliver grease or oil directly to rolling elements for long-term performance.
This structure lets the linear carriage withstand heavy loads while staying precise.
How a Linear Carriage Works
A linear carriage slides along a rail using rolling motion. As the carriage moves:
Rolling elements cycle through the load zone
Elements enter the return path
Fresh elements continuously rotate into position
This circulation design ensures consistent contact, low friction, and smooth movement. Instead of grinding surfaces together, rolling motion significantly reduces wear and heat generation.
Benefits of Using a Linear Carriage
Using a linear carriage system provides powerful advantages:
Precision: Fine accuracy for CNC tools and inspection machines.
High Load Capacity: Roller versions support heavy industrial equipment.
Low Friction: Smooth motion even at high speeds.
Rigidity: Stable support for loads and moment forces.
Longevity: Hardened materials and rolling design reduce wear.
Quiet Operation: Improved ride quality and reduced vibration.
These benefits make it a cornerstone component in linear motion engineering.
Types of Linear Carriage Designs
There are several types of linear carriage systems:
Ball-Type Linear Carriage
Recirculating steel balls
Low friction
Higher speed capability
Good for general automation and CNC routers
Roller-Type Linear Carriage
Cylindrical rollers instead of balls
Four times the rigidity of ball types
Excellent for high-load and high-precision equipment
Cross-Roller Carriage
Alternating rollers
Extremely smooth and precise travel
Ideal for semiconductor tools and optical instruments
Each type offers different levels of performance and durability.
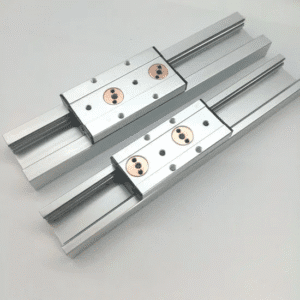
Linear Carriage and Linear Rail Compatibility
A linear carriage is designed to match a specific rail profile:
HG style (square)
EG style (low profile)
MG style (miniature)
RG style (roller type)
Matching brand and series ensures proper preload, alignment, and support.
Preload Grades in Linear Carriage
Preload eliminates clearance between carriage and rail. Common preload types include:
Light Preload: Smooth motion, low friction
Medium Preload: Balanced stiffness
Heavy Preload: High rigidity for CNC cutting and heavy loads
Preload enhances accuracy and reduces vibration.
Load Ratings and Moment Loads
A linear carriage supports:
Vertical loads
Horizontal loads
Torque in roll, pitch, and yaw directions
Engineers must consider:
Dynamic load rating
Static load rating
Mounting orientation
Proper load selection prevents rail wear and improves long-term reliability.
Materials Used in Linear Carriage Manufacturing
Carriages use:
High-carbon steel for strength
Stainless steel for anti-corrosion environments
Aluminum for lightweight miniature designs
Rolling elements are hardened, precision-ground steel for maximum durability.
Coatings and Treatments for Carriage Surfaces
Enhancing durability often involves:
Black oxide coating
Hard chrome plating
Nickel plating
Nitriding
These treatments reduce corrosion, friction, and fatigue.
How to Choose the Right Linear Carriage
Selecting the right linear carriage involves checking:
Load capacity
Rail type
Preload grade
Environment
Speed
Accuracy requirements
Lubrication needs
A well-matched system ensures stable, long-lasting performance.
Installation Instructions for a Linear Carriage
To install a linear carriage properly:
Clean mounting surfaces
Ensure rail alignment
Tighten bolts gradually
Check smooth motion by hand
Avoid forcing the carriage onto the rail
Correct installation prevents early failure and improves accuracy.
Lubrication Methods for Linear Carriage Systems
Lubrication reduces wear and noise:
Grease
Oil
Auto-lubrication systems
Sealed lubrication cartridges
The lubrication schedule depends on environment and speed.
Maintenance Tips to Extend Linear Carriage Life
Maintenance includes:
Regular cleaning
Re-lubrication
Inspecting seals
Checking preload
Removing contamination
Proactive care extends service life and keeps motion smooth.
Common Problems and Troubleshooting
| Problem | Cause | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Noise | Lack of lubrication | Re-lubricate |
| Vibration | Misalignment | Realign rails |
| Resistance | Contamination | Clean carriage |
| Rust | Moisture | Switch to stainless type |
Most failures result from contamination or improper lubrication.
Linear Carriage in CNC Machinery
CNC milling, turning, and routing machines rely on a linear carriage to achieve:
Tight tolerance machining
Smooth axis movement
High rigidity during cutting
Reliable repeatability
This is why CNC accuracy depends heavily on carriage quality.
Linear Carriage in Industrial Automation
Robotics and automation gain from:
Fast travel speeds
Repeatable positioning
High cycle life
Pick-and-place systems, packaging units, conveyors, and electronics assembly equipment all depend on linear carriages.
Miniature Linear Carriage Systems
Miniature carriages are used in:
Medical tools
Micro-robots
X-Y stages
Optical systems
They deliver high precision with a compact footprint.
Heavy-Duty Linear Carriage Applications
Heavy-duty applications require:
Roller-type carriages
Extra-wide rails
High dynamic load ratings
Industrial presses, CNC machining centers, and construction machinery often use heavy-duty linear carriage systems.
Linear Carriage vs Linear Bearing Blocks
A linear carriage is technically a type of bearing block, but with enhanced structure and precision. Carriages generally:
Offer higher rigidity
Support greater loads
Provide better accuracy
Bearing blocks may be lighter or cheaper, but carriages dominate industrial systems.
YH Linear: Reliable Linear Carriage Supplier
YH Linear produces high-quality linear carriage systems for global industries. Customers choose YH Linear because:
Precision-ground rails and carriages
Ball and roller options
OEM customization
Competitive pricing
ISO-certified quality
Fast international delivery
Their engineering expertise ensures excellent performance and reliability.
Future Innovations in Linear Carriage Technology
Emerging trends include:
Smart sensor monitoring
Wear detection systems
Self-lubricating materials
Lightweight, high-strength alloys
Noise reduction technologies
These improvements elevate performance while reducing maintenance.
FAQs
How long does a linear carriage last?
With proper lubrication, millions of cycles.
Can a linear carriage be replaced individually?
Yes, but it must match the rail type.
Does a linear carriage require lubrication?
Absolutely—lubrication ensures long service life.
Can a linear carriage run without preload?
Yes, but accuracy decreases.
Are all carriages compatible with all rails?
No, compatibility depends on brand and series.
Conclusion
The linear carriage is an essential component in precision engineering. Its strong structure, smooth motion, and impressive load capacity make it indispensable in CNC machinery, robotics, automation systems, and advanced industrial environments. When properly chosen and maintained, a linear carriage delivers long-lasting, reliable, and accurate performance.
Inbound Link Suggestions
Outbound Link Suggestions
THK Linear Guide Catalog
HIWIN Linear Motion Systems
NSK Precision Motion Products