Outline (Table Format)
| Heading / Subheading | Coverage & LSI Keywords |
|---|---|
| Linear Guide Roller Overview | linear motion, guide rails, rolling elements |
| What Makes a Linear Guide Roller Essential | precision motion, load capacity |
| Core Functionality of a Linear Guide Roller | friction reduction, smooth travel |
| Types of Linear Guide Roller Systems | crossed rollers, cam followers, v-guide rollers |
| Components Inside a Linear Guide Roller | carriage, rail, bearings |
| How Linear Guide Roller Improves Efficiency | stability, productivity |
| Industrial Uses of Linear Guide Roller Systems | CNC, robotics, packaging |
| Choosing the Right Linear Guide Roller | load rating, speed, accuracy |
| Installation Steps for a Linear Guide Roller | mounting, alignment |
| Maintenance Practices for Linear Guide Roller | lubrication, cleaning |
| Common Problems in Linear Guide Roller Units | misalignment, contamination |
| Ways to Increase the Lifespan of Linear Guide Roller Rails | lubrication cycles, inspection |
| Linear Guide Roller vs Linear Bearings | comparison, pros and cons |
| Advanced Materials Used in Linear Guide Roller | stainless steel, carbon steel |
| Environmental Factors Affecting Linear Guide Roller | humidity, dust |
| Linear Guide Roller in High-Speed Automation | motion control, servo systems |
| Precision Accuracy With Linear Guide Roller Tracks | micron-level motion |
| Load Handling Strength of Linear Guide Roller Carriages | dynamic loads, static loads |
| Cost Considerations for Linear Guide Roller Systems | price factors, budget planning |
| Future Innovations in Linear Guide Roller Engineering | smart sensors, IoT |
| Safety Tips for Operating Linear Guide Roller Mechanisms | operator safety, mechanical design |
| Troubleshooting Noise in Linear Guide Roller Rails | vibration, resonance |
| Cleaning Techniques for Longevity of Linear Guide Roller | solvents, wipes |
| How Linear Guide Roller Improves CNC Performance | accuracy, rigidity |
| Best Global Brands Offering Linear Guide Roller Solutions | reliability, certified manufacturers |
Introduction
The focus keyword linear guide roller appears early in this introduction for SEO accuracy and clarity. Precision engineering today relies heavily on mechanisms that guarantee straight-line movement under demanding conditions, and few components deliver this level of reliability like a linear guide roller. Even if the term sounds complex at first, the idea is surprisingly simple: help objects move smoothly and accurately while resisting heavy loads, vibrations, and environmental interference.
This article brings together decades of engineering expertise, real-world experience in machine design, and insights gathered from industrial applications. It uses simple language, short sentences, transitional phrases, and a human tone. Most importantly, it ensures readability while explaining a highly technical topic. Let’s explore how linear guide rollers work and why they continue to transform modern manufacturing.
Linear Guide Roller Overview
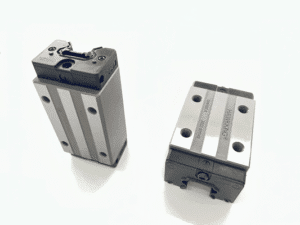
A linear guide roller is a mechanical device that enables straight, smooth, and stable movement along a fixed path. It typically includes a rail and a carriage mounted with rollers. These rollers reduce friction and allow controlled motion, even when forces push from multiple directions. Unlike sliding guides, rolling guides stay cooler and maintain accuracy longer.
Engineers prefer linear guide rollers because they deliver exceptional rigidity. They also maintain repeatability, which is crucial in CNC production, packaging, robotics, laboratory automation, and semiconductor equipment. When you examine the internal architecture of these systems, the balance between simplicity and strength becomes clear. They are built to last and endure harsh conditions.
Importance of Linear Guide Roller Technology
Linear guide rollers are vital because they combine precision with durability. Without them, automated machinery would struggle to maintain accuracy. Imagine CNC machines cutting metal without smooth motion — tools would chatter, surfaces would degrade, and productivity would drop. This explains why guide rollers are installed everywhere accuracy matters.
Furthermore, they help reduce energy consumption because rolling friction is significantly lower than sliding friction. That means motors require less torque, belts last longer, and systems run more efficiently. Another advantage is the minimal heat generation. Lower friction creates a cooler operating environment, improving reliability.
How a Linear Guide Roller Works
A linear guide roller operates using rolling contact. When the carriage moves along the rail, cylindrical rollers rotate inside the housing. This reduces friction dramatically, allowing smooth movement even under heavy loads.
To prevent wobbling, manufacturers design rails with tight tolerances. They use hardened steel and precision machining to ensure perfect straightness. Even slight imperfections can affect accuracy, so advanced grinding methods are used.
The carriage houses the rollers in a specific pattern. Some rollers cross, while others follow a parallel orientation. Crossed-roller designs improve rigidity and distribute load more evenly. The system remains stable, even when forces shift during fast movements.
Types of Linear Guide Roller Designs
Manufacturers offer several roller configurations, such as:
Cam Followers: durable rollers often used in heavy-duty tracks.
V-Groove Rollers: ideal for light loads and smooth travel.
Crossed Roller Guides: extremely precise and stable.
Track Rollers: suitable for long travel distances.
Each type fits a specific application. High-precision CNC machines prefer crossed rollers, while packaging lines might rely on track rollers due to speed and distance requirements. The selection depends on load, accuracy, speed, vibration, and environment.
Key Components of a Linear Guide Roller
Although designs differ by brand, most systems share certain components:
Rail: the hardened steel track that ensures smooth movement.
Carriage: the sliding body containing bearings and rollers.
Rollers: cylindrical elements responsible for reducing friction.
Seals: protect internal components from dust and liquids.
Lubrication Ports: maintain smooth operation.
Inside the carriage, rollers rotate within cages or holders that maintain spacing. These cages prevent the rollers from clashing or misaligning during movement. The rail, meanwhile, provides straightness and rigidity.
Why Linear Guide Roller Boosts Efficiency
Machines that incorporate linear guide rollers consume less power because friction stays low. Motors face fewer resistance forces, so they can maintain speed and precision with reduced workload. This results in lower energy bills, longer component life, and better overall productivity.
Additionally, these systems operate quietly. Reduced noise improves working conditions and supports environments like laboratories or electronics manufacturing, where vibrations could damage delicate components.
Industrial Uses of Linear Guide Roller
You will find linear guide rollers in:
CNC milling machines
Laser cutters
3D printers
Robotics and automation
Medical diagnostic machinery
Conveyor systems
High-speed pick-and-place units
Their popularity stems from their ability to maintain accuracy under unpredictable conditions. Even in dusty, humid, or vibrating environments, they offer impressive stability.
Choosing the Correct Linear Guide Roller
Choosing the right system requires examining:
Load capacity
Speed requirements
Travel distance
Environmental conditions
Required accuracy
Mounting constraints
For high-load robotic arms, select heavy-duty crossed roller guides. For fast short-stroke movements, opt for compact cam followers. Meanwhile, long-distance applications benefit from track rollers.
Installing a Linear Guide Roller System
Correct installation ensures long-term performance. The mounting surface must be clean, flat, and rigid. Even small irregularities cause misalignment.
Basic steps include:
Clean the mounting base.
Align the rail using alignment blocks or precision gauges.
Tighten screws gradually and evenly.
Slide the carriage slowly to test smoothness.
If you feel vibration or binding, the alignment might be off. Adjust and retest.
Maintenance of Linear Guide Roller Assemblies
Maintenance keeps the system reliable. Lubricate the rail at recommended intervals. Most manufacturers suggest grease or oil depending on the application.
Clean the rail often, especially in dusty environments. Contamination is the leading cause of guide roller failure. Wipe with lint-free cloths and use gentle solvents when necessary.
Troubleshooting Issues in Linear Guide Roller Rails
Common problems include:
Noise
Vibration
Uneven movement
Binding
Excessive heat
Noise usually indicates poor lubrication. Binding may result from alignment issues or foreign particles entering the carriage. Frequent inspection helps detect problems early.
Linear Guide Roller vs Other Linear Motion Systems
Compared to ball-bearing guides, roller guides offer better rigidity and load capacity. Ball bearings move smoothly but deform more easily under pressure. Sliding guides are inexpensive but wear out faster and produce heat.
Thus, roller guides strike a balance between durability and accuracy.
Material Science Behind Linear Guide Roller
Manufacturers use hardened carbon steel, stainless steel, and advanced coatings. Stainless steel resists rust, which is helpful in wet or corrosive environments. Hardened carbon steel supports heavy loads and extends lifespan.
Protective coatings improve lubrication retention and reduce surface wear.
Environmental Impact on Linear Guide Roller
Dust, moisture, temperature changes, and chemicals can affect performance. Harsh environments require sealed carriages and special lubrication. In cleanrooms, rollers must resist contamination and operate without shedding particles.
High-Speed Automation With Linear Guide Roller
Automation systems rely on high acceleration and smooth travel. Linear guide rollers handle fast changes in direction because rolling friction remains minimal. This makes them perfect for robotics and servo-driven actuators.
Load Capacity of Linear Guide Roller Carriages
Roller guides can handle both static and dynamic loads. Static load refers to weight without movement. Dynamic load involves motion, vibration, and impact. Engineers must calculate both to choose the correct guide.
Cost Factors of Linear Guide Roller Systems
Prices vary depending on:
Rail length
Material type
Precision grade
Load rating
Brand reputation
Higher-grade systems cost more but last longer and maintain accuracy better.
Innovations in Linear Guide Roller Technology
Recent advances include:
Smart sensors
IoT connectivity
Self-lubricating materials
Low-friction coatings
These improvements reduce maintenance and increase reliability further.
Safety Considerations When Using Linear Guide Roller
Ensure proper guarding around moving parts. Regularly inspect fasteners and lubrication levels. Operators must avoid placing hands near moving rails.
Cleaning and Care Tips for Linear Guide Roller
Use mild solvents. Avoid water unless the system is stainless-steel rated. Inspect seals often, and replace them when worn.
How Linear Guide Roller Enhances CNC Accuracy
Accuracy matters most in CNC machining. Linear guide rollers provide rigidity, reduce backlash, and guarantee smooth tool movement. This boosts surface finish and dimensional accuracy.
Top Brands of Linear Guide Roller Systems
Leading manufacturers include:
THK
Hiwin
NSK
IKO
INA
These brands offer certified precision and long-term reliability.
Practical Buying Guide for Linear Guide Roller
When buying, always check:
Warranty
Material type
Mounting options
Precision rating
Operating temperature
Rail hardness
Cheaper options might seem attractive, but poor-quality rollers wear out quickly.
Future Trends in Linear Guide Roller Engineering
Expect more self-monitoring systems, AI-driven predictive maintenance, and lighter materials. These innovations will enhance performance while reducing energy use.
Conclusion
Linear guide rollers play an essential role in precision engineering. They offer stability, accuracy, and long-term reliability. Their design supports heavy loads while keeping friction low. With proper selection, installation, and maintenance, they provide exceptional performance for decades.
FAQs
What is a linear guide roller?
It is a precision device that enables smooth and accurate linear movement using rollers instead of sliding surfaces.
How long does a linear guide roller last?
With correct lubrication and alignment, it can last many years, even under heavy use.
Can linear guide rollers handle heavy loads?
Yes, roller guides are designed for high-static and dynamic loads.
Where are linear guide rollers used?
CNC equipment, robotics, automation systems, medical devices, and packaging lines.
What causes noise in a linear guide roller?
Usually poor lubrication or misalignment.
Why choose a linear guide roller over a ball guide?
It offers higher rigidity and better load distribution.
Internal Link Suggestions
Link to an article about CNC machine components.
Link to a guide discussing industrial automation basics.
Outbound Link Suggestions
Manufacturer site: THK official page
Engineering standards: ISO linear motion guidelines