Comprehensive Outline
| Main Topics | Detailed Coverage |
|---|---|
| Machine Rails Overview | Definition and industrial importance |
| Evolution of Machine Rail Technology | From sliding ways to rolling rails |
| Machine Rails Working Principles | Linear motion fundamentals |
| Core Components of Machine Rails | Rail, carriage, rolling elements |
| Materials Used in Machine Rails | Steel grades and durability |
| Heat Treatment and Surface Finish | Wear and corrosion resistance |
| Load Capacity and Rigidity | Static, dynamic, and moment loads |
| Precision and Accuracy | Repeatability and stability |
| Types of Machine Rails | Ball rails, roller rails, slide rails |
| Machine Rails vs Traditional Slideways | Performance comparison |
| Installation Requirements | Mounting and base preparation |
| Alignment and Preload Control | Motion optimization |
| Lubrication Systems | Oil and grease solutions |
| Maintenance and Service Life | Long-term reliability |
| Vibration and Noise Control | Smooth motion benefits |
| CNC Machine Applications | Milling, turning, grinding |
| Automation and Robotics | Gantry and pick-and-place |
| Heavy Industrial Machinery | Presses and tooling systems |
| Medical and Precision Equipment | Clean and accurate motion |
| Selecting the Right Machine Rails | Technical considerations |
| Common Selection Mistakes | Oversizing and misalignment |
| Cost Efficiency and ROI | Long-term value analysis |
| YH Linear Machine Rails | Brand strengths and solutions |
| Future Trends in Machine Rails | Smart and high-rigidity systems |
Introduction
Modern industrial machinery depends on accurate and stable motion. At the center of this motion lies a critical component: machine rails. Whether used in CNC machining centers, automation systems, or heavy industrial equipment, machine rails ensure controlled linear movement with high precision and reliability.
At YH Linear, years of experience in linear motion engineering have shown that the correct choice of machine rails directly impacts productivity, accuracy, and equipment lifespan. Poor rail selection leads to vibration, wear, and downtime. This article explores how machine rails work, their advantages, applications, and why YH Linear machine rails are trusted across industries.
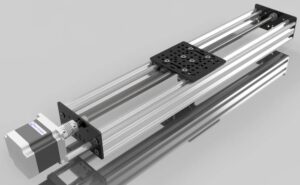
Machine Rails
Machine rails are linear guidance components that support and guide moving parts of machinery along a straight path. They are designed to provide smooth, accurate, and repeatable linear motion while carrying loads from multiple directions.
Unlike simple sliding guides, modern machine rails often use rolling elements such as balls or rollers. This rolling contact significantly reduces friction and wear. As a result, machine rails enable higher speeds, improved accuracy, and longer service life.
In practical terms, machine rails form the backbone of precision motion systems. Without them, modern manufacturing would simply not function at its current level.
Evolution of Machine Rail Technology
Early machines relied on plain slideways and dovetail guides. While robust, these systems generated high friction and required frequent adjustment and lubrication.
The introduction of rolling-element machine rails transformed linear motion technology. By replacing sliding contact with rolling contact, engineers achieved smoother movement and improved efficiency.
Over time, advancements in materials, heat treatment, and precision grinding further enhanced machine rail performance. Today, machine rails represent a mature technology optimized for demanding industrial environments.
Working Principles of Machine Rails
The core principle behind machine rails is controlled linear motion. Rolling elements move along hardened raceways, distributing load evenly and minimizing resistance.
Preload is often applied to eliminate internal clearance. This increases rigidity and positioning accuracy, especially in precision applications such as CNC machining.
Machine rails are also designed to handle complex load conditions. Vertical loads, lateral forces, and moment loads are absorbed simultaneously, ensuring stable motion under dynamic conditions.
Core Components of Machine Rails
A typical machine rail system includes the rail itself, one or more carriages, rolling elements, seals, and lubrication channels.
The rail is precision-ground and hardened to maintain straightness and durability. The carriage houses the rolling elements and transfers load between the machine structure and the rail.
Seals protect against contamination, while lubrication ports ensure smooth long-term operation. At YH Linear, every component is manufactured under strict quality control standards.
Materials and Surface Treatment
Material selection plays a crucial role in machine rail performance. High-strength alloy steels are commonly used due to their durability and load-bearing capability.
Heat treatment processes increase surface hardness while maintaining core toughness. Surface finishes and coatings improve wear resistance and corrosion protection.
YH Linear machine rails are designed to perform reliably even in harsh industrial environments.
Load Capacity and Rigidity
Machine rails must withstand heavy static and dynamic loads. Cutting forces, acceleration, and vibration all place stress on the rail system.
Roller-type machine rails offer exceptional rigidity due to line contact between rollers and raceways. Ball-type rails provide excellent speed and smoothness for lighter loads.
Proper load calculation ensures optimal rail selection. YH Linear provides technical support to help customers achieve the right balance between strength and efficiency.
Precision, Accuracy, and Repeatability
Precision is one of the defining advantages of modern machine rails. Tight manufacturing tolerances and controlled preload deliver excellent repeatability.
This accuracy ensures consistent positioning over long production cycles. Machines equipped with high-quality rails maintain dimensional stability and surface finish quality.
For industries where precision defines product value, machine rails are indispensable.
Types of Machine Rails
Machine rails are available in several configurations. Ball rails are widely used in automation and general machinery. Roller rails are preferred for heavy-duty and high-rigidity applications.
Slide rails serve simpler systems where speed and precision demands are lower. Each type addresses specific performance needs.
YH Linear offers a complete portfolio of machine rails to suit diverse industrial requirements.
Installation and Alignment Best Practices
Correct installation is critical for machine rail performance. Mounting surfaces must be flat, rigid, and clean.
Alignment ensures even load distribution and smooth motion. Misalignment leads to increased wear and reduced accuracy.
Following manufacturer guidelines during installation helps maximize service life and performance.
Lubrication and Maintenance
Machine rails require regular lubrication to minimize wear and prevent corrosion. Grease and oil lubrication systems are commonly used.
Automatic lubrication systems ensure consistent supply during continuous operation. Routine inspection further extends service life.
With proper maintenance, machine rails operate reliably for many years.
Applications of Machine Rails
Machine rails are used across a wide range of industries. In CNC machines, they support precise axis movement. In automation, they enable smooth gantry and pick-and-place motion.
Heavy industrial machinery relies on machine rails for stability under load. Medical and precision equipment depend on their accuracy and smoothness.
Their versatility makes machine rails essential across modern manufacturing.
YH Linear Machine Rails
YH Linear specializes in high-performance machine rails designed for precision, durability, and reliability. Each product reflects extensive industry experience and strict quality standards.
By combining advanced manufacturing with responsive technical support, YH Linear delivers motion solutions that perform consistently in real-world applications.
Choosing YH Linear means choosing long-term stability and engineering confidence.
Future Trends in Machine Rails
The future of machine rails includes smarter designs with integrated sensors for condition monitoring. Improved coatings and optimized geometries will further enhance performance.
As automation and precision manufacturing continue to advance, machine rails will remain a critical foundation. YH Linear continues to invest in innovation to meet future industry demands.
FAQs
What are machine rails used for?
They guide linear motion in machinery with precision and stability.
How do machine rails differ from slideways?
Machine rails use rolling elements, reducing friction and wear.
Are machine rails suitable for heavy loads?
Yes, especially roller-type machine rails.
Do machine rails require lubrication?
Yes, regular lubrication ensures smooth motion and long service life.
Can machine rails operate in harsh environments?
With proper sealing and coatings, they perform reliably.
Why choose YH Linear machine rails?
YH Linear offers quality manufacturing, technical expertise, and dependable performance.
Conclusion
Machine rails are the foundation of modern precision motion systems. Their ability to deliver smooth, accurate, and reliable movement makes them essential across industries.
With proven expertise and a commitment to quality, YH Linear continues to support manufacturers worldwide with dependable machine rail solutions. Choosing the right machine rails today ensures productivity, accuracy, and long-term success.
Suggested Internal Links
YH Linear machine rail product pages
YH Linear linear motion system solutions
Suggested Outbound Links
Industrial linear motion standards organizations
CNC and automation engineering resources