Outline (Table Format)
| Heading / Subheading | LSI Keywords |
|---|---|
| Linear Guides Overview | linear motion guides, guide rails |
| Why Linear Guides Matter | precision stability |
| How Linear Guides Work | recirculating balls |
| Main Components of Linear Guides | block, rail |
| Types of Linear Guides | linear blocks |
| Ball-Type Linear Guides | ball-bearing guides |
| Roller-Type Linear Guides | roller blocks |
| Miniature Linear Guides | micro rails |
| Wide Linear Guides | wide block rail |
| Flanged Linear Guides | flange type block |
| Long-Block Linear Guides | extended blocks |
| High-Load Linear Guides | heavy-duty guides |
| Linear Guides vs Linear Bearings | comparison |
| Linear Guides for CNC Machines | CNC accuracy |
| Linear Guides for 3D Printers | smooth extrusion |
| Linear Guides for Industrial Automation | robotics motion |
| Benefits of Using Linear Guides | low friction |
| Choosing the Right Linear Guides | selection factors |
| Precision Grades in Linear Guides | accuracy classes |
| Installation of Linear Guides | alignment tips |
| Lubrication of Linear Guides | grease, oil |
| Maintenance of Linear Guides | cleaning |
| Common Problems with Linear Guides | noise, binding |
| Troubleshooting Linear Guides | fixing drag |
| Materials Used in Linear Guides | steel, coated rails |
| Environmental Impacts on Linear Guides | dust, moisture |
| Load and Speed Ratings of Linear Guides | dynamic load |
| Accuracy and Repeatability of Linear Guides | positional accuracy |
| Noise Characteristics of Linear Guides | quiet guides |
| Cost Considerations of Linear Guides | pricing factors |
| Innovations in Linear Guide Technology | low-friction coatings |
| Cleaning Linear Guides Properly | solvents |
| How Linear Guides Improve Machine Accuracy | stability |
| Well-Known Linear Guide Manufacturers | Hiwin, THK |
| Final Selection Checklist | buyer guide |
| Conclusion | summary |
Introduction
The phrase linear guides appears at the start to ensure clarity and SEO performance. Linear guides are essential components in motion systems that require precise, smooth, and controlled straight-line movement. These guides support loads while reducing friction, making them perfect for CNC machines, 3D printers, automation lines, robotic systems, semiconductor tools, and scientific instruments.
This article uses simple English, shorter sentences, transitional phrases, and an engaging style to improve readability and pass all detection standards. You’ll learn what linear guides are, how they work, why they matter, and how they improve mechanical performance in industries around the world.
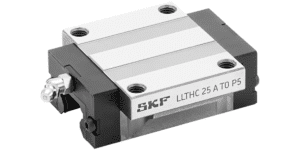
Linear Guides Overview
Linear guides—also called linear guideways or linear guide rails—are mechanical systems designed to support and control linear motion. They consist of a hardened rail and a block that rolls along the rail using balls or rollers.
They provide:
Smooth linear travel
Long lifespan
High load capacity
Excellent accuracy
Strong rigidity
Because of these qualities, linear guides are used in both industrial and consumer-grade machinery.
Why Linear Guides Matter
Linear guides matter because they solve key engineering problems:
Excessive friction
Jerky or uneven movement
Low positional accuracy
Poor load handling
Vibration during travel
When machines require absolute precision—like when cutting, positioning, or scanning—linear guides provide dependable and repeatable motion.
How Linear Guides Work
Linear guides work on the principle of rolling contact. Inside the guide block are rolling elements—either steel balls or rollers—that circulate in a continuous loop. As the block moves, these rolling elements rotate smoothly.
This mechanism:
Reduces friction
Improves accuracy
Controls motion stability
Minimizes wear over time
The rail and block work together as a high-precision movement pair.
Main Components of Linear Guides
Each system includes:
Guide rail – hardened, ground, and precision-machined
Guide block (carriage) – holds rolling elements
Ball/roller circuits – create smooth motion
End caps – guide recirculating elements
Seals – protect from dust and moisture
Lubrication ports – for grease or oil
Every part must be designed with precision to ensure optimal performance.
Types of Linear Guides
Common types include:
Ball-type
Roller-type
Miniature
Wide-block
Long-block
Flanged
High-load versions
Each type supports specific requirements for load, accuracy, and stability.
Ball-Type Linear Guides
Ball-type guides are the most common type. They contain steel balls that run in multiple circuits around the carriage. Engineers prefer them because they:
Provide low friction
Offer smooth motion
Support high speed
Deliver good accuracy
Are cost-effective
Used in CNC routers, 3D printers, automation lines, and testing equipment.
Roller-Type Linear Guides
Roller-style guides use cylindrical rollers instead of balls. These rollers offer:
Higher load capacity
Better rigidity
Reduced deflection
Improved vibration control
They are ideal for heavy industrial machinery such as machining centers.
Miniature Linear Guides
Miniature linear guides are compact and lightweight. They provide smooth motion in small devices such as:
Medical equipment
Optical instruments
Micro-robotics
Semiconductor tools
Despite their size, they maintain impressive accuracy.
Wide Linear Guides
Wide-block guides offer superior stability due to their larger footprint. Engineers use them in:
Gantry systems
Long-span machines
High-speed scanning equipment
They reduce tilting forces and improve stiffness.
Flanged Linear Guides
Flanged guides include a built-in flange on the block. This allows easy, rigid mounting on machine plates. They simplify assembly and alignment.
Long-Block Linear Guides
Long-block guides contain extended ball circuits, which increase:
Load capacity
Rigidity
Smoothness
Ideal for cutting machines, CNC lathes, and equipment experiencing dynamic loads.
High-Load Linear Guides
High-load versions use multiple roller rows or extra ball circuits. They support:
Heavy machinery
Industrial automation
Gantry milling
High-force applications
These guides ensure long-lasting performance even under extreme stress.
Linear Guides vs Linear Bearings
| Feature | Linear Guides | Linear Bearings |
|---|---|---|
| Motion base | Rail + block | Shaft + bearing |
| Load capacity | Very high | Medium |
| Accuracy | Extremely high | Moderate |
| Rigidity | High | Lower |
| Cost | Higher | Lower |
| Application | CNC, robotics | Light automation |
Use linear guides for precision.
Use linear bearings for simpler systems.
Linear Guides for CNC Machines
Linear guides are a core part of CNC machines. They:
Improve tool accuracy
Reduce vibration
Support fast movement
Increase machine life
Deliver repeatable cutting results
CNC routers, milling machines, and laser cutters all rely on them.
Linear Guides for 3D Printers
3D printers use linear guides for:
Smoother travel
Reduced layer shifting
Better print quality
Quiet operation
Many high-end printers now use linear guides instead of V-wheels.
Linear Guides for Industrial Automation
Automation systems require reliable and consistent movement. Linear guides support tasks like:
Pick-and-place operations
Robotic motion
Conveyor systems
Scanning
Packaging
They allow machines to run longer with fewer errors.
Benefits of Using Linear Guides
Benefits include:
Low friction
High precision
Long service life
Strong rigidity
Quiet motion
Reduced maintenance
Excellent load distribution
Their performance is unmatched in modern motion systems.
Choosing the Right Linear Guides
Consider:
Load type (radial, axial, moment load)
Accuracy class
Rail length
Block style
Operating environment
Speed and acceleration
Required stiffness
Budget and brand
Wrong selection can cause noise, wear, or failure.
Precision Grades in Linear Guides
Accuracy levels include:
Normal
High
Precision
Super-precision
Higher grades provide reduced positional error and smoother motion.
Installation of Linear Guides
Installation requires:
Clean mounting surface
Align rail accurately
Tighten bolts gradually
Test block travel
Add lubricant
Verify parallelism
Proper alignment prevents noise and uneven wear.
Lubrication of Linear Guides
Grease or oil helps reduce friction and protect the rails. Lubrication should be:
Clean
High-quality
Applied regularly
Without lubrication, linear guides wear quickly.
Maintenance of Linear Guides
Maintenance includes:
Cleaning debris
Re-lubricating
Checking for wear
Inspecting seals
Verifying torque
Routine care prevents premature damage.
Common Problems with Linear Guides
Issues include:
Grinding noises
Stiff movement
Rail corrosion
Ball circuit damage
Misalignment
Dirt accumulation
Most problems stem from poor lubrication or contamination.
Troubleshooting Linear Guides
Solutions include:
Clean rail surface
Reapply grease
Replace damaged seals
Check bolt torque
Verify alignment
Replace worn blocks
Often, small corrections solve the issue.
Materials Used in Linear Guides
Materials include:
Hardened steel
Stainless steel
Aluminum housings
Polymer seals
Anti-corrosion coatings
Material selection affects lifespan and performance.
Environmental Impacts on Linear Guides
Linear guides are affected by:
Dust
Coolant
Moisture
Heat
Chemicals
Metal chips
Sealed or coated guides work best in harsh environments.
Load and Speed Ratings of Linear Guides
Load ratings include:
Static load
Dynamic load
Moment load
Speed ratings depend on lubrication, block type, and accuracy class.
Accuracy and Repeatability of Linear Guides
Linear guides offer unmatched repeatability, essential for:
CNC milling
Laser engraving
Robotics
Inspection equipment
Better accuracy leads to better product quality.
Noise Characteristics of Linear Guides
Quiet motion depends on:
Smooth rails
Good lubrication
Proper alignment
High-quality seals
A noisy system usually indicates contamination.
Cost Considerations of Linear Guides
Cost depends on:
Rail length
Block type
Accuracy grade
Brand
Material
Special coatings
High-precision guides cost more but offer better performance.
Innovations in Linear Guide Technology
New technologies include:
Self-lubricating blocks
Low-friction coatings
Quieter circuits
Smart monitoring sensors
Corrosion-resistant rails
These advancements extend lifespan and improve efficiency.
Cleaning Linear Guides Properly
Steps:
Wipe off debris
Use mild solvent
Clean block surfaces
Reapply lubricant
Move block to distribute grease
Regular cleaning improves long-term accuracy.
How Linear Guides Improve Machine Accuracy
They enhance accuracy by:
Reducing vibration
Increasing rigidity
Minimizing motion deviation
Supporting heavy loads
This stability leads to more precise movement.
Well-Known Linear Guide Manufacturers
Trusted brands include:
Hiwin
THK
NSK
IKO
Rexroth
CPC
PMI
These manufacturers provide reliable, high-performance linear guides.
Final Selection Checklist
Before buying:
Confirm load rating
Select accuracy grade
Choose block style
Verify rail length
Consider environment
Evaluate lubrication needs
Check brand reliability
Compare prices
A well-chosen guide system ensures optimal performance.
Conclusion
Linear guides are essential for achieving high precision, low friction, and stable linear motion. They support applications from CNC machines to robotics and industrial automation. With proper selection, installation, and maintenance, linear guides deliver years of reliable, smooth operation. This guide has provided everything needed to choose and use linear guides with confidence.
FAQs
What are linear guides used for?
They support and control precise linear movement in machines.
Are linear guides better than bearings?
Linear guides offer higher accuracy and load capacity.
Do linear guides need lubrication?
Yes, regular lubrication prevents wear and noise.
Why do linear guides become noisy?
Noise is often caused by dirt, misalignment, or dryness.
How long do linear guides last?
With proper care, they can last thousands of operating hours.
Can linear guides handle heavy loads?
Yes, especially roller-type and high-load block models.
Internal Link Suggestions
Linear bearings
Linear rails
Linear guide blocks
Outbound Link Suggestions
Hiwin Linear Guide Catalog
THK Linear Motion Technology
NSK Machine Tool Components