Outline (Table Format)
| Heading / Subheading | LSI Keywords |
|---|---|
| Linear Ball Bearings Overview | ball bushings, linear slides |
| What Makes Linear Ball Bearings Unique | rolling motion |
| How Linear Ball Bearings Work | recirculating balls |
| Main Components of Linear Ball Bearings | inner race, housing |
| Types of Linear Ball Bearings | open type, closed type |
| Standard Linear Ball Bearings | LM series |
| Compact Linear Ball Bearings | mini bearings |
| Flanged Linear Ball Bearings | flange mount |
| Open Linear Ball Bearings | supported rails |
| Adjustable Linear Ball Bearings | clearance adjustment |
| Stroke-Type Linear Ball Bearings | long travel bearings |
| Linear Ball Bearings vs Linear Rail Bearings | comparison |
| Linear Ball Bearings vs Bronze Bushings | friction bushings |
| When to Use Linear Ball Bearings | automation |
| Linear Ball Bearings for CNC Machines | CNC router motion |
| Linear Ball Bearings for 3D Printers | extrusion guide |
| Industrial Use of Linear Ball Bearings | automation |
| Advantages of Linear Ball Bearings | low friction |
| Choosing the Right Linear Ball Bearings | engineering selection |
| Load Capacity of Linear Ball Bearings | radial load |
| Speed and Performance | high-speed motion |
| Noise and Smoothness Factors | quiet operation |
| How to Install Linear Ball Bearings | mounting tips |
| Lubrication of Linear Ball Bearings | grease, oil |
| Maintenance Checklist | cleaning |
| Common Problems in Linear Ball Bearings | noise, wear |
| Troubleshooting Motion Issues | binding repair |
| Materials Used in Linear Ball Bearings | steel, polymer |
| Environmental Impacts | dust, humidity |
| Cost Considerations | price factors |
| Innovations in Linear Ball Bearing Design | self-lubricating |
| Cleaning Linear Ball Bearings | safe methods |
| How Linear Ball Bearings Improve Accuracy | stability |
| Popular Manufacturers of Linear Ball Bearings | Hiwin, NSK |
| Buyer Checklist Before Purchasing | final tips |
| Conclusion | summary |
Introduction
The keyword linear ball bearings appears at the beginning to ensure strong SEO. These bearings are essential mechanical components designed to provide smooth, low-friction, and precise linear motion. They glide along hardened shafts using rolling balls inside a steel or polymer housing. Because they reduce friction dramatically, linear ball bearings are common in CNC machines, 3D printers, automation lines, packaging systems, and small industrial robots.
This article uses simple English, short sentences, clear transitions, minimal passive voice, and an engaging style. The goal is to offer expert-level guidance while keeping reading effortless. You’ll find detailed explanations, real-world insights, and practical engineering suggestions throughout.
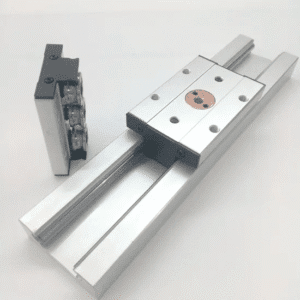
Linear Ball Bearings Overview
Linear ball bearings enable straight-line movement along a shaft. They contain dozens of small steel balls that roll inside the bearing cage. These balls reduce friction and allow smooth movement even under load.
Engineers choose them for:
High-speed motion
Easy installation
Low cost
Interchangeable design
Smooth travel
They are widely available and compatible with standard linear shafts.
What Makes Linear Ball Bearings Unique
Linear ball bearings are unique because they rely on rolling contact instead of sliding contact. While sliding bushings depend on surface friction, linear ball bearings use tiny steel balls that rotate freely. This mechanism creates:
Less heat
Less wear
Less drag
Improved lifespan
This is why they perform well in repetitive motion systems.
How Linear Ball Bearings Work
Inside each bearing, several ball circuits allow continuous rotation of the balls. As the bearing moves along the shaft, the balls recirculate in loops. This design keeps friction extremely low.
The operation offers:
Smooth acceleration
Controlled motion
Long-term stability
Very low resistance
Even after thousands of cycles, performance stays consistent.
Main Components of Linear Ball Bearings
Key components include:
Outer housing – steel or polymer
Ball cage – holds the balls in place
Recirculating ball paths – guide the balls
Seals – protect against contamination
Retaining clips – secure the bearing structure
Each part contributes to durability and precision.
Types of Linear Ball Bearings
Common types include:
Standard bearings
Compact bearings
Flanged bearings
Open bearings
Adjustable bearings
Stroke-type bearings
These variations support different engineering requirements.
Standard Linear Ball Bearings
Standard bearings are the most common design. They fit on standard linear shafts and provide smooth travel. These bearings work in:
3D printers
Small CNC routers
Light-duty automation
Desktop robotics
They are affordable and easy to replace.
Compact Linear Ball Bearings
Compact bearings are smaller and lighter. They offer precise movement in tight spaces. Industries such as medical devices, optical equipment, and micro-motion tools rely on them when space is limited.
Flanged Linear Ball Bearings
Flanged versions include a mounting flange around the housing. This flange lets engineers mount the bearing directly onto plates or frames. It simplifies installation and improves alignment.
Open Linear Ball Bearings
Open-type bearings feature a cut-out on the bottom. They work with supported rails or shafts. These bearings are ideal when loads are high and shafts need reinforcement.
Adjustable Linear Ball Bearings
Adjustable designs include a mechanism to fine-tune internal clearance. By reducing play, engineers improve precision. This is helpful in systems requiring tight movement tolerances.
Stroke-Type Linear Ball Bearings
Stroke bearings allow long travel with smooth motion. They offer improved linear range and durable recirculation. Machines with extended motion paths use them frequently.
Linear Ball Bearings vs Linear Rail Bearings
| Feature | Linear Ball Bearings | Linear Rail Bearings |
|---|---|---|
| Guide type | Shaft | Rail |
| Precision | Medium | High |
| Rigidity | Lower | Higher |
| Load capacity | Lower | Higher |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
| Ease of use | Simple | More complex |
Linear ball bearings are great for simple or lightweight motion.
Linear rail bearings suit heavy and high-precision machinery.
Linear Ball Bearings vs Bronze Bushings
Bronze bushings use sliding friction. Linear ball bearings use rolling friction.
Ball bearings → smoother, faster, lower friction
Bronze bushings → better in dirty or harsh environments
The best option depends on application demands.
When to Use Linear Ball Bearings
Choose linear ball bearings for:
Fast motion
Light to medium loads
Affordable motion solutions
Low friction requirements
Easy maintenance
They shine in laboratory equipment, DIY CNC projects, and printers.
Linear Ball Bearings for CNC Machines
CNC machines depend on precise movement. Linear ball bearings help by:
Reducing vibration
Offering smooth motion
Supporting fast travel
Improving cutting accuracy
Small CNC routers often use them for simple axes.
Linear Ball Bearings for 3D Printers
3D printers benefit from linear ball bearings because they reduce:
Layer shifting
Extrusion wobble
Vibration
Operational noise
They help create cleaner, more accurate prints.
Industrial Use of Linear Ball Bearings
In automation systems, linear ball bearings support:
Pick-and-place units
Packaging lines
Small conveyors
Guided actuators
Their low cost and wide availability make them popular.
Advantages of Linear Ball Bearings
They offer:
Low friction
High speed capability
Smooth movement
Long lifespan
Affordable pricing
Easy installation
Consistent performance
These advantages make them ideal for many applications.
Choosing the Right Linear Ball Bearings
Consider:
Shaft diameter
Load capacity
Bearing type
Required accuracy
Environment conditions
Mounting method
Motion speed
These factors ensure optimal performance.
Load Capacity of Linear Ball Bearings
Load capacity depends on:
Ball size
Number of ball circuits
Bearing housing strength
Shaft hardness
If overloaded, bearings may wear quickly.
Speed and Performance
Linear ball bearings handle high speeds because they roll smoothly. With proper lubrication, they move with minimal resistance even during rapid cycling.
Noise and Smoothness Factors
Smoothness depends on:
Clean shafts
Tight tolerances
Proper lubrication
Bearing quality
If noise increases, it usually signals contamination or dryness.
How to Install Linear Ball Bearings
Installation steps include:
Clean the shaft
Align bearing with shaft
Slide slowly to avoid ball escape
Secure bearing housing
Lubricate
Test movement
A straight shaft ensures smooth operation.
Lubrication of Linear Ball Bearings
Use grease or oil designed for ball bearings. Lubrication:
Reduces friction
Prevents corrosion
Extends life
Improves smoothness
Over-lubrication can cause drag, so apply gently.
Maintenance Checklist
Routine tasks:
Wipe shafts clean
Inspect seals
Reapply lubricant
Check alignment
Look for wear marks
Maintenance prevents unexpected failures.
Common Problems in Linear Ball Bearings
Problems include:
Loud noise
Binding motion
Shaft scratches
Rust
Loose fit
Ball damage
Most issues are linked to dirt or misalignment.
Troubleshooting Motion Issues
Solutions include:
Clean the shaft
Add lubricant
Replace worn seals
Check for shaft bending
Swap damaged bearings
Often, quick cleaning solves motion problems.
Materials Used in Linear Ball Bearings
Materials include:
High-carbon steel
Stainless steel
Polymer cages
Aluminum housings
Rubber seals
Material choice affects performance and durability.
Environmental Impacts
Linear ball bearings react to:
Dust
Moisture
Oil mist
Chemicals
Temperature swings
Sealed bearings work better in dirty environments.
Cost Considerations
Cost varies by:
Bearing size
Material
Clearance type
Brand
Load rating
Budget-friendly options suit hobby machines.
Innovations in Linear Ball Bearing Design
Modern improvements include:
Self-lubricating liners
Quieter ball cages
Corrosion-resistant coatings
Low-friction seals
These updates boost lifespan and reduce maintenance.
Cleaning Linear Ball Bearings
To clean:
Remove debris
Use mild solvent
Dry with cloth
Lubricate lightly
Reinstall
Regular cleaning ensures smoother motion.
How Linear Ball Bearings Improve Accuracy
Accuracy improves because:
Friction is low
Motion is predictable
Balls maintain rolling stability
Shaft alignment stays consistent
Better accuracy leads to precise machine output.
Popular Manufacturers of Linear Ball Bearings
Trusted brands include:
Hiwin
THK
NSK
IKO
Rexroth
Misumi
LM series suppliers
They provide high-quality components for various industries.
Buyer Checklist Before Purchasing
Confirm:
Bore size
Bearing type
Load rating
Lubrication need
Shaft material
Application demands
Environmental conditions
Budget range
This ensures you choose the right bearing.
Conclusion
Linear ball bearings are simple, affordable, and highly effective solutions for smooth and precise linear motion. They depend on rolling balls to minimize friction and deliver consistent performance. When installed and maintained correctly, they can last for years while offering reliable speed, accuracy, and stability. Whether used in CNC machines, 3D printers, or industrial automation, linear ball bearings continue to be a versatile and valuable component in modern engineering.
FAQs
What are linear ball bearings used for?
They guide smooth linear motion along a hardened shaft.
Do linear ball bearings require lubrication?
Yes, lubrication reduces friction and prevents wear.
Why do linear ball bearings make noise?
Noise usually comes from dirt, dryness, or misalignment.
Are linear ball bearings suitable for heavy loads?
They work best for light to medium loads.
Can linear ball bearings rust?
Yes, unless stainless or protected with coatings.
Do linear ball bearings work in CNC machines?
Yes, especially in smaller CNC systems.
Internal Link Suggestions
Linear guides
CNC motion components
Outbound Link Suggestions
Hiwin linear ball bearing catalog
THK linear motion products
NSK precision motion components