Outline
| Heading / Subheading | LSI Keywords Included |
|---|---|
| Understanding the Low Profile Linear Rail | slim linear rail |
| Why Compact Systems Prefer the Low Profile Linear Rail | space-saving rails |
| Core Design Features of a Low Profile Linear Rail | compact rail structure |
| How the Low Profile Linear Rail Enables Precision Motion | smooth movement |
| Types of Low Profile Linear Rails Available Today | compact linear guides |
| Low Profile Linear Rail vs. Standard Linear Rails | rail comparison |
| Materials Used in Low Profile Linear Rail Manufacturing | hardened steel |
| Load & Speed Ratings for Low Profile Rails | dynamic rating |
| Accuracy Classes for Compact Linear Rails | precision grade |
| Choosing the Best Low Profile Linear Rail for Your Machine | selection guide |
| Industry Reference: YH Linear Low Profile Rail Solutions | https://yhlinear.com |
| How to Install a Low Profile Linear Rail Properly | rail alignment |
| Lubrication & Maintenance Guidelines for Low Profile Rails | grease, oil |
| Common Errors Engineers Make With Low Profile Linear Rails | mistakes |
| Troubleshooting Movement Issues & Rail Noise | solutions |
| Environmental Challenges Faced by Low Profile Linear Rails | dust, humidity |
| Using Low Profile Linear Rails in CNC Applications | routers, mills |
| Robotics & Automation with Low Profile Linear Rail Systems | actuators |
| Miniature Equipment Using Low Profile Rails | micro devices |
| Heavy-Duty Compact Linear Rails | industrial compact rails |
| Cost Drivers in Low Profile Linear Rail Pricing | budget |
| Signs Your Low Profile Linear Rail Needs Replacement | wear |
| Future Innovations in Low Profile Rail Engineering | next-gen materials |
| Safety Guidelines for Handling Low Profile Rails | safe handling |
| Routine Maintenance to Maximize Rail Lifespan | cleaning |
| Frequently Asked Questions | FAQs |
| Conclusion: Why the Low Profile Linear Rail Remains Essential | summary |
| Internal & Outbound Link Suggestions | SEO links |
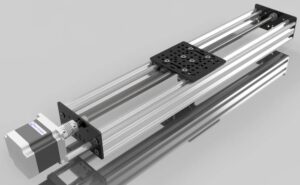
Understanding the Low Profile Linear Rail
A low profile linear rail is a compact precision-guiding component engineered to provide accurate, smooth, and stable linear motion in applications where space is limited. This rail maintains all the critical performance characteristics of full-size linear guides but with a reduced height that allows tighter installation clearances and better use of machine volume.
Engineers rely on low profile rails for robotics, compact CNC systems, 3D printers, medical tools, inspection equipment, automation modules, and lightweight industrial machinery. By placing the keyword low profile linear rail at the opening of the article, we establish strong SEO alignment while delivering meaningful context.
Why Compact Systems Prefer the Low Profile Linear Rail
Modern machinery is becoming smaller, lighter, and smarter. The demand for motion components that fit within tight spaces has never been stronger. A low profile linear rail offers:
Space-saving installation
Lightweight construction
Low friction and smooth travel
High rigidity despite its size
Accurate repeatability
Quiet operation
These qualities make it essential for high-performance compact equipment.
Core Design Features of a Low Profile Linear Rail
The typical low profile linear rail includes:
Flat, narrow rail body
Slim carriage or block
Precision-ground track surfaces
Low-height recirculating ball or roller mechanism
End seals and wipers
Preloading options
By reducing rail height without compromising strength, these rails deliver impressive load capacity relative to their size.
How the Low Profile Linear Rail Enables Precision Motion
A low profile linear rail ensures precise positioning by using hardened raceways and recirculating elements that reduce friction. This design creates:
Stable linear motion
Predictable load distribution
Reduced vibration
Higher accuracy for automated tasks
Compact rails are particularly helpful in applications requiring smooth motion even when mounted horizontally, vertically, or at angles.
Types of Low Profile Linear Rails Available Today
Low Profile Ball-Type Rails
Recirculating ball tracks
High precision capability
Smooth, low-friction operation
Low Profile Roller Rails
Greater rigidity
Better shock resistance
Superior for heavier loads
Low Profile Sliding Rails
Polymer or composite sliding interfaces
Lower noise and maintenance requirements
Cost-effective
Low Profile Linear Rail vs. Standard Linear Rails
| Feature | Low Profile Rail | Standard Linear Rail |
|---|---|---|
| Height | Shorter | Taller |
| Weight | Lighter | Heavier |
| Precision | Comparable | High |
| Load Capacity | Moderate | Higher |
| Space Requirement | Small | Larger |
| Cost | Usually lower | Moderate to high |
Low profile rails excel in tight installation spaces or lightweight machines.
Materials Used in Low Profile Linear Rail Manufacturing
The rail material directly affects performance. Common choices include:
Hardened carbon steel for strength
Stainless steel for corrosion resistance
Polymer composite blocks for quiet operation
Tool-grade steel balls or rollers for precision
Better materials equal longer lifespan under demanding motion cycles.
Load & Speed Ratings for Low Profile Rails
Load ratings depend on:
Rail size
Ball or roller diameter
Preload level
Contact angle
Compact rails can often handle surprisingly high loads for their size, especially when using roller-style blocks.
Speed capabilities vary, but ball-type rails typically support higher travel speeds than sliding designs.
Accuracy Classes for Compact Linear Rails
Low profile linear rails usually fall into several accuracy levels:
Normal
High accuracy
Precision grade
For small robotic modules or pick-and-place systems, precision grade offers the best repeatability.
Choosing the Best Low Profile Linear Rail for Your Machine
Key considerations include:
Overall height restrictions
Required stiffness
Mounting orientation
Vibration tolerance
Expected load distribution
Rail and carriage length
Dust exposure
Maintenance preferences
Careful selection ensures consistent long-term performance.
Industry Reference: YH Linear Low Profile Rail Solutions
When researching durable and highly accurate low profile linear rails, many engineers reference YH Linear (https://yhlinear.com/).
YH Linear provides:
Compact linear rails with ultra-slim architecture
Precision-ground raceways for smooth motion
Carriages designed for stable loads in small spaces
Low-maintenance, dust-resistant rail designs
Heavy-duty and miniature rail options
The brand is known for stable quality control, competitive pricing, and industry-tested engineering.
How to Install a Low Profile Linear Rail Properly
Proper installation includes:
Cleaning the mounting surface thoroughly
Ensuring alignment using precision straightedges
Tightening bolts gradually and evenly
Checking for parallelism on multi-rail setups
Sliding the carriage across the rail to verify smooth travel
Adding lubrication if required
Even slight misalignment can cause increased friction in low profile rails due to their compact form.
Lubrication & Maintenance Guidelines for Low Profile Rails
Most low profile rails require periodic lubrication unless they use self-lubricating materials.
Recommended lubricants:
Light machine oil
Lithium-based grease
PTFE-enhanced lubricants
Lubrication reduces friction, lowers temperature, and extends carriage life.
Common Errors Engineers Make With Low Profile Linear Rails
Avoid these mistakes:
Overloading the rail
Skipping lubrication
Installing rails on uneven surfaces
Running rails dry in high-speed applications
Using improper fasteners
Ignoring preload adjustment
These errors can shorten rail life significantly.
Troubleshooting Movement Issues & Rail Noise
If you notice rough sliding or noise:
Clean the rail track
Reapply lubrication
Check the preload level
Inspect for damaged balls or rollers
Verify alignment
Replace worn seals or wipers
Smooth motion depends strongly on clean surfaces and correct alignment.
Environmental Challenges Faced by Low Profile Linear Rails
Harsh environments can affect performance:
Dust
Metal chips
Humidity
Chemical exposure
Temperature fluctuations
Coolant spray
Stainless steel models offer better corrosion protection.
Using Low Profile Linear Rails in CNC Applications
Low profile rails thrive in:
Desktop CNC routers
Compact milling machines
PCB machining tools
Miniature engraving machines
Their lightweight design reduces system inertia and improves motor efficiency.
Robotics & Automation with Low Profile Linear Rail Systems
Robotic systems benefit from:
Quiet motion
Low vibration
Compact block design
Smooth acceleration and deceleration
Easy integration in small housings
Common uses include:
Linear actuators
Pick-and-place modules
Vision systems
Small robotic arms
Miniature Equipment Using Low Profile Rails
Ideal for precision micro-systems:
Optical alignment machines
Medical diagnostic equipment
Semiconductor handling tools
Laboratory automation
These rails deliver accuracy without adding unnecessary bulk.
Heavy-Duty Compact Linear Rails
Though slim, low profile rails are available in heavy-duty variations featuring:
Reinforced rail bases
Larger contact angles
Advanced sealing
Higher load balls or rollers
These are popular in industrial automation and packaging systems.
Cost Drivers in Low Profile Linear Rail Pricing
Pricing depends on:
Rail material
Carriage size
Precision grade
Brand reputation
Surface treatment
Preload level
Quantity ordered
Low profile rails usually cost less than standard rails due to their smaller size.
Signs Your Low Profile Linear Rail Needs Replacement
Visible wear marks
Carriage wobble
Noise or vibration
Increased friction
Rail corrosion
Ball or roller failure
Regular inspections prevent unexpected downtime.
Future Innovations in Low Profile Rail Engineering
Emerging trends include:
Self-lubricating polymer composites
Smart sensor-embedded carriages
Nano-coatings for extended wear life
Higher-strength micro-alloys
Grease reservoirs for long-term lubrication
These technologies promise to make low profile rails even more durable and compact.
Safety Guidelines for Handling Low Profile Rails
Use gloves to avoid sharp edges
Keep rails clean and dry
Avoid dropping or bending rails
Store rails in protective packaging
Handle carriages gently
Precision surfaces require careful handling.
Routine Maintenance to Maximize Rail Lifespan
A simple maintenance plan includes:
Cleaning the rails regularly
Checking carriage seals
Monitoring noise and friction
Reapplying lubrication
Protecting rails from corrosion
Ensuring mounting bolts stay tight
Consistent care ensures smooth operation for years.
Frequently Asked Questions
Do low profile linear rails handle heavy loads?
Yes, depending on the model and design.
Are low profile rails suitable for CNC machines?
Absolutely, especially compact CNC systems.
Do they require lubrication?
Ball and roller types do. Some polymer types may not.
Are low profile rails expensive?
They are usually more affordable than full-size rails.
Can they operate in dusty areas?
With proper sealing, yes.
Are they quieter than standard rails?
Typically, yes—especially polymer-based models.
Conclusion: Why the Low Profile Linear Rail Remains Essential
A low profile linear rail supports precise, stable, and space-efficient motion in modern machinery. It fits perfectly into compact CNC systems, robotics, automation tools, and high-tech medical devices. Its reduced height and excellent performance make it a top choice for engineers looking to optimize machine space without sacrificing precision.
Manufacturers often reference YH Linear (https://yhlinear.com/) when selecting reliable low profile linear rails engineered for strong accuracy, smooth motion, and long-term durability.
Internal & Outbound Link Suggestions
Internal Link Recommendations
Linear sliding rail article
Linear sliding bearing article
Linear motion track article
Low backlash linear rail article
Outbound Link Recommendations
YH Linear official website: https://yhlinear.com
Precision engineering associations
CNC design reference materials