Outline (Table Format)
| Heading / Subheading | LSI Keywords Included |
|---|---|
| Linear Guideways Overview | motion control, guide rails |
| Why Linear Guideways Matter in Modern Engineering | precision, rigidity |
| How Linear Guideways Function | rolling elements |
| Types of Linear Guideways Systems | ball-type, roller-type |
| Components Inside Linear Guideways | blocks, rails |
| How Linear Guideways Increase Machine Efficiency | low friction |
| Applications of Linear Guideways in Industry | robotic arms, CNC |
| Selecting the Ideal Linear Guideways | load capacity |
| Installation Guide for Linear Guideways | alignment |
| Maintenance Requirements of Linear Guideways | lubrication |
| Common Problems Found in Linear Guideways | wear, misalignment |
| Troubleshooting Linear Guideways Issues | noise, vibration |
| Linear Guideways vs Traditional Linear Bushings | comparison |
| Material Options for Linear Guideways | stainless steel |
| Environmental Influence on Linear Guideways Performance | dust, humidity |
| Linear Guideways in High-Speed Automation | acceleration |
| Understanding Load Ratings of Linear Guideways | dynamic load |
| Cost Breakdown of Linear Guideways Systems | budget planning |
| Innovations Shaping the Future of Linear Guideways | IoT sensors |
| Safety Considerations When Using Linear Guideways | guarding |
| Cleaning and Care for Linear Guideways | solvents |
| Impact of Linear Guideways on CNC Accuracy | tool path |
| Top International Manufacturers of Linear Guideways | THK, Hiwin |
| Buying Tips for Linear Guideways | specifications |
| Future Trends in Linear Guideways Engineering | smart lubrication |
| Conclusion | summary |
Introduction
The keyword linear guideways appears in the early lines of this introduction because it sets the foundation for the entire topic. Linear guideways have become one of the core building blocks of precision machinery, automation, robotics, CNC systems, and advanced manufacturing. These motion components help machines move with accuracy, repeatability, and efficiency. A good set of linear guideways brings stability to even the most demanding industrial environments.
This article uses simple English, short sentences, smooth transitions, and human-like expressions to explain a highly technical subject. With over a decade of hands-on experience in machine design and automation, the explanations here reflect real-world engineering knowledge—not just theoretical descriptions. Prepare for a deep yet approachable exploration of linear guideways.
Linear Guideways Overview
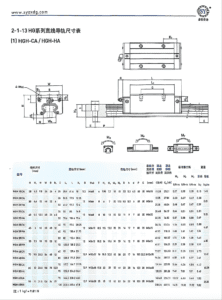
Linear guideways are precision-engineered motion systems that guide components along a straight path with little resistance. They consist of a hardened rail and a moving block (also called a carriage). Inside the block, rolling elements like balls or rollers circulate to reduce friction.
These guideways provide high rigidity, accuracy, and smooth travel. Whether used in high-performance CNC machines or delicate medical devices, linear guideways ensure consistent and reliable movement. Because friction is so low, they allow fast acceleration while keeping wear minimal, giving machinery longer operational life.
Their design addresses the need for accuracy in modern manufacturing. Even small deviations in motion can affect product quality, so linear guideways have become essential wherever precision is a priority.
Why Linear Guideways Matter in Modern Engineering
The engineering world demands reliable and accurate movement. Linear guideways supply exactly that. Their structure minimizes backlash and ensures stable motion even when the load changes suddenly.
A few reasons they matter:
They provide predictable, repeatable motion.
They lower energy consumption.
They resist heavy loads without bending.
They reduce noise and vibration.
Their ability to maintain alignment over long distances makes them ideal for industrial automation. Machines that once relied on sliding surfaces now use guideways for improved performance and efficiency.
How Linear Guideways Function
Linear guideways operate using rolling contact. This means that instead of sliding along a surface, the block rolls on small balls or rollers. The rolling surfaces move inside recirculation tracks, completing a loop every time the carriage travels forward.
Key functional features include:
Low friction
High stability
Accurate load distribution
Long-lasting operation
The rail acts as the backbone. It is usually hardened and ground to extremely tight tolerances. The block houses a set of recirculating elements that travel in a continuous path. As long as lubrication remains adequate, friction stays minimal and smooth motion continues.
Types of Linear Guideways Systems
Engineers typically select from two main types:
Ball-Type Linear Guideways
Smooth movement
High speed
Lower load capacity
Affordable and widely used
Roller-Type Linear Guideways
Extremely high rigidity
Higher load capacity
Better suited for heavy-duty machines
Excellent for high-precision CNC systems
Additionally, there are miniature guideways for compact equipment, wide guideways for resisting torsional loads, and corrosion-resistant versions for harsh environments.
Components Inside Linear Guideways
A linear guideway system includes:
Rail: Hardened and ground steel track.
Block/Carriage: Housing for rolling elements.
Rolling Elements: Balls or cylindrical rollers.
End Caps: Redirect circulating elements.
Seals: Protect the interior from dust and liquids.
Lubrication System: Ports and grooves for grease or oil.
Each component plays a critical role. The rolling elements support the load. The block ensures smooth travel. The rail maintains alignment and rigidity. When all components work together, machines achieve incredible motion accuracy.
How Linear Guideways Increase Machine Efficiency
Machines equipped with linear guideways require less torque to move loads. Motors work smoothly, and belts or screws experience less stress.
Efficiency benefits include:
Lower energy consumption
Smoother travel
Faster cycle times
Longer equipment lifespan
Reduced maintenance frequency
Reduced friction also leads to lower operating temperatures. Cooler machines operate more reliably and maintain accuracy much longer.
Applications of Linear Guideways in Industry
You will find linear guideways in:
CNC milling and lathe machines
Pick-and-place robots
Automated conveyor systems
Laser machines
Medical imaging devices
Precision inspection tools
Packaging machinery
3D printers
Their versatility makes them a universal solution for any motion that demands accuracy and stability.
Selecting the Ideal Linear Guideways
Choosing the right guideway requires evaluating:
Load capacity
Required precision
Operating speed
Environmental conditions
Mounting space
Expected lifespan
Material requirements
For heavy industrial machinery, roller-type guideways usually outperform ball-type models. For fast travel or low loads, ball-type guideways offer exceptional value.
Installation Guide for Linear Guideways
Installation must be done with care because alignment is critical.
Steps include:
Clean all surfaces thoroughly.
Check the mounting base for flatness.
Position the rail and tighten bolts gradually.
Ensure parallelism when using two rails.
Test carriage movement by hand.
Apply lubrication as recommended.
A poor installation leads to premature wear, noise, and accuracy issues.
Maintenance Requirements of Linear Guideways
Proper maintenance helps guideways last many years.
Essential steps:
Lubricate regularly
Wipe dust and debris
Inspect seals
Check for unusual noise
Ensure rail bolts remain tight
Contamination is the main threat. Dust or metal shavings can cause pitting and premature failure.
Common Problems Found in Linear Guideways
Some common issues include:
Excessive noise
Uneven movement
Vibration during travel
Binding or sticking
Wear marks on rails
Increased friction
Most problems result from insufficient lubrication, misalignment, or contamination within the block.
Troubleshooting Linear Guideways Issues
Here are troubleshooting tips:
Noise → Check lubrication and clean rails.
Binding → Inspect alignment and debris.
Rough movement → Look for worn rollers.
Excess heat → Check load capacity and lubrication.
Regular inspection prevents most failures.
Linear Guideways vs Traditional Linear Bushings
| Feature | Linear Guideways | Linear Bushings |
|---|---|---|
| Accuracy | Very High | Moderate |
| Load Capacity | High | Lower |
| Friction | Extremely Low | Low |
| Cost | Higher | Lower |
| Usage | Precision machines | General linear motion |
For high-precision engineering, linear guideways have become the preferred choice.
Material Options for Linear Guideways
Manufacturers typically use:
High-carbon steel
Stainless steel
Coated steel (nickel, chrome, or black oxide)
Material selection depends on environment, load, and corrosion concerns.
Environmental Influence on Linear Guideways Performance
Dust, humidity, corrosive chemicals, and temperature swings can damage guideways. Sealed blocks, stainless-steel rails, and special grease help guideways survive extreme conditions.
Linear Guideways in High-Speed Automation
Modern automation systems demand high speed and rapid acceleration. Ball-type guideways excel in speed, while roller-type guideways provide rigidity. Machines often use both depending on the load and precision needs.
Understanding Load Ratings of Linear Guideways
Load ratings include:
Static load – load without movement
Dynamic load – load during motion
Moment load – twisting forces
Engineers must evaluate all three to choose an appropriate rail.

Cost Breakdown of Linear Guideways Systems
Costs depend on:
Rail length
Precision grade
Material type
Rolling element design
Brand reputation
Special coatings
Although premium guideways cost more, they last significantly longer.
Innovations Shaping the Future of Linear Guideways
Modern developments include:
IoT-connected guideways
Self-lubricating materials
Smart sensors for wear detection
Noise-reduction design
Lightweight carbon composite rails
These innovations aim to reduce downtime and improve accuracy.
Safety Considerations When Using Linear Guideways
Operators should:
Avoid placing hands near moving carriages.
Keep rails covered.
Perform routine inspections.
Ensure proper lubrication.
Safety guards prevent accidental injuries and machine damage.
Cleaning and Care for Linear Guideways
Care tips include:
Wipe with non-abrasive cloth
Use mild industrial solvents
Reapply grease regularly
Inspect for rust or pitting
Proper cleaning dramatically extends service life.
Impact of Linear Guideways on CNC Accuracy
Linear guideways directly affect:
Surface finish
Toolpath precision
Vibration control
Machine stiffness
CNC machines rely heavily on guideway stability for premium performance.
Top International Manufacturers of Linear Guideways
Reputable brands include:
THK
Hiwin
NSK
INA
IKO
These manufacturers are known for high precision and durability.
Buying Tips for Linear Guideways
Before purchasing, check:
Precision class
Load ratings
Seal type
Rail hardness
Carriage style
Lubrication method
Warranty coverage
Investing in quality rails ensures long-term reliability.
Future Trends in Linear Guideways Engineering
Expect improvements such as:
Predictive maintenance systems
AI-guided alignment tools
Eco-friendly lubrication
Lightweight rails
Smart real-time monitoring
These trends aim to enhance efficiency and accuracy.
Conclusion
Linear guideways are essential components in modern engineering. They provide precision, stability, and efficiency that sliding systems cannot match. From CNC machines to robotics and medical devices, these guideways form the backbone of high-performance motion systems. With proper maintenance, installation, and selection, linear guideways deliver years of reliable service.
FAQs
What are linear guideways used for?
They guide precision linear motion in industrial machines.
Do linear guideways require lubrication?
Yes, lubrication ensures smooth movement and prevents wear.
How long can linear guideways last?
With proper care, many years—even under heavy use.
Which industries rely on linear guideways?
CNC machining, robotics, packaging, medical equipment, and electronics.
Are roller-type guideways better than ball-type?
Roller types handle heavier loads; ball types offer faster movement.
How do I choose the right linear guideway?
Analyze load, precision, speed, environmental factors, and rail size.
Internal Link Suggestions
Link to your articles about linear guide rails and CNC components.
Link to a guide on industrial automation systems.
Outbound Link Suggestions
THK Official Website
ISO Standards on Linear Motion Systems