Outline
| Headings & Subheadings | LSI / Related Keywords |
|---|---|
| Introduction to Linear Slides and Guides | linear motion components, mechanical systems |
| What Are Linear Slides and Guides | linear guideways, motion precision, carriage |
| Design and Functionality | slider blocks, guide rails, bearings |
| Components of Linear Slides and Guides | rail, block, bearing system, preload |
| Working Mechanism | linear movement, rolling contact, friction control |
| Main Types of Linear Slides and Guides | ball guides, roller guides, plain slides |
| Comparison Between Linear Slides and Linear Guides | motion accuracy, stiffness, cost |
| Advantages of Linear Slides and Guides | smooth motion, high precision, durability |
| Applications in Modern Industries | robotics, CNC, automation equipment |
| Choosing the Right Linear Slides and Guides | load capacity, environment, precision needs |
| Material and Construction Options | steel, aluminum, stainless, polymer |
| Installation Best Practices | alignment, preload, lubrication |
| Common Issues and Solutions | binding, contamination, uneven wear |
| Maintenance Tips | cleaning, inspection, lubrication |
| Linear Slides and Guides in Robotics | compactness, precision, flexibility |
| Smart Linear Motion Systems | IoT, sensors, predictive maintenance |
| Future Trends in Linear Slides and Guides | magnetic, self-lubricating, corrosion-resistant |
| Cost and Performance Considerations | value, service life, efficiency |
| Top Manufacturers | YH Linear, THK, HIWIN, IGUS |
| FAQs | lifespan, materials, maintenance |
| Conclusion | summary, importance in automation |
Introduction to Linear Slides and Guides
Linear slides and guides are essential components in any system where motion precision, stability, and repeatability are key. These devices enable controlled, low-friction, straight-line movement — a necessity in modern automation, CNC machining, laboratory instruments, and robotics.
From industrial production lines to delicate semiconductor inspection tools, linear slides and guides form the foundation for accurate, efficient linear motion. Manufacturers like YH Linear, THK, and HIWIN have developed advanced designs to meet ever-tightening performance demands.
What Are Linear Slides and Guides
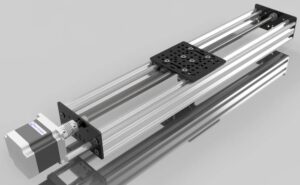
A linear slide or linear guide is a mechanical system that enables linear motion through either rolling or sliding contact between two main elements: a stationary guide rail and a moving slider (or carriage).
These components replace traditional bushings and plain bearings with sophisticated systems that minimize friction and wear, allowing smoother, more accurate motion. Whether you’re moving a robot arm, adjusting an optical table, or aligning a cutting head, linear slides and guides provide the accuracy you need.
Design and Functionality
The design of linear slides and guides centers on a simple yet precise structure:
Guide Rail: The stationary base that determines the path of motion.
Slider / Carriage: The moving element that travels along the rail.
Rolling Elements: Balls or rollers that recirculate between the rail and block.
Seals and End Caps: Protect the bearings and retain lubrication.
Preload Adjustments: Fine-tune stiffness and reduce play.
This combination ensures that loads are distributed evenly, friction is minimized, and motion remains accurate over millions of cycles.
Components of Linear Slides and Guides
| Component | Description | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Rail | Hardened steel or aluminum base | Provides linear path |
| Block / Slider | Moving platform | Supports load and motion |
| Bearings | Balls or rollers | Enable low-friction travel |
| End Seals | Rubber or polymer covers | Protect from dust, debris |
| Mounting Holes | Precision alignment points | Secure rail to machine frame |
| Preload System | Internal spring or ball tension | Adjusts stiffness and precision |
Working Mechanism
When force is applied to the slider, it moves along the guide rail in a controlled, linear fashion. In ball-type linear guides, balls circulate continuously inside the block, ensuring minimal friction. In roller or plain slides, rolling or sliding elements move along the rail, converting applied force into linear displacement.
This design minimizes stick-slip motion, reduces heat generation, and enables high-speed, high-accuracy movement — even under varying loads.
Main Types of Linear Slides and Guides
Ball Bearing Guides: Offer high precision and smooth operation; widely used in CNC and automation.
Roller Guides: Provide higher stiffness and load capacity, ideal for heavy machinery.
Plain Bearing Slides: Rely on polymer or composite materials; best for low-speed, cleanroom, or food applications.
Miniature Linear Guides: Compact designs for lab automation, electronics, or optical devices.
Cross Roller Guides: Use cylindrical rollers for ultra-high precision with minimal deflection.
Each type addresses a specific balance between precision, load, and operating environment.
Comparison Between Linear Slides and Linear Guides
| Aspect | Linear Slides | Linear Guides |
|---|---|---|
| Mechanism | Typically sliding motion | Rolling motion |
| Friction Level | Moderate | Very low |
| Precision | Medium | High to ultra-high |
| Load Capacity | Medium | High |
| Maintenance | Low to moderate | Moderate to high |
| Best For | Simpler motion systems | High-performance automation |
While both serve similar roles, linear guides often excel in accuracy-critical applications, whereas slides offer simplicity and cost efficiency.
Advantages of Linear Slides and Guides
Smooth Linear Motion: Ensures vibration-free operation.
High Precision: Enables micron-level accuracy for automation.
Low Friction and Wear: Rolling elements reduce surface contact.
Rigidity and Load Support: Maintains stability under dynamic conditions.
Compact Design: Saves space without compromising performance.
Extended Lifespan: Quality materials and lubrication extend operational cycles.
Versatility: Suitable for horizontal, vertical, or inclined motion systems.
These benefits make them indispensable in industries requiring continuous accuracy and efficiency.
Applications in Modern Industries
CNC Machines: Tool head positioning and bed movement.
Robotics: Arm articulation and pick-and-place operations.
Medical Equipment: Imaging tables and scanning mechanisms.
Semiconductor Manufacturing: Wafer alignment and precision handling.
Packaging Automation: Labelers, conveyors, and cartoners.
In all these cases, linear slides and guides ensure reliability, speed, and consistent performance.
Choosing the Right Linear Slides and Guides
When selecting a system, consider these factors:
| Criteria | Description |
|---|---|
| Load Capacity | Maximum weight supported dynamically and statically |
| Speed & Acceleration | Operational limits for desired throughput |
| Precision Requirements | Alignment and repeatability tolerance |
| Operating Environment | Exposure to moisture, dust, temperature |
| Material & Coating | Corrosion resistance and strength |
| Maintenance Frequency | Ease of lubrication and access |
Choosing the right model ensures balanced performance, long service life, and minimal downtime.
Installation Best Practices
Ensure flat, rigid mounting surfaces for accurate alignment.
Parallel mounting for dual-rail systems to avoid binding.
Apply correct preload for optimal stiffness.
Use clean, lubricated components during assembly.
Verify smooth travel manually before full operation.
Proper setup significantly improves both performance and longevity.
Common Issues and Solutions
| Issue | Possible Cause | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Binding or Sticking | Misalignment | Re-level and realign rails |
| Excessive Noise | Lack of lubrication | Apply proper grease or oil |
| Uneven Wear | Overload or vibration | Balance load and tighten mounts |
| Shortened Lifespan | Contamination | Use protective seals or covers |
Addressing issues early prevents expensive repairs and downtime.
Future Trends in Linear Slides and Guides
Smart Monitoring Systems with built-in sensors.
Lubrication-Free Materials using advanced polymers.
Magnetic Levitation Guides for contactless motion.
Lightweight Composite Rails for high-speed robotics.
Green Manufacturing Techniques to reduce material waste.
These innovations will define the next generation of linear motion technology.
FAQs
What is the difference between linear slides and guides?
Linear slides use sliding motion, while linear guides use rolling motion for higher precision.
Do linear slides need lubrication?
Yes, most require lubrication unless they use self-lubricating polymers.
How do I maintain linear guides?
Clean regularly, lubricate, and check for alignment or bearing wear.
Can linear guides be used vertically?
Yes, with proper preload and load capacity consideration.
What materials are used in linear guides?
Typically, hardened steel, stainless steel, or aluminum for rails and carriages.
Conclusion
Linear slides and guides are vital to the success of any motion control system. They offer unmatched precision, load-bearing strength, and reliability across diverse industries. Investing in high-quality components like those from YH Linear ensures smooth operation, extended service life, and superior machine performance.