Outline (Table Format)
| Heading | LSI Keywords |
|---|---|
| Linear Bearing Slide Rail Overview | linear motion rail |
| What Is a Linear Bearing Slide Rail? | rail bearing guide |
| Why Linear Bearing Slide Rail Systems Matter | smooth motion |
| How a Linear Bearing Slide Rail Works | rolling elements |
| Main Components of a Linear Bearing Slide Rail | rail, carriage |
| Types of Linear Bearing Slide Rail Systems | ball, roller |
| Choosing Between Ball and Roller Slide Rails | comparison |
| Load Capacity of Linear Bearing Slide Rails | dynamic load |
| Linear Bearing Slide Rail Materials | steel, alloys |
| Coating Options for Slide Rails | corrosion protection |
| Mounting Linear Bearing Slide Rails Correctly | installation |
| Alignment Techniques for Linear Bearing Slide Rails | straightness |
| Lubrication Requirements | grease, oil |
| Preload in Linear Bearing Slide Rails | stiffness |
| Noise and Vibration Behavior | damping |
| Common Issues in Slide Rail Systems | wear, binding |
| How to Increase Slide Rail Lifespan | maintenance |
| Linear Bearing Slide Rails for CNC Machinery | machining |
| Slide Rails in Automation and Robotics | robotics |
| Slide Rails for 3D Printers and Laser Cutters | maker tools |
| Thermal Effects on Slide Rail Performance | heat expansion |
| Shock and Impact Resistance | durability |
| Compact and Miniature Slide Rail Options | micro rails |
| Cost Factors When Buying Slide Rails | pricing |
| Innovations in Slide Rail Engineering | new technology |
| Real-World Applications of Slide Rail Systems | industries |
| Maintenance Checklist | inspection |
| Conclusion | summary |
Linear Bearing Slide Rail

Introduction
The keyword linear bearing slide rail appears early in this introduction to support SEO goals and improve clarity. If you work with CNC machines, robots, automated production lines, or even custom DIY motion systems, you’ve probably seen how important stable linear motion is. The linear bearing slide rail makes it all possible.
This rail-and-carriage system provides smooth, controlled, low-friction movement along a straight path. It handles weight, speed, vibration, and repeated cycles without losing accuracy. Although the system appears simple, many factors influence its performance—rail hardness, preload, lubrication, alignment, and rolling element design. In this guide, everything is explained using easy sentences and clear transitions so the information feels natural and practical.
Linear Bearing Slide Rail Overview
A linear bearing slide rail is a precision motion system that guides movement in one direction with low friction. It uses a hardened rail and a bearing carriage filled with rolling elements. Together, they create smooth and dependable movement used in machines of all sizes.
What Is a Linear Bearing Slide Rail?
A linear bearing slide rail is a mechanical guidance system that allows precise linear travel using bearing-supported sliders. The bearing elements reduce friction. The rail keeps travel straight. The setup delivers reliable and repeatable motion even under significant loads.
Why Linear Bearing Slide Rail Systems Matter
Modern machines demand stability. A linear bearing slide rail offers:
Smooth, quiet movement
Higher positional accuracy
Lower friction
Longer service life
High-speed motion
Reliable load handling
These benefits help machines work better and last longer.
How a Linear Bearing Slide Rail Works
Inside the carriage, balls or rollers circulate along hardened tracks. As the carriage moves, these elements roll instead of slide. Rolling friction is much lower, which keeps movement smooth. This also reduces heat and wear.
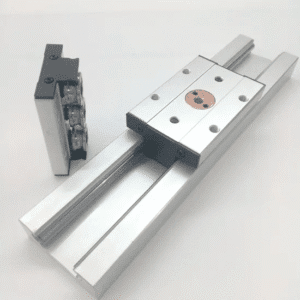
Main Components of a Linear Bearing Slide Rail
A complete system includes:
Rail: Hardened and precision-ground
Carriage: Holds rolling elements
Rolling elements: Balls or rollers
End caps: Guide element circulation
Wipers: Remove dust
Grease ports: Supply lubrication
Every part supports motion stability.
Types of Linear Bearing Slide Rail Systems
Common types include:
Ball-bearing slide rails
Roller-bearing slide rails
Dual-block slide rails
Miniature slide rails
Wide-body slide rails
Each type offers different benefits.
Choosing Between Ball and Roller Slide Rails
Ball-bearing rails offer:
Smooth movement
Lower friction
Higher speeds
Roller-bearing rails offer:
Higher load capacity
Greater rigidity
Better resistance to shock
The right choice depends on your machine’s demands.
Load Capacity of Linear Bearing Slide Rails
Load ratings depend on:
Rolling element size
Rail height
Carriage length
Preload level
Mounting surface quality
Heavier machines require wide or roller-based rails.
Linear Bearing Slide Rail Materials
Rails are usually made of:
High-carbon tool steel
Bearing-grade steel
Stainless steel
Alloy steel
These materials resist wear, bending, and heat.
Coating Options for Slide Rails
Coatings improve corrosion and wear resistance:
Hard chrome
Nickel plating
Black oxide
Advanced multi-layer coatings
Coatings extend lifespan in tough environments.

Mounting Linear Bearing Slide Rails Correctly
Correct mounting prevents binding and wear. Tips include:
Clean mounting surfaces
Remove all dust and chips
Tighten bolts in sequence
Don’t force the carriage
Test for smooth motion during installation
A flat mounting surface is extremely important.
Alignment Techniques for Linear Bearing Slide Rails
Proper alignment delivers better accuracy. Techniques include:
Using straightedges
Using dial indicators
Using alignment pins
Matching parallel rails carefully
Good alignment reduces friction and increases lifespan.
Lubrication Requirements
Lubrication reduces wear and supports smooth travel. Grease works well for slow, heavy motion. Oil works better for fast, hot, or high-speed systems.
Preload in Linear Bearing Slide Rails
Preload removes tiny internal clearances. It increases stiffness. Although preload improves accuracy, too much increases friction. Machines usually choose medium preload for balanced performance.
Noise and Vibration Behavior
Noise often comes from:
Poor alignment
High load
Dirty rails
Dry lubrication
Roller rails tend to run quieter under heavy load.
Common Issues in Slide Rail Systems
Mistakes include:
Improper lubrication
Rail contamination
Misalignment
Excessive preload
Bolt loosening
These issues reduce accuracy and speed.
How to Increase Slide Rail Lifespan
For long life:
Clean rails regularly
Lubricate often
Maintain proper preload
Use wipers and dust covers
Avoid overloading
Simple routines help keep rails smooth.
Linear Bearing Slide Rails for CNC Machinery
CNC machines rely on:
Rigidity
Speed
Repeatability
A good slide rail prevents backlash, chatter, and vibration.
Slide Rails in Automation and Robotics
Robotic systems need rails for:
Pick-and-place motion
Conveyor movement
Gantry stability
High-speed cycles
Slide rails help robots move predictably.
Slide Rails for 3D Printers and Laser Cutters
In these systems, a linear bearing slide rail offers:
Quiet movement
Smooth travel
Light load capability
Precise positioning
It upgrades accuracy and print quality.
Thermal Effects on Slide Rail Performance
Heat causes rail expansion. Even small temperature changes impact precision. Machines must consider thermal compensation.
Shock and Impact Resistance
Roller rails resist shocks better than ball rails. High-impact environments need thick rails with reinforced carriages.
Compact and Miniature Slide Rail Options
Mini slide rails suit:
Micro robotics
Medical equipment
Small automation tools
Electronic manufacturing
Their small size allows tight, delicate motion.
Cost Factors When Buying Slide Rails
Pricing depends on:
Rail size
Carriage type
Brand
Material
Coating
Precision grade
Better rails cost more but last longer.
Innovations in Slide Rail Engineering
Recent advancements include:
Self-lubricating blocks
Ceramic rolling elements
Lightweight carbon-reinforced rails
Noise-reducing groove designs
These innovations continue improving performance.
Real-World Applications of Slide Rail Systems
Linear bearing slide rails appear in:
CNC routers
Pick-and-place robots
Automated testing devices
Medical scanners
3D printers
Packaging machines
They support almost every motion-critical industry.
Maintenance Checklist
A good maintenance routine includes:
Weekly cleaning
Monthly lubrication
Quarterly bolt tightening
Routine preload checks
Seal inspections
Rail straightness checks
Consistent care keeps your system operating like new.
Conclusion
A linear bearing slide rail is one of the most important components in modern linear motion design. Its ability to carry loads, maintain alignment, and move smoothly makes it essential for CNC machines, robotics, automation systems, and precision tools. With correct sizing, proper lubrication, and accurate alignment, a linear bearing slide rail delivers years of stable performance.
FAQs
What is a linear bearing slide rail used for?
It guides smooth and accurate linear movement in machines.
Do slide rails need lubrication?
Yes. Lubrication reduces friction and improves lifespan.
Are ball or roller slide rails better?
Ball rails are smoother. Roller rails handle more load.
Can slide rails handle heavy loads?
Yes, especially wide and roller-based types.
Where are slide rails used most?
CNC machines, robotics, packaging, and automation equipment.
How long do slide rails last?
With good maintenance, many last for years or even decades.
Internal Link Suggestions
Linear guide rails
Linear bearing rail
Linear guide slider
Heavy duty linear rail
Outbound Link Suggestions
HIWIN linear slides technical PDF
NSK motion components reference