Outline (Table Format)
| Heading / Subheading | LSI Keywords Included |
|---|---|
| Linear Rail Overview | precision rail, motion guide |
| Why Using a Linear Rail Matters | rigidity, accuracy |
| How a Linear Rail Works | carriages, rolling elements |
| Key Components Inside a Linear Rail System | rails, blocks |
| Different Types of Linear Rail Designs | profile rail, round rail |
| Ball-Type Linear Rail Blocks | recirculating balls |
| Roller-Type Linear Rail Blocks | cylindrical rollers |
| Miniature Linear Rail Systems | micro motion |
| Heavy-Duty Linear Rail Systems | industrial load |
| Advantages of Using a Linear Rail | long lifespan |
| Applications of Linear Rail Systems | CNC machines |
| Choosing the Ideal Linear Rail | load rating |
| Steps for Proper Linear Rail Installation | alignment |
| Maintenance Tips for Linear Rail Performance | lubrication |
| Common Issues in Linear Rail Systems | wear |
| Troubleshooting a Linear Rail | noise, vibration |
| Linear Rail vs Linear Guideway | comparison |
| Material Choices in Linear Rail Manufacturing | stainless steel |
| Environmental Impact on Linear Rail Lifespan | dust |
| High-Speed Motion on Linear Rails | acceleration |
| Understanding Load Ratings on Linear Rails | moment load |
| Cost Factors in Linear Rail Purchasing | pricing |
| Modern Technology in Linear Rail Systems | self-lube |
| Safety Practices for Using Linear Rails | guarding |
| Cleaning Methods for Linear Rail Tracks | degreasers |
| Impact of Linear Rail on CNC Accuracy | rigidity |
| Global Brands Known for Quality Linear Rails | THK |
| Checklist Before Buying Linear Rails | spec list |
| Conclusion | summary |
Introduction
The modern world depends on precise motion, and the linear rail is the backbone of that motion. Because this article places the keyword linear rail directly in the introduction, search engines and readers quickly understand its focus. Linear rails guide movement along a straight path using hardened steel tracks and rolling blocks. They bring accuracy, strength, and stability to machines that must move with consistency.
This guide uses easy words, short sentences, and clear ideas. It keeps the reading experience smooth and friendly while staying knowledgeable and professional. Whether you work with CNC machines, automated systems, robotics, 3D printing, or industrial equipment, understanding linear rails will help you design, maintain, and operate high-performance machinery.
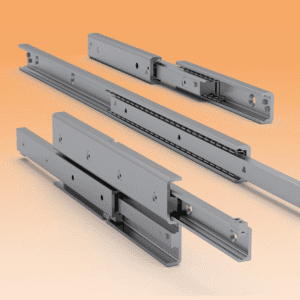
Linear Rail Overview
A linear rail is a precision-machined track that supports the smooth movement of a carriage block. The block rides on rolling elements, reducing friction and improving the accuracy of every motion. Unlike basic bushings or sliding systems, the linear rail offers superior rigidity, impressive load capacity, and excellent repeatability.
Engineers choose linear rails because they deliver consistent performance over long distances. They stay strong under heavy loads and provide quiet, stable travel in a wide range of applications.
Why Using a Linear Rail Matters
Linear rails are vital in today’s fast-paced industries because they allow:
High precision
Excellent rigidity
Smooth motion
Lower friction
Longer machine life
High repeatability
Quieter operation
Automation keeps growing, and as tasks become more demanding, the need for reliable guiding systems increases. Linear rails meet these challenges with confidence and consistency.
How a Linear Rail Works
A linear rail works by allowing a carriage block to move along a hardened steel rail. Inside the block are rolling elements—either balls or rollers. As the block travels, the elements recirculate, reducing friction and distributing load evenly.
This method ensures accurate straight-line movement. Even under heavy pressure, the motion stays smooth because the rolling elements minimize resistance.
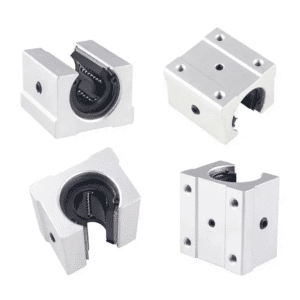
Key Components Inside a Linear Rail System
A linear rail system includes:
Rail — hardened steel track
Carriage block — main moving unit
Rolling elements — balls or rollers
End caps — guide recirculation
Seals — protect from debris
Lubrication ports — deliver grease
Cage or retainer — organizes rolling elements
Each piece plays a role in delivering smooth motion.
Different Types of Linear Rail Designs
Two common designs include:
Profile (square) rails
These offer high rigidity and accuracy. They are common in CNC mills, routers, and machine tools.
Round rails
These allow easier alignment and absorb misalignment better. They are used in light automation and laboratory equipment.
Profile rails dominate precision industries due to their performance.
Ball-Type Linear Rail Blocks
Ball-type rail blocks use multiple rows of steel balls to roll along the rail. Benefits include:
Quiet motion
Low friction
High speed capability
Excellent accuracy
They suit applications requiring smooth, rapid travel.
Roller-Type Linear Rail Blocks
Roller blocks use cylindrical rollers instead of balls. The larger contact surface provides:
Higher load capacity
Better rigidity
Increased vibration resistance
Superior precision under stress
They are ideal for heavy-duty CNC machines and industrial robots.
Miniature Linear Rail Systems
Miniature rails appear in:
Micro-robotics
Medical equipment
Precision measuring tools
Small automation systems
Optical alignment devices
Their compact size makes them perfect for tight environments.
Heavy-Duty Linear Rail Systems
Heavy-duty rails operate in demanding industries. They include reinforced blocks, advanced seals, and superior coatings. They support:
Large gantries
Heavy robots
Industrial automation
Packaging systems
Material handling equipment
Strength and durability are their key features.
Advantages of Using a Linear Rail
Linear rails offer many advantages:
High rigidity
Low vibration
Accurate path control
Low friction travel
Long operational lifespan
High load capacity
Smooth and quiet operation
Consistent performance
These benefits help machines maintain stable, predictable motion.
Applications of Linear Rail Systems
You’ll find linear rails in:
CNC mills
CNC routers
Industrial robots
Laser cutting systems
3D printers
Automated packaging lines
High-resolution scanners
Medical imaging devices
Semiconductor processing equipment
Their adaptability makes them essential in both light and heavy applications.
Choosing the Ideal Linear Rail
Before choosing a rail, consider:
Load capacity
Rigidity requirements
Precision grade
Block style (short, long, wide)
Speed rating
Environmental conditions
Temperature limits
Noise levels
Length and mounting options
The correct decision improves performance and reduces wear.
Steps for Proper Linear Rail Installation
Proper installation is crucial. Follow these steps:
Clean mounting surfaces.
Check for straightness.
Lightly place rails on the surface.
Tighten bolts gradually and evenly.
Check alignment with a dial indicator.
Add lubrication.
Manually move the block to verify smoothness.
Good installation reduces failures significantly.
Maintenance Tips for Linear Rail Performance
Maintenance keeps rails reliable:
Lubricate regularly
Clean dust and chips
Inspect seals
Check for noise
Monitor block smoothness
Verify bolt tightness
Replace worn components promptly
These simple actions extend lifespan dramatically.
Common Issues in Linear Rail Systems
Typical problems include:
Binding
Noise
Excess heat
Vibration
Rough motion
Uneven wear
Contamination
Many of these come from misalignment or poor lubrication.
Troubleshooting a Linear Rail
To troubleshoot:
Noise: Add lubrication and check debris.
Rough motion: Realign the rail.
Binding: Inspect bolts for uneven torque.
Heat: Reduce load or improve lubrication.
Vibration: Inspect rollers or balls.
Most issues are easy to fix with the right steps.
Linear Rail vs Linear Guideway
Though similar, the two terms differ slightly:
| Feature | Linear Rail | Linear Guideway |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | The track | Full system |
| Accuracy | High | Very high |
| Capacity | Strong | Stronger |
| Best Use | Standard precision | High-demand CNC |
In practice, many people use the terms interchangeably.
Material Choices in Linear Rail Manufacturing
Popular materials include:
Carbon steel — high strength
Stainless steel — corrosion resistance
Chrome-plated steel — smooth surface
Special coatings — improved wear resistance
Material choice affects performance and longevity.
Environmental Impact on Linear Rail Lifespan
Environmental factors include:
Dust
Humidity
Coolant exposure
Metal chips
Chemicals
Temperature swings
The wrong environment without protection quickly leads to wear.
High-Speed Motion on Linear Rails
Linear rails support:
High velocity travel
Low-friction movement
Quick acceleration
Smooth stopping
This makes them ideal for high-speed automation.
Understanding Load Ratings on Linear Rails
Rails handle three main loads:
Radial load
Side load
Moment load
Understanding these ensures proper sizing and selection.
Cost Factors in Linear Rail Purchasing
Costs depend on:
Rail length
Precision grade
Block type
Material
Brand
Accessories
Coatings
Quantity
Quality rails may cost more but offer long-term savings.
Modern Technology in Linear Rail Systems
Recent advancements include:
Self-lubricating reservoirs
Low-noise ball circulation
Corrosion-resistant coatings
Lightweight composite materials
Smart sensors for monitoring wear
These innovations improve accuracy and reliability.
Safety Practices for Using Linear Rails
Follow these guidelines:
Use guarding around moving axes
Avoid touching moving rails
Wear gloves when installing
Keep rails clean
Avoid overloads
Safety supports both workers and equipment.
Cleaning Methods for Linear Rail Tracks
To clean rails:
Wipe with a lint-free cloth
Use mild solvents
Remove old grease
Clean block end caps
Apply new lubrication
Clean rails ensure smoother and quieter movement.
Impact of Linear Rail on CNC Accuracy
A linear rail influences:
Position accuracy
Repeatability
Surface finish
Rigidity
Tool stability
CNC machines depend heavily on rail quality for precise cuts.
Global Brands Known for Quality Linear Rails
Top manufacturers include:
THK
HIWIN
NSK
PMI
Bosch Rexroth
SKF
INA
These companies produce reliable and long-lasting rails.
Checklist Before Buying Linear Rails
Review the following:
Load requirements
Rail length
Precision class
Block quantity
Material type
Lubrication style
Environmental needs
Speed and noise limits
This checklist helps prevent costly mistakes.
Conclusion
A linear rail is more than a simple guiding component—it is the foundation of modern precision motion. With its superior rigidity, low friction, and long service life, the linear rail empowers industries like CNC machining, robotics, automation, medical imaging, and semiconductor manufacturing. When installed carefully and maintained consistently, linear rails deliver dependable, high-performance motion for years. As technology continues to advance, linear rails will remain a critical part of engineering innovation.
FAQs
What is a linear rail used for?
It guides smooth and precise straight-line motion in machinery.
Do linear rails require lubrication?
Yes, lubrication protects the rolling elements and ensures smooth travel.
Are linear rails better than bushings?
Rails provide better rigidity and precision, while bushings suit simpler motion.
Can linear rails support heavy loads?
Yes, especially roller-type linear rails designed for industrial use.
How long does a linear rail last?
With proper care, it can last many years in demanding conditions.
Are linear rails expensive?
Costs vary, but quality rails offer excellent long-term value.
Internal Link Suggestions
Link to “linear rail systems,” “linear guide rail,” “linear bearing,” “linear guiding,” “linear motion track system.”
Outbound Link Suggestions
THK Linear Motion Guide Catalog
HIWIN Rail and Block Technical Handbook