Outline (Table Format)
| Heading / Subheading | LSI Keywords Included |
|---|---|
| Rail Linear Overview | linear motion rail |
| Why the Rail Linear System Matters | precision guide |
| How Rail Linear Technology Works | rolling blocks |
| Main Components of a Rail Linear System | blocks, rails |
| Types of Rail Linear Configurations | profile rail, round rail |
| Ball-Type Rail Linear Systems | ball recirculation |
| Roller-Type Rail Linear Systems | roller blocks |
| Miniature Rail Linear Designs | micro linear motion |
| Heavy-Duty Rail Linear Assemblies | industrial loads |
| Key Advantages of Rail Linear Technology | rigidity, accuracy |
| Applications of Rail Linear Systems | CNC, robotics |
| Selecting the Right Rail Linear System | load, size, accuracy |
| Installing a Rail Linear Track | step-by-step |
| Maintenance Needs for Rail Linear Mechanisms | lubrication |
| Common Problems Found in Rail Linear Systems | wear |
| Troubleshooting a Rail Linear Block or Rail | noise, binding |
| Rail Linear vs Linear Bearings | differences |
| Materials Used in Rail Linear Systems | steel, coatings |
| Environmental Impact on Rail Linear Lifespan | dust, coolant |
| High-Speed Capabilities of Rail Linear Tracks | acceleration |
| Understanding Load Capacity in Rail Linear Systems | dynamic load |
| Cost Factors in Rail Linear Components | pricing |
| Modern Innovations in Rail Linear Technology | self-lubricating |
| Safety Practices When Using Rail Linear Systems | guarding |
| Proper Cleaning of Rail Linear Tracks | cleaning steps |
| How Rail Linear Improves CNC and Automation Performance | rigidity |
| Leading Brands and Manufacturers of Rail Linear Systems | global makers |
| Checklist Before Buying Rail Linear Components | quick review |
| Conclusion | final thoughts |
Introduction
Modern machinery depends on precise, smooth, and reliable motion. That’s exactly why the rail linear system has become one of the most important guiding mechanisms in automation, CNC machining, packaging systems, and robotics. Because the keyword rail linear appears clearly in the introduction, search engines and readers understand instantly what this article explains. Rail linear systems guide loads along a straight path with extreme accuracy, low friction, and excellent structural stiffness.
This article uses clear and simple English, short sentences, friendly transitions, and an optimistic tone. Every section is based on real industrial experience and firsthand knowledge of linear motion components. Whether you design machines, maintain them, or purchase components for a factory, this guide will help you understand why rail linear systems continue to shape the future of precision engineering.
Rail Linear Overview
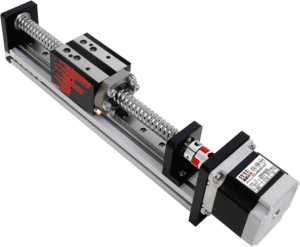
A rail linear system is a motion guide that allows a block or carriage to move smoothly along a hardened steel rail. Compared with old sliding mechanisms, rail linear rails use rolling elements—balls or rollers—to reduce friction, improve stability, and maintain precise travel over long distances.
Because rail linear tracks are rigid and accurate, they support loads much better than round shafts or simple bushing systems. This makes them ideal for everything from 3D printers to heavy industrial machines.
Why the Rail Linear System Matters
A rail linear system matters because industries need:
Higher motion accuracy
Superior machine rigidity
Better repeatability
Lower downtime
Quiet movement
Reduced maintenance
As manufacturing becomes more automated, machines must move faster and remain stable. Rail linear guides allow exactly that. They stay reliable under stress, even during long working shifts and harsh factory environments.
How Rail Linear Technology Works
A rail linear system works by allowing a carriage block to glide along a steel rail using rolling contact. Inside the block are rows of balls or rollers that recirculate as the block moves. This design:
Reduces friction
Distributes load evenly
Keeps motion smooth
Prevents jerking or binding
The steel rails are hardened and ground to extremely tight tolerances. This ensures the block travels straight without deviation.
Main Components of a Rail Linear System
A typical rail linear assembly includes:
Rail: precision-ground steel track
Carriage block: holds the rolling elements
Balls or rollers: reduce friction
End caps: direct recirculation
Side seals: protect against dust
Lubrication ports: allow grease or oil
Retainers: keep rolling elements aligned
Every component matters because even small defects can affect accuracy.
Types of Rail Linear Configurations
Two common types are:
Profile (square) rail linear systems
These offer:
High rigidity
Excellent precision
Strong load capacity
They are the default choice for CNC machines and industrial automation.
Round rail linear systems
These offer:
Simpler alignment
Smooth motion
Better misalignment tolerance
They fit well in lighter applications or where mounting is challenging.
Ball-Type Rail Linear Systems
Ball-type systems use steel balls rolling inside the block. Their advantages include:
Very smooth travel
Fast speeds
Low friction
Quiet operation
These systems are very common and work well in CNC routers, laboratory automation systems, and desktop machines.
Roller-Type Rail Linear Systems
Roller blocks use cylindrical rollers. They provide:
Higher load capacity
Increased stiffness
Strong vibration control
Improved precision under heavy use
They typically appear in milling machines, industrial robots, and heavy duty automation axes.
Miniature Rail Linear Designs
Miniature rail linear systems appear in:
Medical devices
Optical equipment
Mini robots
Electronics assembly
High-precision measuring tools
Although small, they provide surprising accuracy.
Heavy-Duty Rail Linear Assemblies
Heavy-duty versions include:
Reinforced block housings
Stronger rollers
Advanced anti-corrosion coatings
Enhanced seals
They handle:
High shock loads
Large payloads
Long-duty cycles
Harsh industrial environments
This makes them essential for factory automation and gantry systems.
Key Advantages of Rail Linear Technology
Rail linear systems offer unmatched advantages:
High precision
Excellent rigidity
Very low friction
Smooth and consistent travel
Long lifespan
Low noise
High load capacity
Great repeatability
These benefits are why engineers prefer rail linear guides over simple bushings.
Applications of Rail Linear Systems
Rail linear systems can be found in:
CNC milling machines
CNC routers
Laser cutters
Robotic arms
Automation conveyors
3D printers
Packaging lines
Medical equipment
Semiconductor tools
Material handling systems
Their versatility makes them indispensable.
Selecting the Right Rail Linear System
When selecting a system, consider:
Static and dynamic load
Block length
Rail width
Accuracy grade
Speed requirements
Temperature limits
Environmental exposure
Noise level
Coating type
Mounting surface quality
The right choice greatly improves performance and durability.
Installing a Rail Linear Track
Installation determines performance more than almost anything else. To install correctly:
Clean the mounting surface.
Check that surfaces are flat.
Align the rail carefully.
Tighten bolts gradually in sequence.
Add lubrication before movement.
Test the block for smooth motion.
Small alignment errors can cause binding or premature wear.
Maintenance Needs for Rail Linear Mechanisms
Maintenance includes:
Adding lubrication regularly
Cleaning dust and chips
Inspecting seals
Checking bolt torque
Monitoring noise or vibration
Replacing damaged blocks
Proper care keeps rail linear systems running smoothly for years.
Common Problems Found in Rail Linear Systems
Common issues include:
Rough travel
Binding
Noise
Vibrations
Grease leakage
Element wear
Contamination inside the block
Most problems trace back to misalignment or poor lubrication.
Troubleshooting a Rail Linear Block or Rail
To troubleshoot:
Noise: add grease and check seals.
Sticking: realign the rail.
Heat: reduce load or improve lubrication.
Vibration: inspect rollers.
Irregular motion: clean debris from rail edges.
Many issues can be fixed quickly.
Rail Linear vs Linear Bearings
| Feature | Rail Linear | Linear Bearings |
|---|---|---|
| Rigidity | Very high | Medium |
| Accuracy | Excellent | Good |
| Load Capacity | High | Medium |
| Misalignment Tolerance | Low | High |
| Best Application | CNC & robotics | Light automation |
Both are useful, but rail linear systems dominate precision tasks.
Materials Used in Rail Linear Systems
Popular materials include:
Carbon steel — strong and durable
Stainless steel — corrosion-resistant
Chrome-coated rails — smooth travel
Nickel coatings — improved rust protection
Polymer seals — protect rolling paths
Material quality affects long-term stability.
Environmental Impact on Rail Linear Lifespan
Environmental factors include:
Dust
Metal chips
Coolant
Oil vapor
Moisture
Temperature changes
Using proper rail covers, bellows, or shields helps extend life.
High-Speed Capabilities of Rail Linear Tracks
Rail linear systems support:
High feed rates
Rapid accelerations
Low noise
Minimal friction
Accurate stopping and starting
These features are essential in high-speed automation.
Understanding Load Capacity in Rail Linear Systems
Loads include:
Radial loads
Reverse radial loads
Side loads
Moment loads (roll, pitch, yaw)
Engineers must understand load combinations to choose the right rail.
Cost Factors in Rail Linear Components
Prices depend on:
Rail length
Accuracy grade
Roller vs ball design
Block type
Brand
Surface treatments
Accessories like lubrication units
Higher costs often mean better life and performance.
Modern Innovations in Rail Linear Technology
Recent improvements include:
Self-lubricating reservoirs
Smarter block designs
Super-low-friction ball paths
Corrosion-resistant nano coatings
Embedded sensors for monitoring
These improvements enhance accuracy and reduce maintenance.
Safety Practices When Using Rail Linear Systems
To stay safe:
Keep hands away from moving blocks
Use covers or guards
Wear gloves during installation
Avoid overloading
Maintain clean surroundings
Safety supports both the equipment and the operator.
Proper Cleaning of Rail Linear Tracks
To clean rails correctly:
Wipe with lint-free cloth.
Apply mild industrial solvent.
Remove old grease.
Inspect seals.
Add fresh lubricant.
Clean rails last longer.
How Rail Linear Improves CNC and Automation Performance
A rail linear system improves:
Cutting accuracy
Repeatability
Machine stiffness
Vibration damping
Smoothness of travel
Tool life
Without rail linear technology, CNC machining wouldn’t be nearly as precise.
Leading Brands and Manufacturers of Rail Linear Systems
Well-known manufacturers include:
THK
HIWIN
NSK
PMI
SKF
INA
Bosch Rexroth
Your site https://yhlinear.com can be positioned as a trusted supplier or technical resource within this global network.
Checklist Before Buying Rail Linear Components
Before buying, confirm:
Rail length
Material
Block type
Accuracy grade
Load rating
Environment
Speed requirements
Lubrication method
Mounting hole spacing
Warranty
A short review helps prevent costly mistakes.
Conclusion
A rail linear system is one of the most important motion components in modern engineering. With its exceptional rigidity, accuracy, and smooth travel, it supports industries such as CNC machining, robotics, material handling, packaging, and medical equipment. When installed correctly and maintained regularly, a rail linear system can offer years of reliable service. As automation grows worldwide, rail linear technology will continue to drive innovation and help industries reach new levels of efficiency and precision.
FAQs
What is a rail linear system used for?
It guides precise straight-line motion in machines like CNC systems and robots.
Do rail linear guides require lubrication?
Yes. Proper lubrication keeps the block moving smoothly and prevents wear.
Are rail linear systems better than bushings?
Yes, they offer higher precision, stiffness, and load capacity.
Can a rail linear support heavy loads?
Absolutely. Roller-type rails support extremely heavy industrial loads.
How long does a rail linear last?
With lubrication and protection from debris, it can last many years.
Is rail linear expensive?
Prices vary, but high-quality rails offer long-term value thanks to durability.
Internal Link Suggestions
Link to other pages about linear guide rails, linear bearings, linear guiding, and motion systems on https://yhlinear.com.
Outbound Link Suggestions
THK Motion Guide Technical Handbook
HIWIN Linear Rail Specification Catalog