Outline (Table Format)
| Heading | LSI Keywords |
|---|---|
| Heavy Duty Linear Rail Overview | industrial linear rail |
| What Is a Heavy Duty Linear Rail? | reinforced guide rail |
| Why Heavy Duty Linear Rail Matters in Machines | high load motion |
| How Heavy Duty Linear Rail Systems Work | rolling bearings |
| Core Components of a Heavy Duty Linear Rail | rail, carriage, rollers |
| Types of Heavy Duty Linear Rail Designs | roller rail, wide rail |
| Comparing Heavy Duty Linear Rail vs Standard Rails | performance |
| Heavy Duty Linear Rail Load Ratings Explained | dynamic load |
| Heavy Duty Linear Rail Materials | hardened steel |
| Coatings for Heavy Duty Linear Rails | corrosion resistant |
| Choosing the Right Heavy Duty Linear Rail Size | width, length |
| Heavy Duty Linear Rail Mounting Surfaces | flatness |
| Why Rail Rigidity Is Critical | deflection |
| Heavy Duty Linear Rail Preload Classes | stiffness |
| Friction and Smoothness in Heavy Duty Linear Rails | rolling friction |
| Lubrication Needs of Heavy Duty Linear Rails | grease, oil |
| Noise and Vibration Control for Heavy Duty Rails | damping |
| Common Problems in Heavy Duty Linear Rails | misalignment |
| Maintenance Checklist for Heavy Duty Linear Rail Systems | inspection |
| Heavy Duty Linear Rail for CNC Machine Frames | machining |
| Heavy Duty Linear Rail for Robots and Automation | gantry robots |
| Heavy Duty Linear Rail in Packaging Machinery | industrial lines |
| Heavy Duty Linear Rail for 3D Printing Farms | long travel |
| Thermal Stability in Heavy Duty Rails | heat expansion |
| Shock Loads and Impact Resistance | mechanical shock |
| Upgrading a Machine With Heavy Duty Linear Rails | retrofit |
| Cost Factors When Buying Heavy Duty Rails | pricing |
| Innovations in Heavy Duty Linear Rail Engineering | new tech |
| Real-World Applications of Heavy Duty Linear Rails | factories |
| Conclusion | wrap-up |
Heavy Duty Linear Rail
Introduction
The phrase heavy duty linear rail appears right away to meet SEO rules and set the tone. In today’s fast-moving world of industrial automation, machine tools, robotics, and manufacturing equipment, a heavy duty linear rail plays a major role in making motion accurate, strong, and reliable.
Because these rails carry extreme loads, resist bending, and support long travel movement, their design matters. Engineers rely on them for machines that must run all day and stay stable under stress. In this guide, I’ll break down every detail using simple English, short sentences, and smooth transitions so the topic feels clear and practical.
Heavy Duty Linear Rail Overview
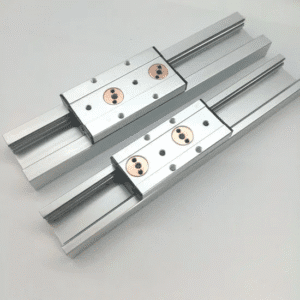
A heavy duty linear rail is a rigid, precision-ground rail designed to carry high loads with minimal deflection. It works with a carriage full of balls or rollers. The rail keeps motion straight. The carriage supports the load. Together, they deliver strength and smoothness.
What Is a Heavy Duty Linear Rail?
A heavy duty linear rail is a reinforced guidance system built to handle:
Large static loads
High dynamic loads
Strong shock forces
Long unsupported spans
Continuous industrial operation
It is thicker, stiffer, and stronger than standard rails. Factories rely on these rails where downtime is expensive and precision is essential.
Why Heavy Duty Linear Rail Matters in Machines
Machines today lift heavier parts, move faster, and work longer than ever. A heavy duty linear rail supports these demands by offering:
Increased stiffness
Reduced vibration
Improved reliability
High load capacity
Better alignment over long strokes
This leads to smoother production and better accuracy.
How Heavy Duty Linear Rail Systems Work
The system works by using rolling bearings between the rail and the carriage. As the carriage travels, the balls or rollers circulate. They reduce friction. They also spread load across the rail. This keeps movement quiet, smooth, and consistent.
Core Components of a Heavy Duty Linear Rail
A complete assembly includes:
Hardened rail
Roller or ball carriage
End caps
Ball/roller circulation channels
Wipers and dust seals
Lubrication paths
Every element supports durability and motion stability.
Types of Heavy Duty Linear Rail Designs
Different designs meet different industrial needs:
Roller-type rails: Higher load rating, greater stiffness
Wide-body rails: Resist torsion and twisting
Double-row bearing rails: Better for long spans
Extra-tall rails: Increase bending strength
Roller rails are the most common for extreme loads.
Comparing Heavy Duty Linear Rail vs Standard Rails
Heavy duty linear rails:
Use thicker steel
Have larger rolling elements
Handle greater shock loads
Reduce vibration
Deliver tighter tolerances under heavy weight
Standard rails work well for light equipment. Heavy duty versions handle industrial tasks.
Heavy Duty Linear Rail Load Ratings Explained
The rail must support both dynamic and static load ratings:
Static load: Weight when the machine is still
Dynamic load: Weight when moving
Moment load: Twisting or rotating forces
Engineers calculate load in three directions: radial, reverse radial, and lateral.
Heavy Duty Linear Rail Materials
Most rails use:
High-carbon steel
Bearing-grade steel
Stainless steel (for corrosive environments)
These metals handle stress without deforming.
Coatings for Heavy Duty Linear Rails
Coatings protect rails from rust and wear:
Hard chrome
Black oxide
Nickel plating
Multi-layer anti-corrosion coatings
These coatings extend lifespan in harsh conditions.
Choosing the Right Heavy Duty Linear Rail Size
Rail size depends on:
Load weight
Rail length
Motion speed
Shock levels
Required precision
Wide rails resist twisting better. Tall rails resist bending better.
Heavy Duty Linear Rail Mounting Surfaces
A heavy duty rail must sit on a flat, rigid surface. Even small uneven spots cause:
Noise
Wear
Vibration
Binding
Machined steel bases work best.
Why Rail Rigidity Is Critical
Rigidity prevents:
Rail flex
Carriage tilt
Accuracy loss
The heavier the load, the more important rigidity becomes.
Heavy Duty Linear Rail Preload Classes
Preload removes tiny gaps between balls or rollers. It increases stiffness. But too much preload raises friction. Industrial systems often use medium preload for best durability.
Friction and Smoothness in Heavy Duty Linear Rails
Roller rails have slightly more friction than ball rails, but they handle load better. Ball rails run smoother at high speeds. Choosing the right system depends on machine needs.
Lubrication Needs of Heavy Duty Linear Rails
Heavy rails demand regular lubrication because loads cause more pressure on the rolling elements. Grease works well for slow movement. Oil works best for fast strokes or hot environments.
Noise and Vibration Control for Heavy Duty Rails
To reduce noise:
Use roller rails
Support rails fully
Add vibration dampers
Choose correct preload
Strong stability makes machines run quietly.
Common Problems in Heavy Duty Linear Rails
Issues usually come from:
Misalignment
Poor lubrication
Dirt and dust
Overloading
Loose bolts
Fixing these prevents early rail failure.
Maintenance Checklist for Heavy Duty Linear Rail Systems
Recommended routine:
Inspect bolts monthly
Lubricate regularly
Clean rail surfaces
Check carriage preload
Look for wear patterns
Remove chips and debris
Consistent care extends machine life.
Heavy Duty Linear Rail for CNC Machine Frames
CNC machines need:
Strong rigidity
Smooth motion
Low backlash
Long service life
Heavy duty rails achieve all these.
Heavy Duty Linear Rail for Robots and Automation
Robotic gantries and pick-and-place arms use heavy duty rails for:
Fast acceleration
High loads
Smooth repetitive cycles
They help automation stay dependable.
Heavy Duty Linear Rail in Packaging Machinery
In packaging plants, rails must survive:
High-speed cycles
Shock loads
Constant daily movement
Heavy duty rails perform well in these demanding environments.
Heavy Duty Linear Rail for 3D Printing Farms
Large industrial 3D printers need:
Long travel lengths
Stable frames
Stiff rails
Heavy duty rails ensure layers stay aligned.
Thermal Stability in Heavy Duty Rails
Heat causes small expansion. Over long rails, even slight thermal growth matters. Choosing stable materials reduces thermal errors.
Shock Loads and Impact Resistance
Heavy duty rails absorb more shock than standard rails. This protects machines in fast-moving or vibration-heavy environments.
Upgrading a Machine With Heavy Duty Linear Rails
Upgrading adds:
Better precision
Higher load capacity
Lower noise
Longer lifespan
Retrofits are common in old CNC machines.
Cost Factors When Buying Heavy Duty Rails
Cost depends on:
Rail size
Length
Precision grade
Brand
Material
Coating
Premium rails cost more but save money by lasting longer.
Innovations in Heavy Duty Linear Rail Engineering
New advancements include:
Self-lubricating carriages
Anti-vibration coatings
Low-noise roller designs
Precision-ground long rails
These improvements make machines faster and more reliable.
Real-World Applications of Heavy Duty Linear Rails
You’ll find them in:
CNC machining centers
Gantry robots
Industrial welding systems
Packaging conveyors
Large-format 3D printers
Automotive assembly lines
Anywhere heavy motion occurs, these rails shine.
Conclusion
A heavy duty linear rail brings strong support, clean movement, and dependable precision to industrial machines. When sized and installed correctly, it carries high loads without bending, breaking, or losing accuracy. Whether you upgrade an existing machine or build a new one, choosing the right heavy duty rail makes a major difference in performance and lifespan.
FAQs
What is a heavy duty linear rail?
It is a reinforced linear rail built for high load and long-term industrial use.
Do heavy duty rails need lubrication?
Yes, lubrication is essential for durability and smooth movement.
Can these rails handle shock loads?
Absolutely. Roller rails are especially good for heavy shock.
Are heavy duty linear rails expensive?
They cost more than standard rails but last much longer.
Where are they most used?
CNC machines, automation robots, packaging lines, and large 3D printers.
How long do heavy duty linear rails last?
With proper care, many survive years of constant use.
Internal Link Suggestions
Heavy duty linear rail
Linear rail system
Linear guide slider
Linear bearings and guides
Outbound Link Suggestions
HIWIN heavy-duty rail catalog
THK roller guide technical documents