Introduction
In modern machinery, precise and smooth linear motion is essential for high performance and efficiency. One of the key components that enable this motion is the carriage bearing.
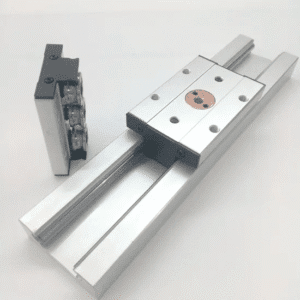
A carriage bearing (sometimes called a linear bearing carriage or linear guide block) is a mechanical system that allows a load-carrying component to move smoothly along a linear rail or guide. These bearings are widely used in CNC machines, 3D printers, industrial robots, automation systems, and packaging machinery.
This article provides a detailed overview of carriage bearings, covering their structure, working principle, types, advantages, applications, selection criteria, and maintenance practices.
What Is a Carriage Bearing?
A carriage bearing is a linear motion device designed to move along a rail or track with minimal friction. It typically consists of:
A carriage block that supports the load.
Rolling elements inside the block (balls or rollers) that reduce friction.
A rail or linear guide along which the carriage moves.
Carriage bearings provide smooth, precise, and repeatable motion, improving efficiency and reducing wear in machinery. They differ from plain bushings in that they use recirculating rolling elements, allowing higher speeds, greater load capacity, and better durability.
Structure of a Carriage Bearing
A standard carriage bearing system has three primary components:
Rail (Linear Guide Track)
A precision-machined rail made of hardened steel, stainless steel, or aluminum.
Provides a straight and stable path for the carriage.
Can bear radial, axial, and moment loads depending on design.
Carriage Block (Bearing Carriage/Slider)
Moves along the rail and carries the load.
Contains recirculating rolling elements such as balls or rollers.
Ensures stability, rigidity, and precision.
Rolling Elements (Balls or Rollers)
Reduce friction by rolling rather than sliding.
Circulate within the carriage block, distributing load evenly.
Provide smooth, accurate, and low-resistance motion.
Additional features may include end caps, seals, lubrication ports, and wipers to prevent contamination and maintain optimal performance.
Working Principle of Carriage Bearings
Carriage bearings operate on the principle of rolling friction:
The carriage moves along the rail with rolling elements facilitating motion.
Balls or rollers recirculate inside the carriage, reducing friction and distributing the load evenly.
The system provides high-precision linear motion with minimal wear.
Carriage bearings handle dynamic and static loads, including radial, axial, and moment forces.
This design allows machinery to achieve high-speed, high-accuracy, and stable motion, making carriage bearings ideal for CNC machines, automation systems, and precision equipment.
Types of Carriage Bearings
Carriage bearings come in different designs to suit various applications:
1. Ball-Type Carriage Bearings
Uses recirculating ball bearings.
Provides high precision and smooth motion.
Common in CNC machines, 3D printers, and light to medium automation equipment.
2. Roller-Type Carriage Bearings
Uses cylindrical rollers instead of balls.
Can carry heavier loads and offers higher rigidity.
Ideal for industrial presses and heavy-duty machinery.
3. Profile Rail Carriage Bearings
Features a compact carriage block with recirculating rolling elements.
Supports multi-directional loads and provides high rigidity.
Widely used in industrial robotics, CNC machining, and automated assembly systems.
4. Miniature Carriage Bearings
Designed for compact machinery and light loads.
Common in medical devices, laboratory automation, and precision electronics.
5. Aluminum Carriage Bearings
Lightweight, corrosion-resistant, often anodized for surface durability.
Ideal for 3D printers, robots, and applications where weight is critical.
Advantages of Carriage Bearings
Carriage bearings offer several key advantages over traditional sliding or bushing systems:
High Precision – Maintains accurate and repeatable linear motion.
Low Friction – Rolling elements reduce energy loss and wear.
High Load Capacity – Supports significant radial, axial, and moment loads.
Smooth Operation – Quiet, vibration-free movement.
Durability – Resistant to wear and deformation under repeated use.
Versatility – Suitable for CNC machines, robotics, 3D printers, packaging equipment, and medical devices.
Easy Installation & Maintenance – Modular designs, pre-drilled rails, and lubrication ports simplify setup and upkeep.
Applications of Carriage Bearings
Carriage bearings are used wherever smooth, precise linear motion is required:
CNC Machines – Precision cutting, milling, and engraving.
3D Printers – Smooth movement of print heads and platforms.
Industrial Robots – Linear actuators for pick-and-place, welding, and assembly.
Medical Equipment – Lab automation, imaging devices, and diagnostic machinery.
Packaging Machinery – Motion guidance for filling, labeling, and sorting.
Semiconductor Manufacturing – High-precision stages for wafer handling.
Automated Assembly Lines – Accurate motion for material handling and assembly operations.
Materials Used in Carriage Bearings
The choice of materials affects load capacity, durability, and environmental resistance:
Hardened Steel – High strength and rigidity, suitable for heavy-duty machinery.
Stainless Steel – Corrosion-resistant, ideal for medical, food, and chemical applications.
Aluminum Alloy – Lightweight and corrosion-resistant, used in robots, 3D printers, and portable equipment.
Composite or Coated Materials – Reduce friction and wear in specialized environments.
How to Choose the Right Carriage Bearing
Selecting the correct carriage bearing involves considering several factors:
Load Capacity – Ensure the bearing supports static and dynamic loads including moments.
Precision Requirements – High-precision applications require tighter tolerances.
Travel Distance – Choose rails and carriages that meet the required motion range.
Environment – Sealed or stainless-steel bearings are necessary for dusty, humid, or corrosive conditions.
Speed & Acceleration – Ensure the system can handle desired operational speeds without vibration.
Maintenance Needs – Look for self-lubricating or easy-to-lubricate designs.
Space Constraints – Miniature or compact carriages may be required in tight installations.
Installation and Maintenance Guidelines
Proper installation and maintenance are critical for performance and longevity:
Alignment – Rails must be mounted on flat, rigid surfaces with precise alignment.
Lubrication – Rolling elements require periodic lubrication to reduce wear.
Cleaning – Remove dust, debris, and contaminants from rails and carriages.
Inspection – Regularly check for wear, looseness, or damage.
Replacement – Replace worn or damaged carriages or rails promptly.
Following these practices ensures smooth motion, high precision, and long service life.
Future Trends in Carriage Bearings
Carriage bearing technology is evolving with innovations in materials, design, and smart features:
Smart Carriage Bearings – Sensors for position, load, and temperature monitoring.
Low-Friction Coatings – Reduce wear and energy consumption.
Compact and Lightweight Designs – Aluminum and composite carriages for weight-sensitive applications.
IoT-Integrated Systems – Real-time monitoring for predictive maintenance in smart factories.
Hybrid Materials – Combining aluminum and steel for lightweight yet strong carriage systems.
These innovations improve precision, durability, and automation efficiency.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is a carriage bearing?
A carriage bearing is a linear motion system consisting of a carriage block and a rail, enabling smooth, precise, and low-friction motion along a straight path.
2. How does a carriage bearing differ from a plain bushing?
Carriage bearings use recirculating rolling elements for low friction, high load capacity, and accuracy, while plain bushings rely on sliding friction, which wears faster and is less precise.
3. What types of carriage bearings are available?
Types include ball-type, roller-type, profile rail, miniature, round shaft, and aluminum carriage bearings.
4. Where are carriage bearings commonly used?
They are used in CNC machines, 3D printers, industrial robots, packaging equipment, medical devices, and semiconductor manufacturing.
5. Can carriage bearings support heavy loads?
Yes, particularly roller-type and steel profile rail carriages, which are designed for high radial, axial, and moment loads.
6. Do carriage bearings require maintenance?
Yes. Regular lubrication, cleaning, and inspection are essential for smooth operation and longevity.
7. What materials are used for carriage bearings?
Hardened steel, stainless steel, aluminum alloy, and composites are used depending on load, precision, and environmental requirements.
Conclusion
A carriage bearing is a vital component in modern machinery and automation systems, enabling accurate, smooth, and low-friction linear motion.
By supporting loads, reducing wear, and providing precise motion, carriage bearings improve efficiency, durability, and accuracy across industries such as CNC machining, robotics, 3D printing, packaging, medical devices, and semiconductor manufacturing.
Proper selection, installation, and maintenance are critical for optimal performance. With continuous advancements in materials and smart technologies, carriage bearings will remain essential for precision engineering and industrial automation.