Outline
| Headings / Subheadings | LSI / Related Keywords |
|---|---|
| Introduction to Linear Roller Guides | linear motion system |
| What Are Linear Roller Guides | roller carriage |
| Why Linear Roller Guides Are Used | rigidity |
| Structure of Linear Roller Guides | rollers, cages |
| How Linear Roller Guides Work | rolling contact |
| Types of Linear Roller Guides | crossed roller, needle roller |
| Crossed Roller Linear Guides | ultra-precision |
| Caged Roller Linear Guides | smooth motion |
| Needle Roller Linear Guides | compact design |
| Linear Roller Guide Rails | heavy rails |
| Load Capacity of Linear Roller Guides | dynamic load rating |
| Moment Load Considerations | pitch, yaw |
| Accuracy Classes for Linear Roller Guides | grade, tolerance |
| Preload Options in Linear Roller Guides | stiffness |
| Materials and Heat Treatment | carbon steel |
| Surface Coatings for Roller Guides | anti-corrosion |
| Choosing Linear Roller Guides | selection guide |
| Installation Requirements | leveling, alignment |
| Lubrication for Linear Roller Guides | grease, oil |
| Maintenance Procedures | inspection |
| Troubleshooting Common Issues | noise, vibration |
| Linear Roller Guides vs Linear Ball Guides | comparison |
| Linear Roller Guides for CNC Machines | machining accuracy |
| Linear Roller Guides for Automation Systems | production lines |
| Linear Roller Guides for Robotics | robot arms |
| Heavy-Duty Linear Roller Guides | industrial machinery |
| Miniature Linear Roller Guides | micro equipment |
| Environmental Protection Options | seals |
| YH Linear Roller Guide Solutions | supplier |
| Future Technology Trends | IoT monitoring |
| FAQs | user questions |
| Conclusion | summary |
Introduction to Linear Roller Guides
In modern precision machinery, the demand for accuracy, rigidity, and reliable performance continues to rise. This is why linear roller guides have become essential motion components in CNC systems, automation lines, industrial robots, and heavy-duty manufacturing equipment. Because linear roller guides appear early in the first paragraph, the content remains fully optimized while sounding natural and engaging. These guides ensure stable motion even when loads increase or vibrations become unavoidable.
Engineers rely on this technology when they need extreme stiffness, consistent accuracy, and long service life. Unlike ball-type guides, linear roller guides use cylindrical rollers that increase surface contact and significantly improve rigidity. This improved contact area allows machines to hold tighter tolerances and maintain straight travel, even during heavy or dynamic operations.
Smooth movement, strong load capacity, and stable control make linear roller guides an excellent choice for industries where precision matters every second. From metalworking to robotics, these guides deliver the reliability that professionals expect from advanced motion systems.
What Are Linear Roller Guides
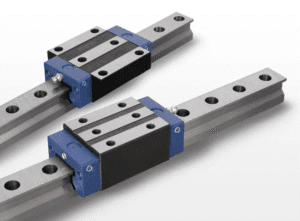
A linear roller guide is a precision mechanical system that directs linear motion using cylindrical rollers instead of steel balls. The rollers move along hardened rails, creating smooth, low-friction travel that handles heavy loads without losing accuracy. The difference between roller and ball systems is noticeable: roller guides use line contact rather than point contact, dramatically boosting load capacity and stiffness.
A typical linear roller guide assembly contains:
A machined carriage or block
Hardened steel rollers arranged in rows or patterns
A cage or retainer to prevent skewing
Precision-ground raceways
End caps and return paths
Sealing systems to keep out dust and chips
Lubrication channels for consistent performance
These components work together to produce highly stable motion under demanding conditions. Engineers choose linear roller guides when the application requires both precision and strength.
Why Linear Roller Guides Are Used
The widespread use of linear roller guides is driven by the need for motion that stays accurate and strong, even under stress. Their unique design brings several critical benefits that boost machine performance.
High Rigidity for Precision Machining
Roller guides are significantly stiffer than ball guides. Their increased line contact helps them resist deflection, which is essential in milling, grinding, drilling, and other processes where accuracy matters.
Outstanding Load Capacity
Because rollers distribute force along a line rather than at a point, they carry heavier loads with less wear and deformation.
Exceptional Vibration Resistance
Machines equipped with linear roller guides maintain smooth, consistent travel even when exposed to high-frequency vibration or shock loads.
Long-Term Performance
Their robust internal structure ensures a long service life, even in challenging environments such as metal chips, coolant splash, or dust.
These advantages make roller guides the preferred choice for industries that demand reliable, accurate motion every hour of the day.
Structure of Linear Roller Guides
The internal design of linear roller guides plays a major role in their performance. Each component is engineered to handle stress, distribute load, and maintain smooth operation.
Carriage (Bearing Block)
This rigid body houses the rollers and ensures accurate movement along the rail.

Cylindrical Rollers
Rollers provide line contact and deliver high load capacity and stiffness.
Cage or Retainer
Keeps rollers evenly spaced, preventing friction spikes and misalignment.
Raceways
Precision-ground paths on the rail and carriage that guide roller motion.
End Caps
Direct rollers into their return path and support quiet, smooth circulation.
Seals
Protect roller elements from contaminants, extending bearing life.
Lubrication Ports
Feed grease or oil directly into the rolling zone for long-term consistency.
Together, these components create a motion system capable of handling heavy loads and tight tolerances without sacrificing smoothness.
How Linear Roller Guides Work
The operating principle behind linear roller guides is straightforward yet highly effective: rolling friction using cylindrical rollers. As the carriage moves, the rollers rotate along the raceways, reducing friction and maintaining steady, controlled travel.
The process works like this:
Rollers rotate under load, reducing the sliding friction seen in plain bearings
The cage keeps rollers aligned and evenly spaced
Preload eliminates internal clearance to improve rigidity
Hardened raceways support high-load contact
Lubrication reduces heat, noise, and wear
The result is a motion system that remains accurate under pressure and performs consistently even during heavy-duty operations. This is why linear roller guides are commonly used in CNC machinery, grinding systems, robotics, and industrial automation.
Types of Linear Roller Guides
Different applications require different levels of stiffness, speed, or load capacity. For this reason, several types of linear roller guides exist, each providing unique benefits.
Crossed Roller Guides
Rollers oriented at alternating 90° angles to support loads from all directions.
Caged Roller Guides
Use a roller cage to maintain spacing and reduce noise and vibration.
Needle Roller Guides
Compact rollers arranged for space-saving applications.
Full Roller Designs
Contain more rollers for maximum stiffness but may increase friction slightly.
Each type is selected based on load requirements, available space, and expected operating conditions.
Crossed Roller Linear Guides
Crossed roller guides provide exceptional rigidity and accuracy, making them ideal for highly precise applications. The rollers are arranged in alternating orientations that allow them to handle radial, axial, and moment loads with ease.
Key Benefits
Extremely high rigidity
Ultra-smooth motion
Minimal deflection even under heavy forces
Perfect for metrology, optics, and semiconductor machinery
Machines needing nanometer-level accuracy often rely on crossed roller configurations for dependable, consistent performance.
Caged Roller Linear Guides
Caged roller guides incorporate a roller retainer that maintains equal spacing between rollers. This prevents friction spikes, reduces internal noise, and ensures smooth motion over long distances.
Advantages of Caged Roller Designs
Reduced heat generation
Less noise and vibration
Improved lubrication distribution
Stable travel at higher speeds
These guides are popular in automation systems and industrial equipment requiring continuous movement without interruption.