Introduction
If you’re dealing with machinery or automated systems, you’ve likely come across the term linear ball bearings. These components are critical for enabling smooth, precise motion along a straight path. In this article, we’ll dive deeply into the world of linear ball bearings, exploring what they are, how they work, their benefits and drawbacks, how to choose the right one, maintenance tips, common applications, and emerging trends. Right from the first paragraph you’ll see the term linear ball bearings and get a clear sense of their importance.
Let’s begin by defining what a linear ball bearing is, how it differs from other motion components, and why engineers and designers rely on them. Then we’ll move through selection criteria, installation, environment compatibility, lifecycle considerations, and future developments.
Linear Ball Bearings

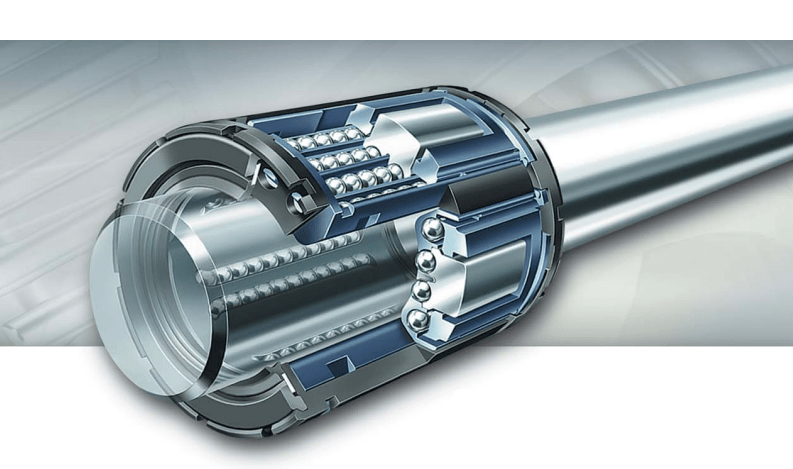
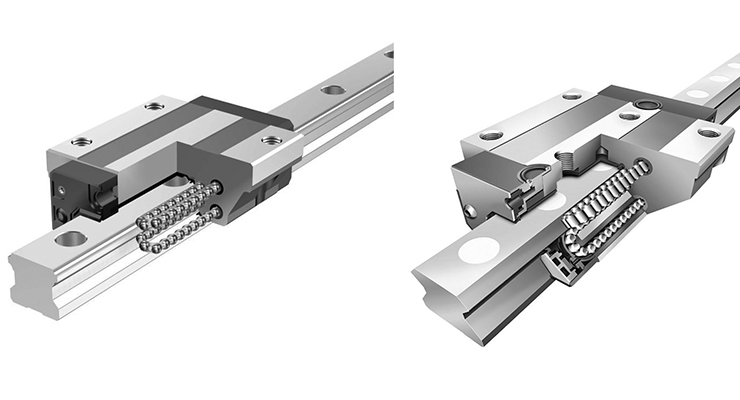
When we talk about linear ball bearings, we mean bearings designed for linear (straight-line) motion rather than rotational motion around an axis. They typically consist of balls (rolling elements) housed in a cage or retainer, guided by raceways inside an outer shell, and mounted to a precision shaft so the bearing can slide back and forth. With proper design, the balls recirculate (in some types) allowing essentially infinite stroke length along the shaft. Ewellix媒体库+2维基百科+2
For example, one manufacturer states that a linear ball bearing consists of a polymer cage with steel raceway plates guiding the ball sets, available sealed or open, self-aligning or rigid, with shaft diameter ranges from ~3 mm to 80 mm. Ewellix
Using linear ball bearings instead of plain bearings (sliding bearings) offers many advantages: lower friction, higher precision, smoother motion, better repeatability. According to PBC Linear: “Linear Ball Bearings are great for linear motion applications where high speed and precision are essential.” PBC Linear+1
However—there are caveats too (we’ll cover them later). For now, understanding that linear ball bearings are engineered for precision linear movement along shafts is key.
How Linear Ball Bearings Work
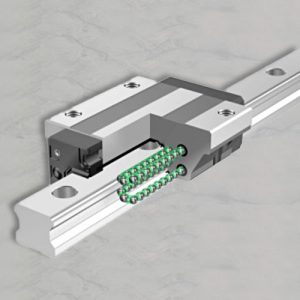
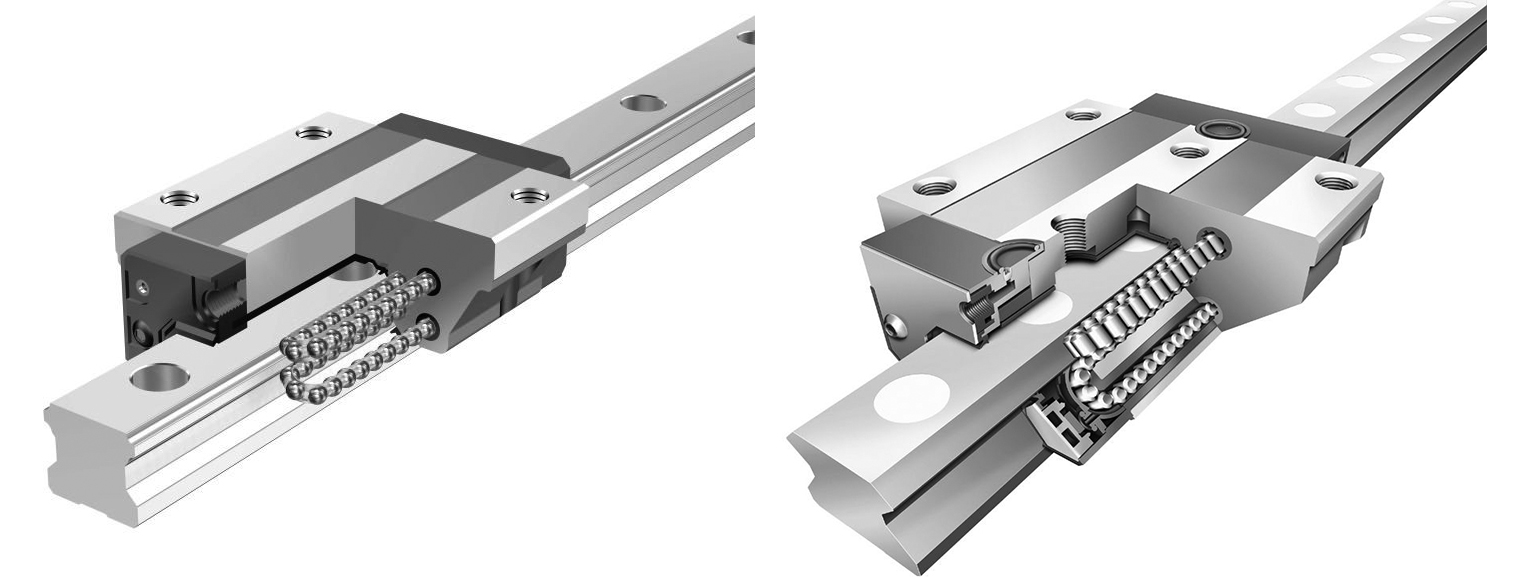
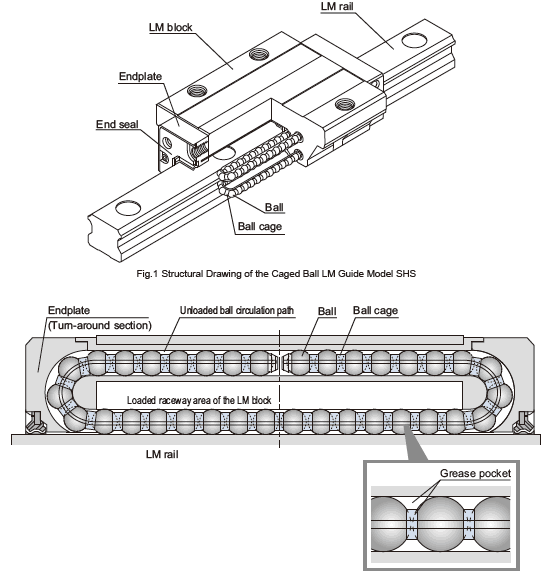
Let’s walk through the mechanism of linear ball bearings. At a high level, the bearing housing contains a row (or multiple rows) of hardened steel balls. These balls rest between an inner shaft (the guide shaft) and an outer shell or raceway plate. As the bearing moves linearly along the shaft, the balls roll (minimizing friction), and in many designs they recirculate—i.e., they return inside the housing so the stroke can keep going indefinitely. Ewellix媒体库+1
Key components include:
A hardened and ground shaft: the surface the balls roll on.
An outer shell or housing: guides the motion and holds the ball cage.
A ball retainer or cage: keeps balls properly spaced and circulating.
Raceway plates or grooves: hardened tracks for the balls.
Seals or shields: to keep lubricant in and contamination out. For example: double-lip seals. Ewellix媒体库+1
The movement is smooth because only the rolling elements and minimal contact friction are involved. As described: “During motion, only the friction between the steel balls must be considered, therefore nearly frictionless linear motion is possible.” Ewellix媒体库
I once used a linear ball bearing system on a small CNC setup where the difference between a plain bushing and a ball bearing slide was dramatic: you could push the axis with a fingertip and it would glide effortlessly. The trick is matching the bearing to the shaft, mounting properly, and using good lubrication (or sealed units).
Benefits of Using Linear Ball Bearings



There are many compelling advantages when you deploy linear ball bearings in suitable applications:
Low friction: Because balls roll instead of sliding, the friction coefficient is much lower. This means less energy required, smoother motion, and less heat. tsklmb.com+1
High precision and repeatability: With well-matched shafts and bearings, motion is smooth and predictable—key for CNC machines, robotics, precision automation. PBC Linear
High speed capability: Some linear ball bearings support high speeds (for example up to ~5 m/s for certain models). Ewellix
Interchangeability and standard sizing: Many linear ball bearings adhere to ISO sizes so shafts, housings, blocks can be standardized. Ewellix
Support of long strokes: Because recirculating ball bearings allow indefinite motion (limited only by shaft length) they work well in long travel applications. Ewellix媒体库
Good for moment and radial loads: Depending on design, some linear ball bearings are optimized for moment loads (e.g., supporting cantilevered setups). PBC Linear
From my experience in automation projects, switching from plain bushes to linear ball bearings not only improved smoothness and accuracy, but also reduced maintenance intervals and improved overall machine uptime.
Limitations and Drawbacks



No technology is perfect, and linear ball bearings do have downsides to consider:
Sensitivity to contamination and misalignment: Rolling elements and precision surfaces require cleanliness. Dirt, chips, or misaligned shafts can lead to premature wear or failure. For instance, one user warned “When installing or replacing linear bearings… do NOT spin them around the axel … These bearings are only designed to go back and forth on the rod.” Reddit
Cost: High-precision linear ball bearings and matched shafts/housings can cost more than simple plain bushings.
Maintenance and lubrication: While some sealed units reduce maintenance, you still often need good lubrication and shaft cleanliness.
Load capacity limits: For extremely heavy loads or shock/vibration environments, plain bearings or roller-type linear guides may be more suitable. Plain bearings may sometimes handle shock loads better.
Installation demands: Shaft straightness, mounting precision, and housing rigidity all become more important. A misaligned shaft can cause binding or uneven wear. Reddit users report issues:
“The balls came out … cheap Chinese linear ball bearings are usually random quality… you’ll struggle to get them all in, you also do want all your bearings even 1 or 2 missing can cause a noticeable bump in the motion.” Reddit+1
Thus, you must weigh the benefits against these limitations and ensure proper installation, environment, and maintenance protocols.
Types and Variants of Linear Ball Bearings



There is quite a range of types of linear ball bearings. Understanding these will help you choose appropriately.
Self-aligning linear ball bearings
These can accommodate slight misalignment between the shaft and housing. For example, one manufacturer offers self-aligning linear ball bearings with twice the load rating or eight times life compared to standard, and they compensate for up to ~1° misalignment. norelem+1
Compact vs. standard series
Manufacturers often segment into compact (ISO series 1) and standard (ISO series 3). For example, one company offers a “Compact linear ball bearing (ISO series 1) available from 3 to 50 mm” and “Standard linear ball bearing (ISO series 3) available from 12 to 80 mm”. Ewellix
Closed vs. open design
Closed linear ball bearings have the full housing and are used for shorter strokes. Open designs allow supported shafts and longer travel. For example: “The closed linear bearing and unit design is more economic and easier to install. For longer shaft length or higher load, the open design ball bearing with supported shafts is a better solution.” Ewellix媒体库
Flange mount, pillow blocks, inserts
Some linear ball bearings come integrated into flange mounts or pillow block units for easy mounting. For example, PBC Linear lists “Linear Ball Bearing Flange Mounts … available in inner diameters from 8 mm to 50 mm … static load capacities up to 15,900 N”. PBC Linear+1
When selecting, you must check whether you need self-alignment, compact size, open vs closed, preload or adjustable clearance, etc.
Key Specifications to Consider
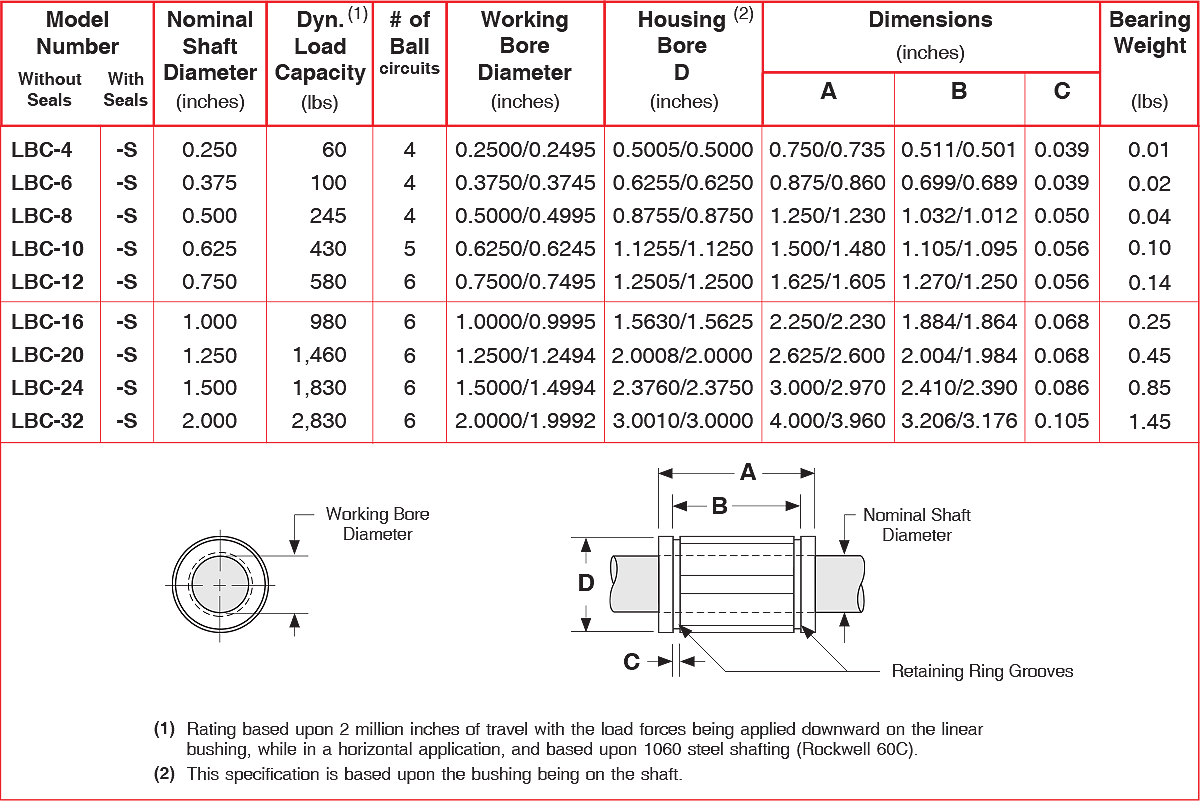
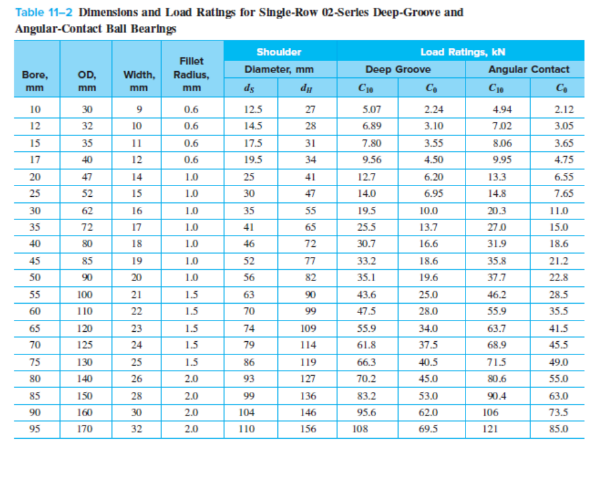

When specifying linear ball bearings for a design, focus on the following parameters:
Shaft diameter: The inner bore must match the shaft size (e.g., 5 mm–80 mm as typical for some ranges). Ewellix
Dynamic load rating (C): The load that the bearing can carry under specified operating conditions while achieving a rated life. e.g., up to ~37,500 N for some heavy-duty models. Ewellix
Static load rating (Co): The maximum load the bearing can withstand without permanent deformation when static. For example up to ~32,000 N in one range. Ewellix
Speed rating: Some linear ball bearings are rated for speeds up to ~5 m/s. Ewellix
Operating temperature: Many ratings specify −20 °C to +80 °C, or –4 °F to +176 °F (~–20 °C to +80 °C) for certain models. PBC Linear
Seals/shields: Whether the bearing is sealed, shielded, or open influences contamination resistance and maintenance.
Series and standard: ISO series 1 vs series 3, or other manufacturer typologies.
Clearance or preload: Some bearings are adjustable to remove play or set preload for rigidity.
Misalignment allowance: For instances where shaft/housing alignment cannot be exact, self-aligning variants allow some deviation.
Material and finish: Material of outer ring, shaft hardness, ball steel, cage material, corrosion resistance.
Environment & stroke length: If your shaft is long and unsupported, you may prefer open design with supported shafts.
Here’s a quick comparison table to help:
| Spec | Why it matters | Typical range/notes |
|---|---|---|
| Shaft diameter | Must match your guide shaft | 3 mm to ~80 mm commonly |
| Dynamic load rating (C) | Determines expected life under motion | Up to ~37 500 N in some heavy types |
| Static load rating (Co) | Maximum cushion for static loads | Up to ~32 000 N in one range |
| Speed rating | For high-travel/high-speed applications | Up to ~5 m/s |
| Temperature range | Ensures material performance in environment | –20 °C to +80 °C |
| Seals/shields | For contamination control, lubrication retention | double-lip seals, shields |
| Series/Standard | Ensures compatibility and interchangeability | ISO Series 1 vs Series 3 |
| Clearance/preload | Affects rigidity and play | Adjustable types available |
| Misalignment allowance | For applications where alignment is imperfect | Some allow ~1° self-alignment |
| Material/finish | Influences wear, corrosion resistance | Hardened steel shaft, surface finish |
In my own design work, I found that specifying a linear ball bearing with minimal clearance improved the stiffness of the motion axis and reduced micro-vibration. It cost a bit more, but the performance gain paid off.
Selection Guide: How to Choose the Right Linear Ball Bearing


Selecting the right linear ball bearing for your application means matching the bearing’s capabilities to your operational demands. Here are steps and tips:
Define the application requirements:
Travel distance (stroke length)
Speed/acceleration
Loads: radial, axial, moments (bending)
Environment: temperature, contamination (dust, chips)
Shaft support: will the shaft be supported or cantilevered?
Alignment precision: Can you guarantee perfect alignment or do you need self-aligning bearings?
Calculate load conditions:
Estimate radial load on bearings (including static and dynamic).
Check moments or cantilever loads; if the carriage or load causes bending moment, select bearings rated for those conditions. Some product literature (e.g., from PBC Linear) gives moment ratings. PBC Linear
Include safety margins.
Select shaft and housing system:
Good guide shafts are hardened and ground; bearing performance is dependent on shaft quality. norelem
Decide housing type: closed or open design. Long strokes usually use open design with supported shafts. Ewellix媒体库
Consider mounting blocks, pillow blocks, or flange mounts for ease of integration.
Choose bearing type and size:
Decide on shaft diameter based on load and stiffness requirements.
Select bearing series (compact vs standard) based on space and load needs.
Choose bearing variants: self-aligning if misalignment is likely; sealed if environment is dirty.
Verify speed and temperature ratings.
Check service and maintenance requirements:
If environment is clean and sealed bearings are possible, maintenance may be minimal.
If dirty or heavy loads, consider open bearings with lubrication plan.
Alignment and installation considerations:
Alignment of shafts is critical: any bending or misalignment will shorten bearing life or cause binding.
Some self-aligning bearings tolerate misalignment (~1°) but even those require care. THN
Ensure mounting surfaces are rigid and shafts are supported properly.
Evaluate lifecycle and cost:
Review expected life based on load rating and usage.
Consider cost of higher-precision bearings vs benefits in performance and maintenance savings.
Make note of compatibility and interchangeability:
If you plan to interchange bearings across designs, ensure standard sizing and ease of sourcing.
By systematically walking through these steps, you’ll arrive at a bearing specification that meets the demands of your design rather than simply picking the “cheapest” option.
Installation, Alignment & Maintenance Tips

Proper installation and maintenance are often what separate a bearing that runs for years vs one that fails early. Here are best practices and first-hand lessons:
Installation
Clean the shaft thoroughly: any burrs, weld spatter, or scratches will degrade bearing performance.
Check shaft straightness and support. For long travel or unsupported shafts, consider intermediate supports.
Press-fit or mount bearings according to manufacturer instructions. Avoid forcing or hammering.
Align housings carefully: parallelism and even tightness of mounting bolts matter.
For bearings with seals or shields, ensure they’re oriented correctly and any protective covers are removed before operation.
Apply lubrication (if required) before first use, unless the bearing is factory pre-lubricated and sealed. For example: bearings with double-lip seals must be greased prior to installation. norelem
Alignment
Use dial indicators or alignment tools to check that shafts are in alignment and housings are mounted to tolerances.
Misaligned shafts cause uneven ball loading, leading to noise, wear, or failure. One Reddit user observed binding when the shaft was not true. Reddit
For self-aligning bearings, you may permit slight misalignment but still aim for best possible alignment.
Maintenance
Inspect periodically for noise, vibration, or wear.
Keep shafts clean and free of chips, dust, or debris. Contaminants are the enemy of precision bearings.
Ensure seals are intact and lubricant is fresh. Some sealed bearings claim “factory pre-lubricated and ready to use.” Ewellix
If operating in harsh environment (dust, metal shavings, coolant splash), consider open or shielded designs and more frequent inspection.
Replace bearings if you detect pitting, ridges, or binding motion—since linear bearings tend not to handle heavy contamination or damage gracefully. For example:
“In my case… I have given up on the polymer bearings… Too much friction.” Reddit
Practical tip from experience
In one project, after a few thousand hours, bearings developed slight “grit” feeling due to metal chips in the environment. We retrofitted additional wipers/seals and switched to replaceable bearing blocks for easier servicing—this saved downtime.
Applications of Linear Ball Bearings


Linear ball bearings find use across many industries and applications:
CNC & Precision Machining: The smooth, precise motion is ideal for axes in milling machines, routers, laser cutters.
Automation & Robotics: Linear axes, pick-and-place machines, actuators rely on low-friction, accurate bearing motion. For example, PBC Linear notes robotics systems as a key application. PBC Linear
Packaging & Assembly Machinery: Where parts must move linearly, often at high speed, bearings support reliability. PBC Linear
Medical Devices: In imaging, positioning tables or automated handling systems, precision linear guides including linear ball bearings are used. Ewellix
Heavy-duty motion systems: Though larger plain bearings or roller guides may dominate, linear ball bearings are used when load and speed permit, especially with supported shafts.
3D Printing & DIY CNC: Many hobby machines use linear ball bearing slides (e.g., LM8UU style) though quality varies. Reddit communities point out issues when improper installation or low‐quality parts are used. Reddit+1
In each case, the design requirements (load, travel, speed, environment) determine whether linear ball bearings are the right choice.
Linear Ball Bearings vs Alternatives: Plain Bearings, Linear Rails
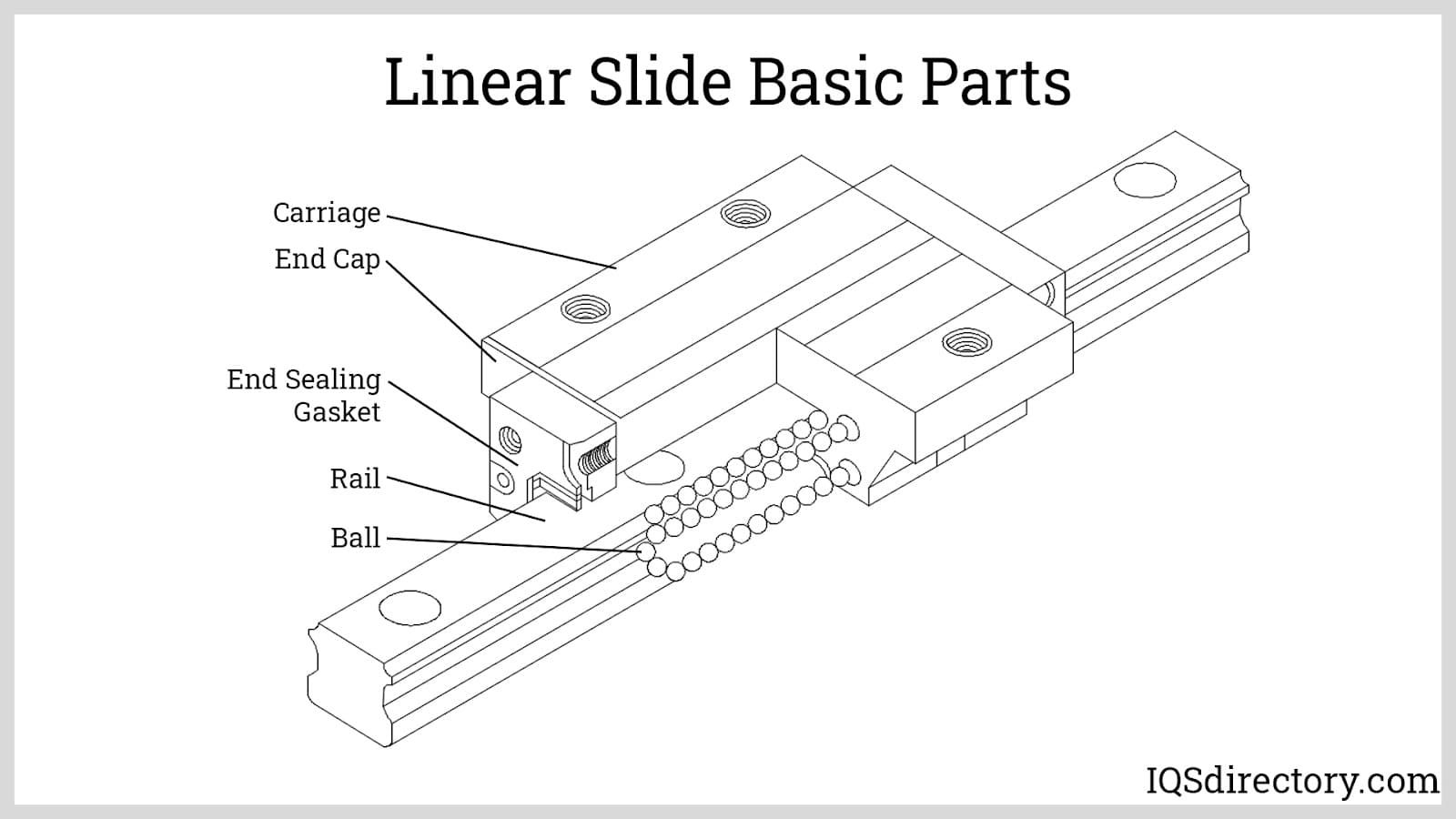

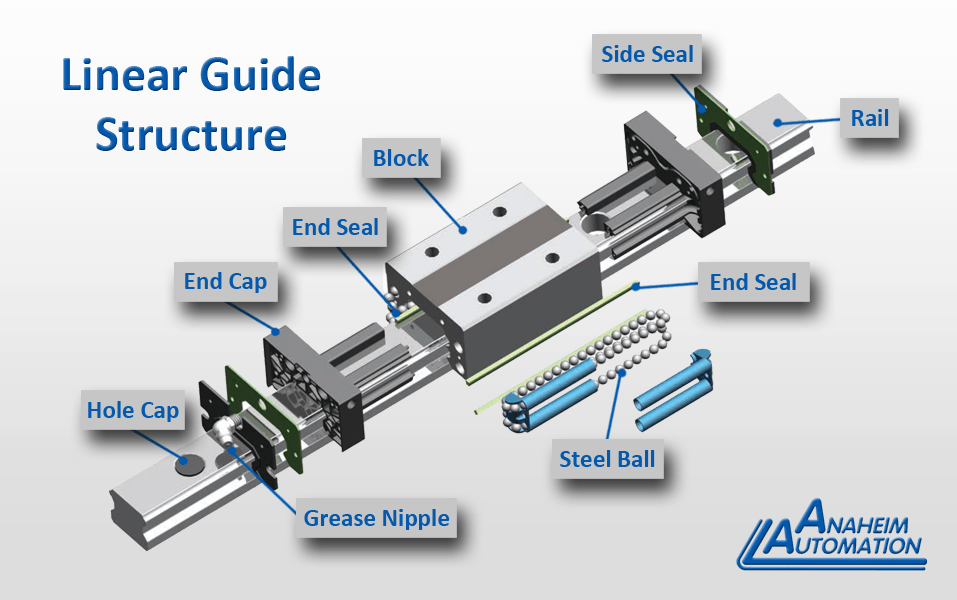
It’s important to compare linear ball bearings with other linear motion solutions so you can choose wisely.
| Feature | Linear Ball Bearings | Linear Plain Bearings | Linear Profile Rails (Block & Rail) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Friction | Low (balls rolling) | Higher (sliding) | Very low (multiple rollers or recirculating balls) |
| Precision | Good to high | Moderate | Very high |
| Load & Moment Capacity | Moderate to high (depends on size) | High for static loads and shock loads | Very high for heavy loads and moments |
| Sensitivity to contamination | High | Lower | Moderate to high (depends on sealing) |
| Speed capability | High | Limited | High |
| Cost | Moderate to high | Lower | Higher (premium) |
| Maintenance | Requires lubrication, cleanliness | May be self-lubricating versions available | Lubrication needed, maintenance intensive for accuracy |
| Installation demands | High precision required | More forgiving | Very high precision required |
For example, plain bearings may be better where shock loads are high and environment is dirty; linear profile rails might be better for highest precision heavy loads; linear ball bearings present a strong compromise when you need relatively high speed, precision, low friction, and cost moderate.
One manufacturer of plain bearings highlights that plain bearings “are suitable for harsh environments… self-lubricating under normal conditions.” Ewellix
Therefore, choose linear ball bearings when your application benefits from low friction, moderate to high load, good speed, and you can maintain the environment reasonably clean and aligned.
Real-World Considerations & Common Mistakes

Here are some real-world lessons and common pitfalls to watch out for:
Neglecting shaft support: If the shaft is long and insufficiently supported, it will bend under load and cause bearing binding. For long strokes or heavy loads, either support the shaft or use open bearing units with supported shafts.
Misalignment of shaft/housing: Even small misalignment can yield uneven ball loading, noise, wear, or failure. Self-aligning bearings can help but aren’t a cure for sloppily built systems.
Contamination ingress: In environments with chips, dust, coolant, metal shavings, linear ball bearings suffer unless sealed and protected. One user noted:
“The cheap chines[e] linear ball bearings are usually random quality. … you’ll struggle to get them all in, you also do want all your bearings even 1 or 2 missing can cause a noticeable bump in the motion.” Reddit
Improper lubrication or using wrong lubricant: Use the lubricant specified by the manufacturer; skipping lubrication or using contaminated lubricant shortens lifespan.
Rotation of the bearing housing rather than linear movement: Some DIY setups spin the bearing instead of letting it slide linearly; this is incorrect.
“When installing or replacing linear bearings… do NOT spin them around the axel like typical ball bearings. These bearings are only designed to go back and forth on the rod…” Reddit
Underestimating the effect of back-lash or thermal expansion: Thermal growth of the shaft or frame can change clearances, alignment, preload—so consider thermal conditions in design.
Buying low-quality bearings: As seen in hobby forums, cheap bearings often lack precision, have missing balls, or poor finish. It may cost more in the long run via downtime and re-work.
By paying attention to these issues—alignment, support, contamination management, lubrication—you’ll tap into the full potential of linear ball bearings rather than fighting avoidable problems.
Innovations and Trends in Linear Ball Bearings


The domain of linear ball bearings is evolving. Here are some trends worth noting:
Energy saving and lightweight cage design: Some manufacturers highlight polymer cage designs that reduce mass and energy consumption during motion. Ewellix
Heavy duty and high moment load variants: There are self-aligning, high-load models designed specifically to handle high loads or long travel distances. THN
Sealed, pre-lubricated, maintenance-reduced versions: More products come ready to install with seals and lubrication, reducing installation and upkeep effort. Ewellix
Materials and coatings: Use of stainless steel, special polymers, advanced coatings to handle corrosion, dirty environments, or higher temperatures. For example: stainless steel versions for shafts. Ewellix媒体库
Smart bearing monitoring: While not yet ubiquitous, integration of sensors (for vibration, temperature) in linear guides is increasing, enabling condition-based maintenance.
Alternative motion systems in harsh environments: For example, lubrication-free polymer guides (e.g., igus’ drylin) are gaining ground when extreme contamination or lack of lubrication is critical. igus.sg
In short: linear ball bearings are not static—they evolve in design, materials, maintenance features and integration into smarter systems.
Here’s a brief commentary on each:
RS PRO Linear Ball Bearing Ø24 mm: A standard precision bearing with 24 mm outer diameter, suitable for moderate loads and motion axes.
RS PRO Linear Ball Bearing Ø28 mm: Slightly larger size—good if you have slightly higher load or want greater stiffness than the Ø24 version.
JUNE LM3UU/LM4UU Linear Ball Bearing: A budget small-size bearing (common in hobby CNC or 3D-printer axes) for light loads and short travel.
Sanon LM8UU Linear Ball Bearing (10 pcs): A bulk kit (10 pieces) of LM8UU (8 mm bore) bearings—commonly used in small machines, DIY setups. Useful when you need multiple units.
INA KB16‑PP Linear Ball Bearing: A premium brand offering (INA) with higher spec—good for demanding applications where durability and brand support matter.
igus dryLin Q Linear Plain (for comparison): Though not a ball bearing (this is a plain bearing), included for contrast and alternative design—especially in environments where a ball bearing might not be the best fit.
The repeat entries of Ø24 and Ø28 show size options and matching your system’s needs.
When choosing a product, always check shaft compatibility (bore size), length of bearing, seal type, load ratings, and make sure your system supports the shaft/housing accordingly.
Maintenance and Troubleshooting Checklist
Here’s a handy checklist you can print and keep near your machine to monitor the health of your linear ball bearings:
| Checkpoint | What to Look For | Frequency |
|---|---|---|
| Shaft cleanliness | No debris, chips, weld spatter, or scratches | Weekly or after heavy use |
| Shaft straightness/support | No visible deflection or sag over length | Monthly |
| Bearing housing / mounting bolts | Tight, even torque, no looseness | Monthly |
| Motion smoothness | No sticking, rough spots, or noise | Every shift or use |
| Lubrication condition | Fresh grease/oil as per spec, seals intact | As per manufacturer or quarterly |
| Visual inspection of seals | Seals not torn, wear rings visible | Quarterly |
| Alignment check | Parallel shafts/housings within spec | Semi-annually |
| Load/moment check | No overload or unexpected loads | Annually |
| Wear signs on bearing | Pitting, scoring, uneven ball wear | If anomalies in motion |
If you detect binding, unusual noise, or degradation in performance, take the machine offline and inspect the bearing and shaft system before continuing. Early intervention often saves major cost later.
FAQs
What is the difference between linear ball bearings and conventional radial ball bearings?
Linear ball bearings are designed for motion along a straight line (translation) rather than rotation about an axis. They contain rolling balls that allow the bearing to slide along a shaft with low friction. Radial ball bearings support rotation of a shaft and typically carry radial and axial loads in rotation, not translation. 维基百科+1
Can I use linear ball bearings in dusty or dirty environments?
Yes—but only if you select the right variant. In dusty or chip-laden environments (e.g., machining, metalworking), you should use sealed or shielded linear ball bearings, ensure shafts are cleaned, and possibly add external wipers or covers. In very harsh conditions, plain bearings or polymer guides may be preferred. Ewellix
How important is shaft support for linear ball bearings?
Very important. If a shaft is unsupported over a long span, it will bend under load, causing misalignment and bearing binding or wear. For long strokes, an open bearing design with supported shafts is often recommended. Ewellix媒体库
What happens if a linear ball bearing is misaligned?
Misalignment causes uneven loads on the balls, increased friction, wear, noise, and shortened life. Self-aligning variants help mitigate small misalignment, but good installation alignment remains essential. norelem
How do I know when to replace a linear ball bearing?
You should replace when you observe any of:
Noticeable increase in motion friction or stick-slip behaviour
Noise like grinding or rattling
Visible pitting or deformation on balls or raceways
Looseness or play that was not designed in
Routine inspection as per maintenance checklist will help you catch these early.
Are linear ball bearings maintenance-free?
Not entirely. While some sealed and pre-lubricated units require less maintenance, you still need to ensure cleanliness, proper lubrication (if serviceable), shaft integrity, and monitor for wear. No bearing is entirely “fit and forget” if precision and long life are expected.
Conclusion
Understanding and leveraging linear ball bearings properly can transform the performance of your machines, automation systems, or precision devices. They provide low-friction, smooth, precise linear motion that many applications demand. Yet, context matters: you must match the bearing to load, speed, environment, and shaft/housing system. When installation, alignment, and maintenance are done right, linear ball bearings deliver exceptional value. When they’re neglected or mis-matched, problems arise quickly.
In short: if you’re designing a system that moves in a straight line and you need precision, good speed, and repeatability, linear ball bearings deserve serious consideration. Pair them with proper shafts, housings, alignment, clean environment, and good maintenance, and you’ll get excellent service life and performance.
Inbound link suggestion (internal):
Link to our “Precision Shaft Design” article for shaft selection best-practices
Link to “Automatic Lubrication Systems for Motion Components” to cover lubrication options
Outbound link suggestion (external):
Link to manufacturer specification sheet for linear ball bearings (e.g., Ewellix catalogue) Ewellix媒体库
Link to educational article on linear-motion bearings from Wikipedia for broader context 维基百科

