Outline for the Article
| Main Headings | Sub-Headings |
|---|---|
| Introduction to Linear Motion Bearing Block | Importance in precision motion |
| What is a Linear Motion Bearing Block | Definition and concept |
| History of Linear Motion Bearing Technology | From early bearings to modern blocks |
| How a Linear Motion Bearing Block Works | Principles of operation |
| Key Components of a Linear Motion Bearing Block | Carriage, housing, rolling elements |
| Types of Linear Motion Bearing Blocks | Ball-type, roller-type, miniature |
| Linear Motion Bearing Block vs Linear Guide Block | Differences explained |
| Advantages of Linear Motion Bearing Blocks | Efficiency, precision, durability |
| Disadvantages of Linear Motion Bearing Blocks | Cost, contamination, maintenance |
| Applications in CNC Machines | Machining and tooling |
| Linear Motion Bearing Block in 3D Printing | Accuracy and stability |
| Industrial Applications | Aerospace, automotive, packaging |
| Robotics and Automation | Role in robotic arms and cobots |
| Material Choices for Bearing Blocks | Steel, stainless steel, aluminum |
| Design Variations of Bearing Blocks | Flange type, compact, heavy-duty |
| Installation of Linear Motion Bearing Blocks | Steps for proper mounting |
| Lubrication and Maintenance | Keeping performance smooth |
| Common Problems with Bearing Blocks | Noise, play, and wear |
| Troubleshooting Linear Motion Bearing Blocks | Preventive and corrective actions |
| Innovations in Bearing Block Technology | Smart bearings, IoT sensors |
| Future of Linear Motion Bearing Blocks | Industry 4.0 and AI integration |
| Cost Factors of Bearing Blocks | Budget vs high-end options |
| Durability and Lifespan | How long they last |
| Top Manufacturers | Leading global brands |
| Linear Motion Bearing Block vs Plain Bearing | Choosing the right one |
| Environmental Considerations | Sustainability in materials |
| Conclusion | Summary and insights |
| FAQs | Commonly asked questions |
Introduction to Linear Motion Bearing Block
Every modern machine that requires precision motion depends on specialized components to move smoothly and accurately. One such component is the linear motion bearing block. Found in CNC machines, robotics, 3D printers, and countless other systems, this device plays a vital role in guiding and supporting linear movement.
Without bearing blocks, friction would wear out machine parts quickly, reducing accuracy and efficiency. With them, industries achieve consistent, reliable, and long-lasting performance.
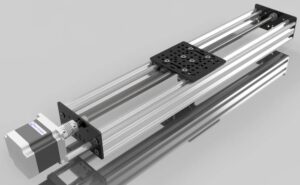
What is a Linear Motion Bearing Block
A linear motion bearing block is a carriage-like structure that slides along a linear rail using rolling elements such as steel balls or rollers. Its purpose is to support loads while enabling friction-reduced, precise linear motion.
Think of it as a train carriage moving smoothly on tracks, but at the micro-precision level required in engineering and automation.
History of Linear Motion Bearing Technology
Early Era: Simple grooves and sliding wood structures.
Industrial Revolution: Introduction of metal-on-metal bearings.
20th Century: Ball bearings revolutionized precision engineering.
Modern Day: Compact bearing blocks integrated with linear rails dominate CNC, robotics, and aerospace industries.
How a Linear Motion Bearing Block Works
The principle is straightforward:
A rail provides the path.
The bearing block carries the load.
Rolling elements inside the block minimize friction.
As the block moves, balls or rollers circulate continuously, enabling smooth travel.
This allows precise positioning, stability, and high load capacity.
Key Components of a Linear Motion Bearing Block
Block Housing: The rigid body that contains all elements
Rolling Elements: Balls or rollers circulating inside
End Caps: Keep rolling elements in circulation
Seals: Prevent dirt and dust contamination
Mounting Holes: For attaching loads or fixtures
Types of Linear Motion Bearing Blocks
Ball Bearing Blocks – Standard type, smooth, cost-efficient
Roller Bearing Blocks – Handle heavier loads, more rigid
Miniature Bearing Blocks – Compact, used in electronics and 3D printers
Flanged Bearing Blocks – Wider mounting surface for stability
Linear Motion Bearing Block vs Linear Guide Block
Linear Motion Bearing Block: Refers specifically to the block itself, carrying loads and moving along the rail.
Linear Guide Block: Refers to the combined system of rail + block.
Advantages of Linear Motion Bearing Blocks
High Precision: Supports micrometer-level accuracy
Durability: Long service life with proper care
Load Capacity: Can handle both radial and axial forces
Smooth Operation: Reduced friction compared to sliding contact
Versatility: Suitable for multiple industries
Disadvantages of Linear Motion Bearing Blocks
Higher Cost than plain bearings
Requires Maintenance (lubrication, cleaning)
Sensitive to Contamination if seals fail
Installation Precision Needed – Misalignment causes wear
Applications in CNC Machines
Bearing blocks are essential in CNC systems for:
Tool movement with precision
Heavy-load machining
Repetitive, high-speed operations
Without them, CNC machines would lose accuracy and efficiency.
Linear Motion Bearing Block in 3D Printing
For 3D printers, bearing blocks ensure:
Accurate print head positioning
Reduced vibration
Smoother layering process
This results in higher-quality prints.
Industrial Applications
Aerospace: Aircraft part assembly and alignment
Automotive: Robotic welding and manufacturing
Packaging: Fast, repetitive linear motion
Medical: Imaging machines, surgical robots
Robotics and Automation
In robotics, bearing blocks are critical for:
Arm extension and retraction
Pick-and-place systems
Cobots (collaborative robots) for factories
Material Choices for Bearing Blocks
Carbon Steel: Durable, cost-effective, rust-prone
Stainless Steel: Corrosion-resistant, ideal for clean environments
Aluminum: Lightweight, used in smaller applications
Composite Materials: Advanced, lightweight applications
Design Variations of Bearing Blocks
Compact Blocks – Space-saving designs
Heavy-Duty Blocks – For large industrial machinery
Flanged Blocks – Easier mounting and wider load distribution
Installation of Linear Motion Bearing Blocks
Steps for installation:
Clean rail and mounting surfaces
Align rails precisely
Slide blocks onto the rail carefully
Tighten screws to manufacturer’s torque settings
Test for smooth motion
Lubrication and Maintenance
Apply grease or oil regularly
Inspect seals and replace if worn
Keep rails clean from dust
Follow manufacturer’s lubrication intervals
Common Problems with Bearing Blocks
Noise – Usually from lack of lubrication
Play or Looseness – Indicates internal wear
Misalignment – Causes uneven movement
Contamination – Dust or debris inside the block
Troubleshooting Linear Motion Bearing Blocks
Add lubrication for smoother motion
Replace damaged seals to prevent contamination
Realign rails if motion feels uneven
Replace blocks if excessive play develops
Innovations in Bearing Block Technology
Self-lubricating materials reduce maintenance
Smart sensors detect wear and load changes
IoT-enabled systems allow predictive maintenance
Lightweight alloys improve efficiency
Future of Linear Motion Bearing Blocks
The future includes:
AI-powered monitoring for predictive servicing
Eco-friendly materials for sustainability
Nanometer-level precision for electronics
Greater automation integration
Cost Factors of Bearing Blocks
Entry-level blocks: $20–$50
Mid-range industrial blocks: $100–$300
High-precision blocks: $500+
Durability and Lifespan
On average, a linear motion bearing block lasts 5–10 years, depending on:
Load
Speed
Maintenance
Environment
Top Manufacturers
THK (Japan)
HIWIN (Taiwan)
NSK (Japan)
Bosch Rexroth (Germany)
SKF (Sweden)
Linear Motion Bearing Block vs Plain Bearing
Bearing Block: High precision, low friction, heavy-duty
Plain Bearing: Low cost, simpler design, less precise
Environmental Considerations
Manufacturers are adopting:
Recyclable materials
Lubrication-free designs
Energy-efficient production
Conclusion
A linear motion bearing block is a vital component in modern engineering, enabling smooth, precise, and durable linear motion across industries. From CNC machining to 3D printing and robotics, it plays an irreplaceable role in achieving efficiency and accuracy.
As technology advances, bearing blocks will become smarter, more durable, and eco-friendly, making them a cornerstone of Industry 4.0.
FAQs
What is a linear motion bearing block used for?
It is used to guide machine parts along a rail with precision, supporting heavy loads and reducing friction.
How long do bearing blocks last?
Typically 5–10 years with proper care.
Do linear motion bearing blocks need lubrication?
Yes, lubrication is essential for smooth, long-lasting performance.
What’s the difference between bearing blocks and plain bearings?
Bearing blocks use rolling elements for precision, while plain bearings slide directly on a surface.
Are they expensive?
Costs range from affordable hobbyist versions to expensive industrial-grade models.
Which industries rely most on bearing blocks?
CNC machining, aerospace, automotive, packaging, and robotics.
Inbound Link Suggestions
Link to “What is a Linear Guide”
Link to “Linear Tracks Explained”
Link to “CNC Machine Components”