Comprehensive Outline
| Core Topic Areas | Supporting Subtopics |
|---|---|
| Linear Rail Slide Overview | Definition, evolution, modern relevance |
| Engineering Principles | Motion mechanics, rolling contact theory |
| Linear Rail Slide Components | Rails, carriages, bearing elements |
| Materials Used | Steel grades, coatings, corrosion resistance |
| Load Handling Capabilities | Static loads, dynamic loads, moment loads |
| Precision and Accuracy | Tolerances, repeatability, alignment |
| Types of Linear Rail Slide | Ball type, roller type, miniature systems |
| Linear Rail Slide vs Rod Systems | Performance and space comparison |
| Installation Fundamentals | Mounting surfaces, fastening practices |
| Alignment Techniques | Parallelism, preload control |
| Lubrication Methods | Grease, oil, automatic systems |
| Maintenance Practices | Wear detection, service intervals |
| Environmental Resistance | Dust, moisture, temperature extremes |
| Noise and Vibration Control | Smooth motion benefits |
| Linear Rail Slide in Automation | CNC, robotics, pick-and-place |
| Use in Medical Equipment | Imaging, diagnostic machinery |
| Semiconductor Applications | Cleanroom compatibility |
| Aerospace and Defense Use | Precision and reliability needs |
| Industrial Manufacturing | Assembly lines, tooling |
| Load Optimization | Selecting the right rail size |
| Safety Considerations | Failure prevention, redundancy |
| Cost vs Performance | Long-term value analysis |
| Common Selection Mistakes | Oversizing, underspecification |
| Future Trends | Smart rails, sensor integration |
| Linear Rail Slide Buying Guide | Vendor evaluation, standards |
Introduction
The linear rail slide is one of those silent engineering heroes that rarely gets attention, yet it powers much of the modern world. From factory automation to medical imaging machines, these systems quietly deliver smooth, precise, and repeatable linear motion. At first glance, it may seem like a simple mechanical guide. However, beneath the surface lies a carefully engineered solution designed to balance load, accuracy, speed, and durability.
In my early exposure to industrial automation, I witnessed how upgrading to a proper linear rail slide transformed unreliable motion into fluid precision. Suddenly, machines ran quieter, faster, and with fewer failures. That experience alone explains why linear rail technology has become the backbone of precision motion systems today.
Linear Rail Slide
A linear rail slide is a mechanical guidance system designed to support and guide moving components along a straight path with minimal friction. Unlike plain slides, which rely on surface contact, linear rail slides use rolling elements such as balls or rollers. This design dramatically improves efficiency and lifespan.
What truly sets a linear rail slide apart is its ability to handle loads from multiple directions simultaneously. Vertical, horizontal, and moment loads are all absorbed without sacrificing accuracy. As a result, designers can build compact machines without compromising strength.
Moreover, linear rail slides provide consistency. Once installed and aligned correctly, motion remains repeatable over millions of cycles. That reliability explains why they are trusted in industries where failure is not an option. Simply put, the linear rail slide is not just a component; it is a foundation for precision engineering.
Engineering Principles Behind Linear Rail Slide Systems
At the heart of every linear rail slide lies a deceptively simple principle: rolling contact instead of sliding contact. By replacing friction-heavy surfaces with precision-ground rails and bearing elements, motion becomes smoother and far more predictable.
Rolling elements circulate within the carriage, redistributing load evenly along the rail. This circulation minimizes localized stress, which in turn reduces wear. Consequently, service life increases significantly compared to traditional slide systems.
Another critical principle is preload. By applying controlled internal tension, manufacturers eliminate play within the system. This enhances rigidity and improves positioning accuracy. Although preload slightly increases friction, the trade-off often proves worthwhile in precision applications.
Thermal stability also plays a role. Quality linear rail slide systems are designed to compensate for expansion and contraction. This ensures consistent performance, even in environments where temperature fluctuates. These engineering fundamentals work together, quietly delivering motion perfection.

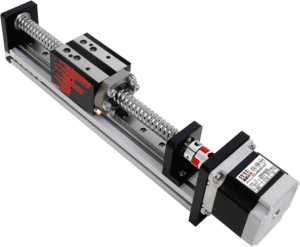
Core Components of a Linear Rail Slide
A linear rail slide typically consists of three essential elements: the rail, the carriage, and the rolling elements. Each component contributes directly to performance and reliability.
The rail serves as the guiding backbone. Manufactured from hardened steel, it features precision-ground raceways that ensure smooth movement. Any imperfection here would translate into vibration or positioning errors.
The carriage houses the rolling elements and distributes load. Its internal geometry is carefully engineered to maintain constant contact with the rail. Meanwhile, the rolling elements, whether balls or rollers, reduce friction and carry the load.
Seals and lubrication ports complete the system. Seals protect against contamination, while lubrication ensures long-term smoothness. Together, these components form a system that balances strength, precision, and longevity with impressive efficiency.
Types of Linear Rail Slide Systems
Not all linear rail slide systems are created equal. The most common types include ball-type and roller-type designs. Each serves a specific purpose.
Ball-type linear rail slides excel in high-speed, low-to-medium load applications. Their point contact design allows fast movement with minimal resistance. This makes them ideal for automation and robotics.
Roller-type systems, on the other hand, use line contact. This increases load capacity and rigidity. As a result, they are preferred in heavy machining and high-precision equipment.
Miniature linear rail slide systems also deserve mention. Designed for compact spaces, they deliver impressive accuracy despite their size. Choosing the right type ensures optimal performance and prevents premature failure.
Installation and Alignment Best Practices
Even the best linear rail slide will underperform if installed incorrectly. Proper mounting surfaces are essential. They must be flat, rigid, and free from distortion.
Alignment follows next. Parallelism between rails ensures even load distribution. Any misalignment introduces stress, increasing wear and reducing accuracy. Therefore, careful measurement during installation pays long-term dividends.
Fastening torque also matters. Over-tightening can distort the rail, while under-tightening compromises stability. Manufacturers provide guidelines for a reason. Following them ensures the system performs exactly as intended.
Applications of Linear Rail Slide Technology
The versatility of the linear rail slide is remarkable. In CNC machines, it enables precise tool positioning. In robotics, it supports smooth, repeatable motion. Medical devices rely on it for accuracy and patient safety.
Semiconductor manufacturing demands ultra-clean, vibration-free motion. Linear rail slides meet these requirements effortlessly. Even aerospace systems depend on them for reliability under extreme conditions.
Across industries, one theme remains constant. Where precision matters, the linear rail slide delivers. Its adaptability ensures continued relevance in an ever-evolving technological landscape.
FAQs
What makes a linear rail slide better than traditional slides?
A linear rail slide offers lower friction, higher accuracy, and longer service life due to rolling contact instead of sliding contact.
How long does a linear rail slide last?
With proper lubrication and alignment, a linear rail slide can operate reliably for millions of cycles.
Can linear rail slide systems handle heavy loads?
Yes, especially roller-type designs, which are engineered for high load capacity and rigidity.
Is lubrication necessary for linear rail slide systems?
Absolutely. Proper lubrication reduces wear, prevents corrosion, and ensures smooth operation.
Are linear rail slide systems expensive?
While initial costs may be higher, their durability and performance often reduce long-term expenses.
How do I choose the right linear rail slide?
Consider load requirements, accuracy needs, environmental conditions, and available space.
Conclusion
The linear rail slide represents the perfect balance between simplicity and sophistication. It transforms mechanical motion into a precise, reliable, and efficient process. From heavy industrial machines to delicate medical equipment, its impact is undeniable.
In a world driven by accuracy and efficiency, investing in the right linear rail slide system is not just wise. It is essential. With proper selection, installation, and maintenance, these systems deliver unmatched performance for years to come.
Suggested Internal Links
Guide to industrial automation components
Precision motion control systems overview
Suggested Outbound Links
International linear motion standards organizations
Manufacturer technical catalogs for linear rail slide systems