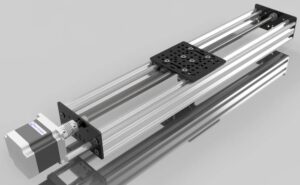
Outline for “Rail with Rollers”
| Main Topic | Subtopics |
|---|---|
| Introduction to Rail with Rollers | Definition, Importance in engineering, Core functions |
| How Rail with Rollers Work | Rolling mechanics, Friction reduction, Load distribution |
| Features of Rail with Rollers | Smooth travel, Load-bearing capacity, Durability |
| Advantages of Using Rail with Rollers | Efficiency, Accuracy, Reduced wear, Cost savings |
| Types of Rail with Rollers | V-guide rails, Flat rails, Curved rail systems, Custom roller rails |
| Materials Used in Rail with Rollers | Steel, Aluminum, Stainless steel, Composite materials |
| Comparing Rails with Rollers vs. Sliding Rails | Friction levels, Maintenance needs, Lifespan differences |
| Industrial Applications | CNC machines, Conveyor systems, Robotics, Packaging lines |
| Rail with Rollers in Robotics | Precision, Repeatability, Load handling |
| Use in CNC and Automation | Cutting accuracy, Stable machining, High-speed applications |
| Role in Transportation and Logistics | Warehouse systems, Automated storage, Material handling |
| Rail with Rollers in Medical Equipment | Imaging devices, Lab automation, Surgical robotics |
| DIY and Small-Scale Uses | 3D printers, Furniture, Home automation |
| Installation and Setup | Alignment, Lubrication, Mounting tips |
| Maintenance and Care | Cleaning, Lubricating, Inspections |
| Troubleshooting Common Problems | Noise, Misalignment, Uneven motion |
| Innovations in Rail with Rollers | Smart monitoring, Self-lubricating rollers, Lightweight designs |
| Buying Guide for Engineers | Load rating, Speed, Material, Environment considerations |
| Environmental Impact | Energy efficiency, Sustainable materials, Recycling |
| Safety Considerations | Overloading risks, Operator training, Preventive checks |
| Future Trends in Rail with Rollers | Miniaturization, IoT integration, Green engineering |
| Rail with Rollers | Importance in precision systems, Versatility, Reliability |
| FAQs | Six detailed FAQs with answers |
| Conclusion | Summary and final thoughts |
| Suggested Internal & External Links | For SEO and authority |
Introduction to Rail with Rollers
A rail with rollers is one of those engineering marvels that seems simple at first glance but plays a massive role in today’s precision-driven world. Unlike sliding rails, which create resistance and wear, rails with rollers allow for smooth, controlled, and efficient motion. They are indispensable in industries where high precision, durability, and low maintenance are critical.
From industrial automation and robotics to medical equipment and DIY projects, the concept is the same: minimize friction, maximize performance. Imagine a production line where parts move seamlessly without jerks or delays — that’s the power of a rail with rollers at work.
How Rail with Rollers Work
The mechanism behind a rail with rollers is straightforward but highly effective.
Rolling Mechanics: Rollers are installed along a track, reducing surface-to-surface contact. Instead of dragging, they roll, cutting friction dramatically.
Friction Reduction: Less friction means less wear and tear, as well as higher energy efficiency.
Load Distribution: Rollers spread weight evenly across the rail, ensuring stable motion even under heavy loads.
This simple principle has transformed entire industries by extending the lifespan of equipment and reducing operational costs.
Features of Rail with Rollers
Rails with rollers come with distinctive features that make them stand out:
Smooth Travel: Rollers glide effortlessly, ensuring vibration-free motion.
High Load-Bearing Capacity: Capable of handling heavy-duty industrial loads.
Durability: Built with materials designed to last in harsh environments.
Versatility: Can be used in both lightweight and heavy machinery.
Low Noise: Reduced friction also means quieter operation, essential in sensitive environments like hospitals.
These features explain why they’ve become a backbone in precision-driven industries.
Advantages of Using Rail with Rollers
The advantages go beyond smooth motion. Some key benefits include:
Efficiency: Less energy wasted on friction translates into higher productivity.
Accuracy: Ensures repeatable precision, vital in CNC machining and robotics.
Reduced Wear: Longer service life with fewer replacements needed.
Cost Savings: Lower maintenance requirements reduce operating expenses.
Flexibility: Works equally well in large-scale automation and small DIY setups.
For businesses, this means fewer breakdowns and higher return on investment.
Types of Rail with Rollers
Not all rails with rollers are the same. Different types serve different needs:
V-Guide Rails: Common in robotics and automation, designed for precise guiding.
Flat Rails: Suitable for heavy loads, often used in transportation systems.
Curved Rail Systems: Perfect for applications requiring circular or arc motion.
Custom Roller Rails: Engineered to meet unique industrial or medical requirements.
Selecting the right type depends on load, speed, and application environment.
Materials Used in Rail with Rollers
Material choice greatly impacts performance:
Steel: Durable, strong, and ideal for high-load industrial applications.
Aluminum: Lightweight and resistant to corrosion, suitable for cleanrooms.
Stainless Steel: Perfect for environments where hygiene is critical, like food processing or healthcare.
Composite Materials: Offer lightweight strength and resistance to chemicals.
Each option balances cost, performance, and environment-specific requirements.
Comparing Rails with Rollers vs. Sliding Rails
It’s worth comparing these systems:
| Feature | Rail with Rollers | Sliding Rail |
|---|---|---|
| Friction | Very low | High |
| Maintenance | Minimal | Frequent |
| Lifespan | Long-lasting | Shorter |
| Noise | Quiet | Noisy |
| Cost | Higher upfront | Lower upfront |
While sliding rails can still be found in basic systems, rails with rollers dominate in performance-focused industries.
Industrial Applications
Rails with rollers are versatile enough to be used in multiple industries:
CNC Machines: For accuracy and repeatability in machining.
Conveyor Systems: Efficient transport in factories and warehouses.
Robotics: Reliable guiding for robotic arms and automation.
Packaging Lines: Smooth operation for high-speed packaging.
Their adaptability makes them indispensable across sectors.
Rail with Rollers in Robotics
Robotics thrives on precision, and rails with rollers make it possible. They provide:
Accurate Positioning: Critical for assembly lines.
Load Handling: Supporting robotic arms carrying heavy components.
Repeatability: Ensuring every movement is consistent over time.
In warehouse automation, for example, rails with rollers ensure that robotic arms handle thousands of cycles daily without errors.
Use in CNC and Automation
CNC systems demand smooth, stable, and precise movement. Rails with rollers deliver just that:
Cutting Accuracy: Eliminates micro-vibrations that can ruin workpieces.
Stable Machining: Handles high speeds without losing control.
Reduced Tool Wear: Because smoother motion reduces machine strain.
They are a key reason why CNC machines can achieve micrometer-level tolerances.
Role in Transportation and Logistics
In warehouses and shipping centers, rails with rollers ensure seamless movement:
Automated Storage Systems: Moving heavy pallets efficiently.
Material Handling: Supporting conveyor systems with precision.
Loading and Unloading: Reducing downtime in logistics operations.
Their ability to carry heavy loads with minimal energy makes them a favorite in logistics.
Rail with Rollers in Medical Equipment
In healthcare, accuracy can be a matter of life and death. Rails with rollers power:
MRI and Imaging Devices: Smooth patient handling systems.
Lab Automation: Precise guiding of samples and equipment.
Surgical Robotics: Quiet, precise motion for delicate procedures.
The low-noise operation is especially valuable in hospital environments.
DIY and Small-Scale Uses
Rails with rollers aren’t just for industries. Makers and hobbyists also benefit:
3D Printers: Consistent movement for quality prints.
Furniture Projects: Sliding doors and drawers with minimal effort.
Home Automation: Automated panels or custom-built systems.
Their affordability and availability make them ideal for DIY innovation.
Installation and Setup
Correct installation ensures longevity:
Alignment: Rails must be parallel to prevent binding.
Lubrication: Essential for reducing wear.
Mounting: Secure with the right fasteners to avoid shifting.
A well-installed system can last for years with minimal issues.
Maintenance and Care
Even though they’re low-maintenance, some care is necessary:
Regular Cleaning: Dust and debris can damage rollers.
Lubrication Schedule: Apply manufacturer-recommended oils or greases.
Inspection: Look for uneven wear or noise as early warning signs.
A proactive approach prevents costly downtime.
Troubleshooting Common Problems
Common challenges include:
Noise: Usually due to contamination or insufficient lubrication.
Misalignment: Leads to uneven wear and reduced efficiency.
Uneven Motion: Often caused by damaged rollers or dirt buildup.
Most issues are easy to fix if caught early.
Innovations in Rail with Rollers
This field is evolving rapidly:
Smart Monitoring: Sensors track performance and predict maintenance needs.
Self-Lubricating Designs: Reduce the need for manual upkeep.
Lightweight Composites: Lower energy use in mobile and robotic systems.
Such innovations ensure that rails with rollers remain relevant in the future of automation.
Buying Guide for Engineers
When selecting a rail with rollers system, consider:
Load Rating: Match the bearing strength with the application.
Speed Requirements: High-speed systems demand specialized rollers.
Environmental Conditions: Dusty or wet environments need corrosion-resistant materials.
Budget: Balance long-term cost savings against initial investment.
Trusted brands like THK, Hiwin, and Bosch Rexroth dominate this sector.
Environmental Impact
Modern designs focus on sustainability:
Energy Efficiency: Lower friction means reduced energy consumption.
Sustainable Materials: Many rails now use recyclable metals and composites.
Longer Lifespan: Fewer replacements reduce industrial waste.
Green engineering is shaping how rails with rollers are manufactured.
Safety Considerations
To ensure safe operation:
Avoid Overloading: Always respect the manufacturer’s load capacity.
Train Operators: Workers must understand proper handling.
Routine Inspections: Catching faults early prevents accidents.
Safety isn’t just a feature — it’s a necessity.
Future Trends in Rail with Rollers
The future looks exciting:
Miniaturization: Smaller systems for micro-robotics and precision instruments.
IoT Integration: Smart rails connected to digital monitoring platforms.
Green Engineering: Eco-friendly materials and production techniques.
These advances will expand their reach into even more industries.
Rail with Rollers
A rail with rollers is far more than a mechanical component. It is the foundation of modern precision systems. From factory floors to hospital labs and DIY workshops, it enables smooth, reliable, and efficient motion. Its versatility, cost-effectiveness, and durability make it an irreplaceable tool in engineering today.
FAQs
What is a rail with rollers used for?
It enables smooth, precise linear motion in machines, conveyors, robotics, and medical devices.
Are rails with rollers better than sliding rails?
Yes. They offer reduced friction, longer lifespan, and higher efficiency.
Do they need lubrication?
Most do, though some modern designs are self-lubricating.
Can they handle heavy loads?
Yes, especially steel and roller-based systems designed for industry.
Are rails with rollers noisy?
No, they are typically quieter than sliding systems.
Can DIY projects use rails with rollers?
Absolutely. They are popular in 3D printing, custom furniture, and home automation.
Conclusion
A rail with rollers may seem like a small part, but its impact is immense. By reducing friction, improving precision, and extending machine life, it has revolutionized industries. Whether in massive logistics centers or small DIY projects, its benefits remain the same: smooth, efficient, and reliable performance.
As technology evolves, rails with rollers will become even smarter, greener, and more versatile, ensuring their role in the future of automation and innovation.
Suggested Links
Internal Links (your site):
Guide to CNC Precision Components
How Robotics Improve Industrial Automation
Maintenance Tips for Linear Motion Systems
External Links (authoritative sources):