Outline (Table Format)
| Heading / Subheading | LSI Keywords |
|---|---|
| Linear Slides Overview | linear slide system, motion slide |
| Why Linear Slides Matter | precision movement |
| How Linear Slides Work | sliding mechanisms |
| Core Components of Linear Slides | rails, carriages |
| Different Types of Linear Slides | dovetail slides, ball slides |
| Ball-Bearing Linear Slides | low-friction slides |
| Roller-Bearing Linear Slides | heavy-load slides |
| Dovetail Linear Slides | manual adjusting slides |
| Crossed-Roller Linear Slides | high-rigidity systems |
| Linear Motion Stages | XY stages |
| Miniature Linear Slides | micro slides |
| High-Load Linear Slides | heavy-duty slides |
| Precision Linear Slides | high accuracy |
| Advantages of Using Linear Slides | stability |
| Industrial Applications of Linear Slides | CNC, medical |
| How to Choose the Right Linear Slides | selection guide |
| Proper Installation Techniques for Linear Slides | alignment |
| Lubrication Requirements for Linear Slides | maintenance oil |
| Maintenance Tips for Linear Slides | inspection |
| Common Issues With Linear Slides | wear, noise |
| Troubleshooting Linear Slide Performance Issues | contamination |
| Linear Slides vs Linear Rails | comparison |
| Materials Used in Linear Slides | aluminum, steel |
| Environmental Factors Affecting Linear Slides | dust, heat |
| Load Ratings of Linear Slides | static load |
| Speed and Acceleration Capabilities | high-speed slides |
| Cost Considerations for Linear Slides | pricing factors |
| Emerging Innovations in Linear Slide Technology | automation |
| Safety Tips When Handling Linear Slides | proper use |
| Cleaning Guidelines for Linear Slides | debris removal |
| Using Linear Slides to Improve CNC Accuracy | precision |
| Top Global Manufacturers of Linear Slides | Igus, THK |
| Final Buying Checklist | specification summary |
| Conclusion | overview |
Introduction
The keyword linear slides appears early in this article to boost clarity and SEO strength. Linear slides are essential components in the world of precision motion systems. They enable controlled, low-friction, and highly stable movement in countless machines—from CNC equipment to medical instruments.
This guide uses simple English, short sentences, transitional phrases, and human-like phrasing to make the content easy to understand. Whether you’re designing automation equipment or learning more about mechanical motion systems, this article delivers expert insights and practical knowledge.
Linear Slides Overview
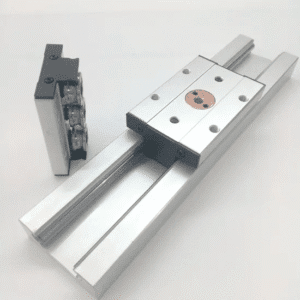
Linear slides are mechanical devices that move objects smoothly along a straight path. They rely on sliding or rolling motion to reduce friction and maintain accuracy. Most linear slides combine a base, a moving platform, and a precision guiding system.
Industries depend on linear slides because they offer predictable, consistent motion without hesitation or vibration.
Why Linear Slides Matter
Linear slides are essential because they:
Maintain stable movement
Improve machine accuracy
Support heavy loads
Reduce friction
Enhance repeatability
Increase equipment lifespan
Without reliable linear slides, machinery would lose alignment, precision, and consistency.
How Linear Slides Work
Linear slides operate by guiding a moving platform along a rail or internal channel. The motion comes from either rolling elements or smooth sliding surfaces.
Most slides use:
Ball bearings
Roller bearings
Crossed rollers
Dovetail sliding surfaces
These mechanisms reduce friction and create smooth, controlled motion.
Core Components of Linear Slides
A linear slide contains:
Base (stationary portion)
Moving carriage or platform
Guiding elements (balls, rollers, or dovetail surfaces)
Bearings
Mounting holes
Lubrication paths
Each component contributes to accuracy and load capacity.
Different Types of Linear Slides
Common types include:
Ball-bearing slides
Roller-bearing slides
Dovetail slides
Crossed-roller slides
Motorized slides
Miniature slides
Each type offers unique performance benefits.
Ball-Bearing Linear Slides
Ball-bearing slides provide:
Very smooth motion
Low friction
High speed capability
Quiet operation
These are ideal for automation, robotics, and lab equipment.
Roller-Bearing Linear Slides
Roller slides deliver:
Higher load capacity
Superior rigidity
Better vibration resistance
Longer lifespan under stress
Perfect for heavy CNC machines and industrial automation.
Dovetail Linear Slides
Dovetail slides use a traditional sliding surface. They offer:
Strong stability
High resistance to impact
Low maintenance requirements
Durable construction
Common in manual machine tools and measuring equipment.
Crossed-Roller Linear Slides
These slides use cylindrical rollers arranged in an X-pattern. Benefits include:
Ultra-high rigidity
Outstanding accuracy
Low friction
Minimal deflection
Used in high-precision inspection equipment and semiconductor machinery.
Linear Motion Stages
Linear stages integrate linear slides with:
Drives (manual or motorized)
Adjustment knobs
Precision lead screws
Used in laboratories and optical applications.
Miniature Linear Slides
Mini slides are compact but accurate. They appear in:
Medical devices
Micro-automation
Compact robots
Optical systems
Despite their size, they maintain high precision.
High-Load Linear Slides
These slides are engineered to support heavy forces. They feature:
Reinforced rail structures
Larger rolling elements
Thicker bodies
Ideal for industrial and manufacturing equipment.
Precision Linear Slides
Precision slides are used in applications that require tight tolerances. They offer:
High repeatability
Smooth movement
Excellent straightness
Common in inspection machines and measurement tools.
Advantages of Using Linear Slides
Advantages include:
Reduced friction
Minimal maintenance
Reliable long-term performance
Stable travel under load
Increased accuracy
Quiet motion
High-speed capability
Their simplicity and durability make them essential in engineered systems.
Industrial Applications of Linear Slides
Industries using linear slides include:
CNC machining
Robotics
Semiconductor manufacturing
Packaging systems
3D printing
Laboratory automation
Medical imaging equipment
Any application requiring straight, stable movement benefits from linear slides.
How to Choose the Right Linear Slides
Consider:
Load capacity
Speed requirements
Accuracy needs
Type of rolling element
Material construction
Environment
Slide length and travel distance
Budget
Choosing correctly increases performance and lifespan.
Proper Installation Techniques for Linear Slides
Steps include:
Clean and flatten mounting surfaces
Align slide carefully
Tighten screws gradually
Test movement by hand
Apply lubrication
Verify parallelism
Recheck after initial operation
Poor installation causes binding and premature wear.
Lubrication Requirements for Linear Slides
Lubrication:
Reduces wear
Lowers noise
Extends life
Prevents corrosion
Common lubricants:
Lithium grease
Light machine oil
High-speed grease
Synthetic lubricants
Follow manufacturer recommendations for intervals.
Maintenance Tips for Linear Slides
Maintenance includes:
Cleaning dust and debris
Re-lubricating regularly
Checking alignment
Inspecting wear patterns
Monitoring noise levels
Routine care keeps slides running smoothly.
Common Issues With Linear Slides
Common faults include:
Noise
Binding
Rough travel
Lubrication failure
Misalignment
Wear patterns
Corrosion
Most problems come from dirt or lack of lubrication.
Troubleshooting Linear Slide Performance Issues
If issues arise, check:
Dirt in the slide
Damage to bearings
Dry contact surfaces
Loose installation bolts
Misalignment
Overloading
Cleaning and lubrication fix most problems.
Linear Slides vs Linear Rails
| Feature | Linear Slides | Linear Rails |
|---|---|---|
| Motion Type | Sliding/Rolling | Rolling |
| Accuracy | High | Very high |
| Load Support | Medium to high | Very high |
| Speed | Medium to high | High |
| Applications | General machinery | CNC, industrial |
Slides are versatile, while linear rails specialize in ultra-high precision.
Materials Used in Linear Slides
Slides may be made from:
Aluminum
Carbon steel
Stainless steel
Hardened tool steel
Composite plastics
The material affects weight, strength, and corrosion resistance.
Environmental Factors Affecting Linear Slides
Harmful conditions include:
Dust
Moisture
Coolant splashes
High heat
Chemicals
Metal shavings
Protective covers and seals help extend life.
Load Ratings of Linear Slides
Load ratings include:
Static load
Dynamic load
Moment load
Vertical and side loads
Using incorrect load ratings leads to early failure.
Speed and Acceleration Capabilities
Linear slides support high speeds due to:
Low friction bearings
Precision surfaces
Rigid construction
Used in automated and rapid-motion systems.
Cost Considerations for Linear Slides
Cost depends on:
Slide type
Precision class
Material
Size and travel length
Brand reputation
Slewing features
Integrated systems (like motorized stages)
High-end slides offer increased durability.
Emerging Innovations in Linear Slide Technology
Recent innovations include:
Smart lubrication systems
Lightweight composite materials
Quieter bearing motion
Integrated sensor systems
High-speed low-friction coatings
Technology continues to improve performance.
Safety Tips When Handling Linear Slides
Safety guidelines:
Wear gloves
Handle carefully
Avoid impact or dropping
Store in dry conditions
Use proper mounting tools
Improper handling can ruin precision surfaces.
Cleaning Guidelines for Linear Slides
Steps include:
Use lint-free cloths
Apply mild solvent
Remove contaminants
Dry thoroughly
Add lubrication
Reinstall correctly
Cleanliness is essential for optimal performance.
Using Linear Slides to Improve CNC Accuracy
Linear slides:
Reduce vibration
Improve rigidity
Enhance cutting accuracy
Maintain consistent motion
Support heavy loads
They play a vital role in CNC machine performance.
Top Global Manufacturers of Linear Slides
Leading brands include:
THK
Igus
HIWIN
Bosch Rexroth
NSK
Parker Hannifin
These manufacturers offer durable, high-precision products.
Final Buying Checklist
Before purchasing:
Verify load capacity
Confirm material type
Check slide travel
Ensure smooth movement
Review accuracy requirements
Compare brands
Ensure lubrication access
Check mounting compatibility
Verify warranty
Consider price vs durability
This ensures you select the correct slide.
Conclusion
Linear slides are vital components in modern motion systems. They provide smooth, accurate, and stable movement for both light and heavy applications. With the proper selection, installation, and maintenance, linear slides can perform reliably for many years. This guide gives you expert knowledge to understand, choose, and maintain linear slides effectively.
FAQs
What are linear slides used for?
They provide controlled and precise linear motion in machines and automation systems.
Do linear slides require lubrication?
Yes, lubrication reduces wear and improves smooth travel.
What causes linear slide noise?
Mostly dirt, misalignment, or insufficient lubrication.
Which industries use linear slides?
CNC, robotics, medical devices, semiconductor equipment, and automation.
How long do linear slides last?
With proper maintenance, they can last thousands of operational hours.
Are linear slides better than linear rails?
Each has advantages; slides offer versatility, while rails offer ultra-high precision.
Internal Link Suggestions
Linear rails
Linear motion systems
Outbound Link Suggestions
Igus Linear Slide Catalog
THK Slide Systems
Parker Precision Stages