Introduction
As industrial equipment continues to demand higher precision, greater load capacity, and improved stability, the square linear guide has become a core component in modern linear motion systems. Widely used in CNC machine tools, automation equipment, robotics, and heavy-duty machinery, square linear guides offer exceptional rigidity, accuracy, and durability.
Compared with compact or round linear guides, square linear guides are designed to handle multi-directional loads and high moments, making them ideal for applications where precision and structural stiffness are critical.
This article provides a comprehensive explanation of square linear guides, including their structure, working principles, types, advantages, applications, selection criteria, installation methods, and maintenance practices.
What Is a Square Linear Guide?
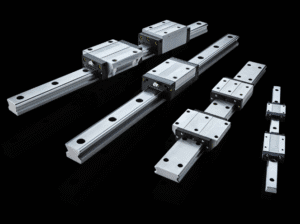
A square linear guide is a type of profiled linear motion guide characterized by its square or rectangular carriage block. It consists of:
A precision-ground rail
A square-shaped carriage (block)
Rolling elements, typically steel balls or rollers
Seals, retainers, and lubrication paths
The square carriage design allows the guide to support loads from multiple directions (radial, reverse radial, and lateral), making it highly versatile for complex mechanical systems.
How a Square Linear Guide Works
Square linear guides operate using recirculating rolling elements:
The carriage moves along the rail.
Steel balls or rollers roll between the rail raceways and carriage grooves.
Rolling elements circulate inside the carriage through return paths.
Load is evenly distributed across multiple contact points.
Friction is minimized while rigidity and positioning accuracy are maximized.
This rolling mechanism enables smooth, precise, and repeatable linear motion even under high loads.
Main Components of a Square Linear Guide
1. Linear Rail
Made of hardened, precision-ground steel
Provides a straight and rigid guiding path
Designed to withstand high loads and wear
2. Square Carriage (Block)
Rectangular or square profile for high stiffness
Houses rolling elements and return channels
Supports multi-directional and moment loads
3. Rolling Elements
Steel balls or cylindrical rollers
Reduce friction and distribute loads evenly
Enable high-speed and high-precision movement
4. End Caps and Retainers
Guide rolling elements through circulation paths
Ensure smooth and continuous motion
5. Seals and Wipers
Prevent dust, debris, and liquid ingress
Extend the service life of the guide
6. Lubrication System
Integrated grease or oil channels
Reduces wear and ensures smooth operation
Types of Square Linear Guides
1. Ball-Type Square Linear Guide
Uses recirculating steel balls
Low friction and high speed
Suitable for CNC machines, automation systems, and pick-and-place equipment
2. Roller-Type Square Linear Guide
Uses cylindrical rollers instead of balls
Higher rigidity and load capacity
Ideal for heavy-duty CNC machines and gantry systems
3. Heavy-Load Square Linear Guide
Larger rail and block size
Designed for high static and dynamic loads
Used in large machining centers and industrial presses
4. Miniature Square Linear Guide
Compact square block design
High precision in limited space
Suitable for medical devices, electronics, and laboratory automation
Materials and Surface Treatments
High-Carbon Hardened Steel – Superior strength and wear resistance
Stainless Steel – Corrosion resistance for harsh or clean environments
Surface Treatments:
Induction hardening
Black oxide coating
Chrome plating
Material selection depends on load conditions, environmental exposure, and lifespan requirements.
Advantages of Square Linear Guides
High Rigidity – Square block design resists deformation
Multi-Directional Load Support – Handles radial, lateral, and moment loads
High Precision and Repeatability
Smooth, Low-Friction Motion
High Load Capacity
Long Service Life
Easy Integration with CNC and Automation Systems
Applications of Square Linear Guides
CNC Machine Tools – Milling machines, lathes, and machining centers
Industrial Automation – Assembly lines and transfer systems
Robotics – Linear axes and positioning stages
Gantry Systems – High-load and long-travel applications
Packaging Machinery – High-speed precision movement
Semiconductor Equipment – Clean and accurate motion control
Square Linear Guide vs. Other Linear Guides
| Feature | Square Linear Guide | Round Linear Guide | Miniature Guide |
|---|---|---|---|
| Load Capacity | High | Medium | Low |
| Rigidity | Very High | Medium | Medium |
| Multi-Directional Load | Excellent | Limited | Moderate |
| Precision | High | Medium | High |
| Common Use | CNC, automation | Light machinery | Compact devices |
Square linear guides are preferred for high-load and high-precision applications.
How to Choose the Right Square Linear Guide
Load Capacity – Static, dynamic, and moment loads
Accuracy Requirements – Positioning precision and repeatability
Travel Length – Required stroke and rail length
Speed and Acceleration
Environmental Conditions – Dust, moisture, chemicals
Mounting Space and Structure
Maintenance Accessibility
Correct selection ensures maximum performance and long-term reliability.
Installation Best Practices
Ensure mounting surfaces are flat and rigid
Align rails carefully to avoid uneven load distribution
Tighten fasteners to specified torque values
Lubricate the guide before operation
Perform test runs at low speed before full load operation
Proper installation directly affects accuracy, lifespan, and smooth operation.
Maintenance and Care
Clean rails and blocks regularly
Check seals and wipers for damage
Re-lubricate according to usage conditions
Inspect for abnormal noise or vibration
Routine maintenance ensures consistent performance and extended service life.
Future Trends in Square Linear Guide Technology
Higher load capacity with compact designs
Advanced surface coatings for extreme environments
Maintenance-free or long-life lubrication systems
Integration with smart monitoring sensors
Greater precision for automated manufacturing
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is a square linear guide used for?
It provides precise and stable linear motion in CNC machines, automation systems, and industrial equipment.
2. Why choose a square linear guide instead of a round guide?
Square linear guides offer higher rigidity and better multi-directional load support.
3. Can square linear guides handle heavy loads?
Yes, especially roller-type and heavy-load square guides.
4. Do square linear guides require lubrication?
Yes, proper lubrication is essential for smooth motion and long service life.
5. Are square linear guides suitable for high-speed motion?
Yes, ball-type square guides are ideal for high-speed and high-precision applications.
Conclusion
Square linear guides are essential components for high-precision, high-rigidity linear motion systems. Their robust square block design, excellent load-bearing capability, and smooth rolling motion make them indispensable in CNC machining, industrial automation, robotics, and heavy machinery.
With proper selection, installation, and maintenance, square linear guides deliver long-term accuracy, reliability, and efficiency in demanding industrial environments.